Smart bulbs offer convenience, energy efficiency, and customizable lighting—but when they start flickering unexpectedly, the experience quickly turns frustrating. Flickering isn't just annoying; it can indicate deeper issues ranging from minor compatibility mismatches to serious electrical problems. While some flickering may seem harmless, persistent or erratic behavior can shorten the lifespan of your bulbs, disrupt routines, and even pose safety risks.
The root causes are often misunderstood. Many users assume a defective bulb is to blame, but in reality, flickering usually stems from one of three areas: device compatibility, electrical supply instability, or firmware and network issues. Addressing these effectively requires more than guesswork—it demands a methodical approach grounded in understanding how smart lighting systems interact with home infrastructure.
Understanding Smart Bulb Flickering: Common Causes
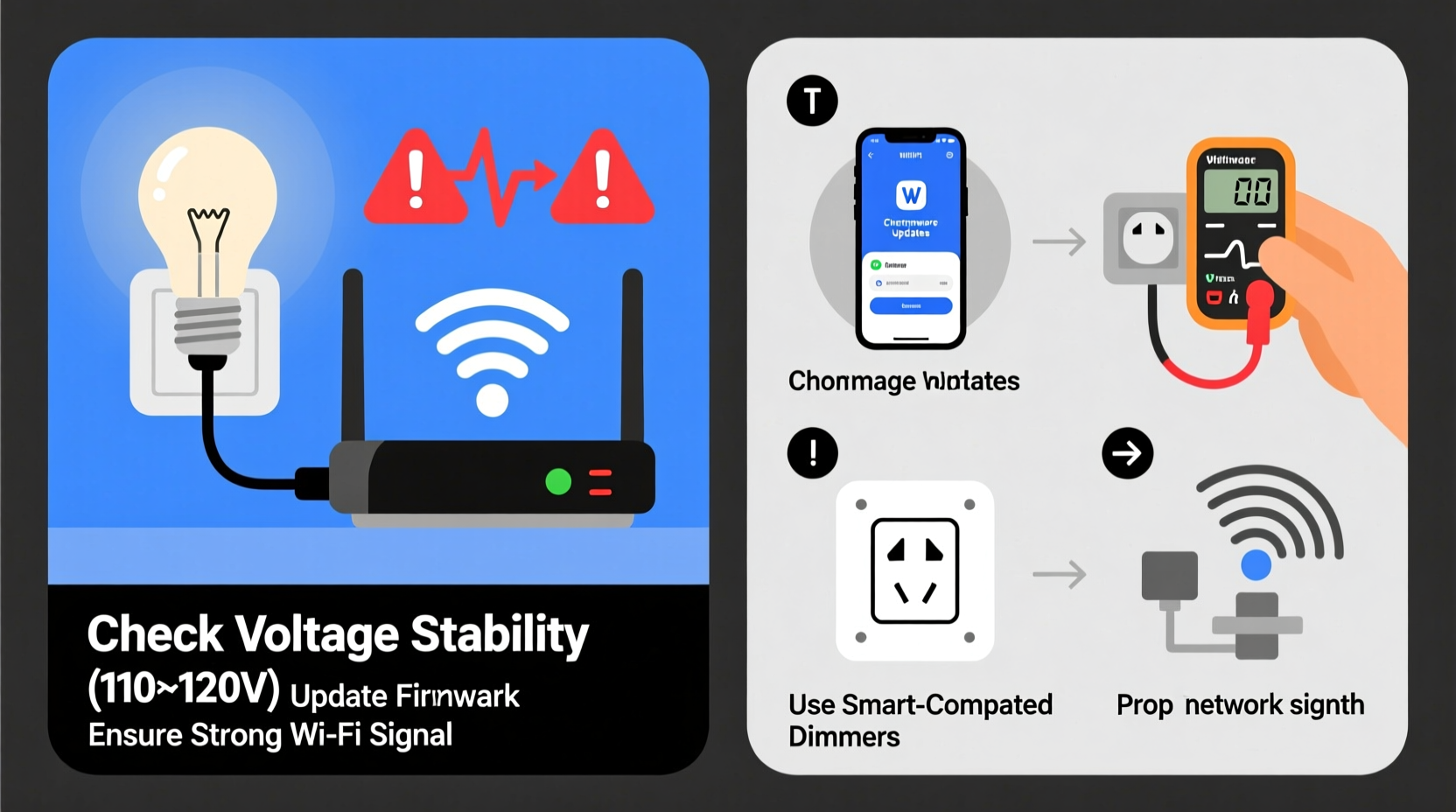
Flickering in smart bulbs doesn’t always mean the bulb is failing. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, smart LEDs rely on complex circuitry that modulates power at high frequencies to control brightness and color. This sensitivity makes them prone to interference from external factors.
- Incompatible dimmer switches: Most smart bulbs aren’t designed for use with standard leading-edge dimmers. These older dimmers reduce voltage by cutting parts of the AC waveform, which can confuse the internal driver of a smart LED.
- Voltage fluctuations: Even small variations in household voltage—especially during peak usage times—can cause temporary instability in low-power devices like smart bulbs.
- Loose connections: A poor connection in the socket, switch, or junction box can create intermittent contact, leading to random flickering.
- Wi-Fi or hub interference: If the bulb loses connectivity momentarily, it may reboot or reset its state, causing a visible flash.
- Firmware bugs: Outdated or corrupted firmware can result in erratic behavior, including pulsing or strobing, especially after updates.
Before replacing hardware, it’s essential to isolate whether the issue lies in the physical setup, electrical environment, or digital ecosystem.
Compatibility Issues: Dimmers, Switches, and Fixtures
One of the most frequent culprits behind flickering is using smart bulbs with incompatible wall switches. Traditional dimmers were built for resistive loads like incandescent bulbs, not the capacitive drivers found in smart LEDs. When paired incorrectly, this mismatch leads to inconsistent power delivery.
There are two main types of dimmers:
- Leading-edge (triac-based): Older technology, commonly used with incandescent and halogen lights. Often causes flickering or buzzing in smart bulbs due to abrupt current cutoff.
- Trailing-edge (electronic low-voltage): Designed for modern LED loads. Provides smoother phase-cutting and better compatibility with smart lighting.
If you're experiencing flicker with a dimmable smart bulb, first confirm whether your switch supports trailing-edge dimming. Some brands, like Lutron, offer models specifically rated for LED and smart bulb integration.
| Dimmer Type | Compatible with Smart Bulbs? | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Leading-Edge (Standard Dimmer) | No – High Risk of Flicker | Replace with trailing-edge or smart switch |
| Trailing-Edge (ELV) | Yes – If Rated for LEDs | Verify load minimums match bulb count |
| Smart Wall Switch (e.g., Lutron Caséta) | Yes – Optimal Control | Use for full automation without conflicts |
| On/Off Only (No Dimmer) | Yes – Best Stability | Ideal for non-dimming smart bulbs |
Additionally, certain enclosed fixtures trap heat, which can trigger thermal protection circuits inside smart bulbs. This results in periodic shutdowns and restarts that appear as flickering. Always check manufacturer guidelines regarding fixture ratings before installation.
Mini Case Study: The Phantom Flicker in a Modern Living Room
A homeowner installed Philips Hue bulbs throughout their living room, all controlled via a central hub. Despite proper setup, one bulb flickered intermittently every evening. Initial suspicion fell on Wi-Fi signal strength, but tests showed strong connectivity. Further investigation revealed that the flickering only occurred when the adjacent kitchen light—a legacy dimmer-controlled halogen fixture—was turned on.
An electrician diagnosed the issue: shared circuit noise. The old dimmer introduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) onto the same line, disrupting the sensitive driver in the Hue bulb. Installing a ferrite choke on the affected circuit and upgrading the kitchen dimmer to a trailing-edge model resolved the flickering completely.
“Many flickering issues stem not from the bulb itself, but from interactions within the broader electrical system. Isolation and measurement are key.” — Rajiv Mehta, Electrical Systems Engineer, Smart Home Institute
Voltage Instability and Power Supply Fixes
Smart bulbs operate on low-voltage DC internally, converting incoming AC through an onboard power supply. This conversion process is highly sensitive to input quality. Voltage drops below 110V or surges above 125V (in a 120V nominal system) can destabilize the driver, leading to flicker.
Common sources of voltage fluctuation include:
- Large appliances cycling on (e.g., HVAC, refrigerators)
- Overloaded circuits
- Poor wiring or corroded connections
- Utility-side inconsistencies, especially in rural areas
To diagnose voltage issues, use a multimeter to measure the outlet or fixture voltage under load. Record readings at different times of day, particularly during peak usage. Consistent deviations beyond ±5% of nominal voltage (i.e., outside 114–126V for a 120V system) warrant attention.
Step-by-Step Guide: Diagnosing and Fixing Voltage Problems
- Measure baseline voltage: Use a digital multimeter at the socket (with bulb removed) while no major appliances are running.
- Test under load: Turn on high-draw devices (washer, microwave, AC) and recheck voltage. Note any significant drop (>5V).
- Check circuit sharing: Identify which other outlets or lights share the same breaker. Overloading increases resistance and reduces voltage.
- Inspect connections: Turn off power and examine wire nuts, terminal screws, and socket contacts for looseness or corrosion.
- Install a dedicated circuit: For critical lighting zones, consider running a separate line from the panel to eliminate interference.
- Add a voltage regulator or UPS: For recurring issues, a small uninterruptible power supply or line conditioner can stabilize input.
Firmware, Network, and Software Troubleshooting
Not all flickering is electrical. In many cases, communication errors between the bulb, hub, and app cause momentary resets or brightness adjustments that manifest as flicker.
Common scenarios include:
- Bulbs briefly flashing when reconnecting to a Zigbee or Wi-Fi network
- Color shifts or pulses triggered by background automation rules
- Firmware update glitches causing unstable operation
To rule out software-related flickering:
- Update all bulbs and hubs to the latest firmware via the manufacturer’s app.
- Disable automations temporarily to see if flickering stops.
- Reset the bulb to factory settings and re-pair it to the network.
- Check for mesh network gaps—Zigbee bulbs rely on proximity to other nodes for stable routing.
Some users report flickering after third-party integrations (e.g., Alexa routines or IFTTT applets). Review recent automation changes and test with native controls only.
Checklist: Eliminate Smart Bulb Flickering
- ✅ Verify the bulb is not used with an incompatible dimmer switch
- ✅ Test the bulb in a known-good fixture to isolate location-based issues
- ✅ Measure voltage at the socket during flickering episodes
- ✅ Ensure secure physical connections in the socket and switch box
- ✅ Update bulb and hub firmware to the latest version
- ✅ Disable automations and scene transitions temporarily
- ✅ Confirm the fixture is not enclosed or overheating the bulb
- ✅ Check for nearby sources of EMI (motors, transformers, wireless devices)
- ✅ Reset the bulb and re-pair it to the network
- ✅ Consult an electrician if flickering persists across multiple bulbs
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a smart bulb flicker because of Wi-Fi issues?
Yes. If a smart bulb loses connection to its hub or router, it may reboot or enter a recovery state, causing a brief flash or color change. This is especially common in Wi-Fi-only bulbs during network congestion or outages. Zigbee and Z-Wave bulbs are generally more stable due to mesh networking.
Is flickering dangerous?
Occasional flickering due to software glitches is typically not hazardous. However, persistent flickering caused by loose wiring, arcing, or voltage instability can generate heat and increase fire risk. If multiple lights flicker simultaneously or you notice buzzing sounds, consult a licensed electrician immediately.
Do all smart bulbs flicker less at full brightness?
Many do. At lower brightness levels, pulse-width modulation (PWM) cycles the LED rapidly to simulate dimming. Low-frequency PWM can be perceptible as flicker, especially in peripheral vision. Higher-end bulbs use high-frequency PWM or analog dimming to minimize this effect. Running at 100% brightness often eliminates the issue.
Final Recommendations and Long-Term Prevention
Resolving smart bulb flickering requires a layered diagnostic approach. Start simple: swap the bulb, check the switch, and verify firmware. Then move to electrical diagnostics—voltage, load balance, and circuit integrity. Finally, assess network health and automation logic.
For long-term reliability, consider investing in compatible smart switches instead of relying solely on bulb-level control. Devices like the Lutron Caséta or TP-Link Kasa allow seamless integration without the pitfalls of legacy dimmers. Additionally, grouping smart bulbs on dedicated circuits prevents interference from large appliances.
Maintain a log of flickering events, noting time, weather conditions, and appliance usage. Patterns often reveal hidden causes that aren’t immediately obvious.
“The future of home lighting is intelligent, but intelligence depends on stability. A flickering bulb isn’t just a nuisance—it’s a signal.” — Dr. Lena Torres, IoT Integration Specialist
Take Action Today
Your smart lighting system should enhance comfort, not detract from it. By systematically addressing compatibility, voltage, and connectivity issues, you can eliminate flickering and enjoy smooth, reliable performance. Don’t ignore subtle signs—early intervention prevents bigger problems down the line. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or working with an electrician, the steps outlined here provide a clear path to resolution. Share your experience, ask questions, or help others troubleshoot in the comments below—because smarter homes start with informed users.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?