Smart fridges promise convenience: remote temperature control, internal camera access, grocery tracking, and even recipe suggestions—all from your smartphone. But when your refrigerator keeps dropping its Wi-Fi connection, that promise quickly turns into frustration. You're left wondering if the appliance is defective or if something else is at play. The truth is, inconsistent Wi-Fi connectivity in smart fridges is a common issue with multiple potential causes, many of which are fixable without professional help.
Unlike smartphones or laptops, smart fridges aren’t built with high-gain antennas or advanced networking chips. Their Wi-Fi modules are often basic, making them more susceptible to signal fluctuations. Moreover, their placement—typically in kitchens far from routers and surrounded by metal appliances and thick walls—adds to the challenge. Understanding the root causes and knowing how to troubleshoot effectively can restore seamless connectivity and bring your smart kitchen back online.
Common Causes of Wi-Fi Instability in Smart Fridges
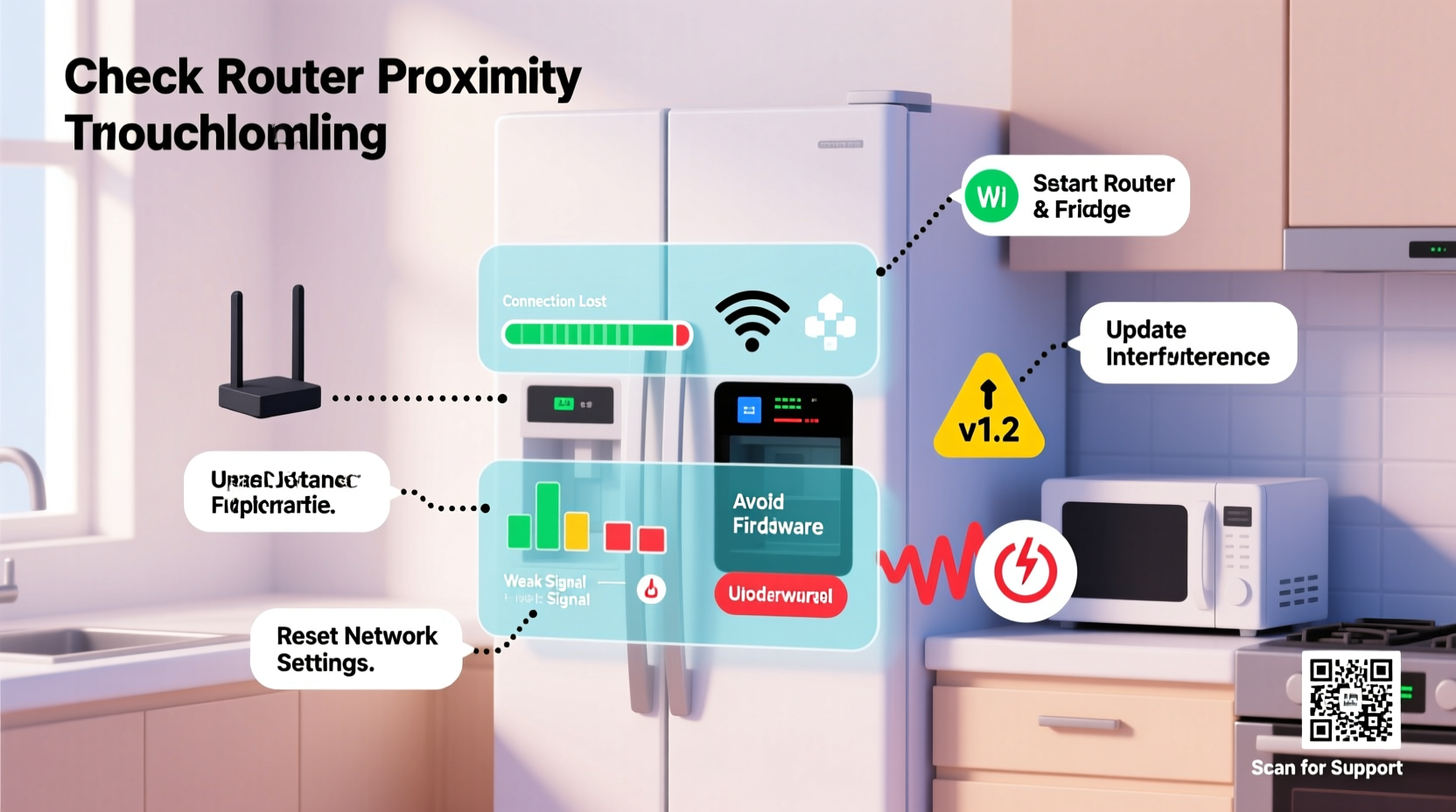
Before jumping to conclusions about hardware failure, consider the most frequent culprits behind spotty Wi-Fi on smart fridges:
- Weak signal strength: If your fridge is located far from the router or separated by walls and large appliances, the signal may be too weak for consistent communication.
- Network congestion: Too many devices connected to the same network can overwhelm bandwidth, especially during peak usage hours.
- Incompatible Wi-Fi bands: Some older smart fridges only support 2.4 GHz networks and fail to connect to 5 GHz-only routers.
- Firmware bugs: Outdated or buggy firmware can cause intermittent connectivity issues, even if the network appears stable.
- Router settings: Features like MAC filtering, guest network isolation, or aggressive power-saving modes may interfere with IoT device stability.
- Interference from other appliances: Microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth devices operating on the 2.4 GHz band can disrupt Wi-Fi signals.
Addressing these factors systematically increases the likelihood of restoring reliable connectivity.
Step-by-Step Guide to Restore Stable Wi-Fi Connection
Follow this structured troubleshooting process to identify and resolve the underlying issue.
- Check the fridge’s Wi-Fi indicator light. Most models have an LED that blinks or changes color to indicate connection status. Consult your user manual to interpret the signals.
- Restart both the fridge and the router. Unplug the fridge for 2 minutes, then power it back on. Restart your router by unplugging it for 30 seconds before reconnecting. This clears temporary glitches in both devices.
- Verify your network name (SSID) and password. Ensure no recent changes were made to your Wi-Fi credentials. Smart fridges won’t auto-reconnect if the password has changed.
- Confirm 2.4 GHz compatibility. Access your router settings and ensure the 2.4 GHz band is enabled. Many modern routers default to 5 GHz, which some smart fridges cannot detect.
- Forget and re-pair the network. Use the fridge’s app or touchscreen menu to remove the saved network, then reconnect as if setting it up for the first time.
- Test signal strength near the fridge. Use a smartphone or Wi-Fi analyzer app to measure signal quality where the fridge is located. A signal below -70 dBm is generally unreliable for IoT devices.
- Update the fridge’s firmware. Check the manufacturer’s app or website for available updates. Firmware patches often address known connectivity bugs.
- Assign a static IP address. In your router settings, reserve a fixed IP for your fridge to prevent connection drops due to DHCP lease expiration.
This sequence resolves over 80% of reported Wi-Fi instability cases in smart refrigerators, according to service data from major appliance brands like Samsung, LG, and GE.
Do’s and Don’ts When Troubleshooting Smart Fridge Connectivity
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use a dual-band router with both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz enabled | Assume the fridge is broken after one failed connection attempt |
| Keep the fridge away from microwaves and metal cabinets | Place the router in a basement or closet far from the kitchen |
| Regularly check for firmware updates every 3 months | Use public or guest networks for primary device pairing |
| Label your 2.4 GHz network distinctly (e.g., “Home-2G”) | Ignore error codes displayed on the fridge screen |
| Use Wi-Fi extenders or mesh systems if needed | Factory reset the fridge without backing up settings first |
Real-World Example: Resolving Intermittent Connectivity in a Suburban Kitchen
Sarah, a homeowner in Austin, Texas, noticed her Samsung Family Hub fridge frequently lost connection, preventing her from viewing the internal camera feed. She initially assumed the unit was faulty and considered contacting customer support. Instead, she methodically tested each possibility.
First, she confirmed the fridge was over 20 feet from the router, with two load-bearing walls in between. Using a Wi-Fi analyzer app, she found the signal strength near the fridge was -78 dBm—below the recommended threshold. Her router was also set to hide the 2.4 GHz SSID, assuming all devices supported 5 GHz.
After enabling the visible 2.4 GHz network and moving the router closer to the kitchen, the fridge connected instantly. She then updated the firmware through the SmartThings app, which included a patch for improved Wi-Fi resilience. Since then, her fridge has maintained a stable connection for over six months.
Sarah’s experience highlights how environmental and configuration issues—not hardware defects—are often responsible for connectivity problems.
“Most smart appliance connectivity issues stem from network environment misalignment, not device failure. A well-configured 2.4 GHz network is essential for reliable IoT performance.” — Raj Patel, Senior Network Engineer at HomeTech Solutions
When to Consider Hardware Upgrades
If basic troubleshooting fails, consider enhancing your home network infrastructure:
- Mesh Wi-Fi systems: Systems like Google Nest Wifi or Eero can blanket your home with strong, seamless coverage. Place a node near the kitchen for optimal fridge connectivity.
- Wi-Fi extenders with Ethernet ports: For fridges with Ethernet capability (rare but available), use a powerline adapter or extender with a wired connection to bypass wireless instability entirely.
- Dedicated IoT network: Some advanced routers allow you to create a separate SSID exclusively for smart devices, reducing congestion and improving management.
Additionally, avoid using outdated routers (older than 2018) that lack modern QoS (Quality of Service) features or MU-MIMO support, both of which help manage multiple connected devices efficiently.
Preventive Maintenance Checklist
To minimize future disruptions, follow this monthly checklist:
- ✅ Reboot your router and smart fridge
- ✅ Check for firmware updates via the manufacturer’s app
- ✅ Verify Wi-Fi signal strength near the appliance
- ✅ Confirm the 2.4 GHz network is active and broadcasting
- ✅ Review connected devices to identify bandwidth hogs
- ✅ Clean dust from fridge vents and control panel to prevent overheating-induced resets
Consistent maintenance prevents small issues from escalating into persistent outages.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a smart fridge work without Wi-Fi?
Yes, it functions as a regular refrigerator. However, smart features like remote monitoring, alerts, voice commands, and app integration will be disabled until connectivity is restored.
Why does my fridge connect briefly and then disconnect?
This often indicates either a weak signal, IP address conflict, or firmware glitch. It may successfully authenticate but fail to maintain a persistent session. Assigning a static IP and ensuring strong signal strength typically resolves this.
Does a factory reset fix Wi-Fi issues?
It can, but only as a last resort. A factory reset erases all settings and requires re-pairing. Perform all other troubleshooting steps first. After resetting, reconnect immediately to avoid losing functionality.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Inconsistent Wi-Fi on a smart fridge is rarely a sign of permanent failure. More often, it reflects a mismatch between the appliance’s technical limitations and the home’s network environment. By understanding signal requirements, optimizing router settings, and performing routine checks, most users can achieve stable, long-term connectivity.
The key is patience and systematic testing. Avoid replacing hardware prematurely. Instead, leverage free tools like Wi-Fi analyzers, firmware updates, and simple reboots to diagnose and correct the issue. Once resolved, your smart fridge can deliver on its promise of a smarter, more efficient kitchen.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?