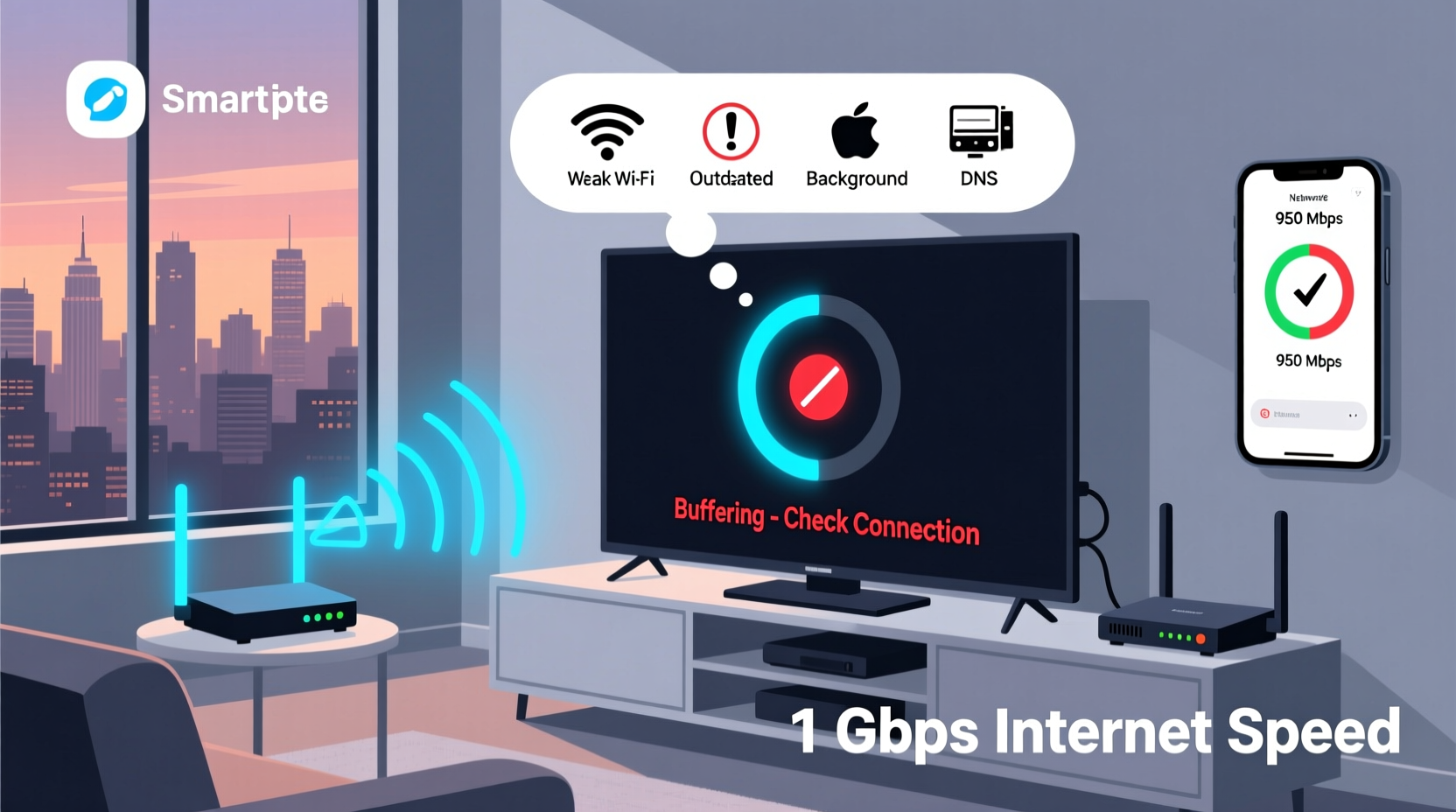
Streaming entertainment should be seamless—especially when you’ve invested in a fast internet plan. Yet, many users find themselves frustrated by constant buffering on their smart TVs, even with gigabit speeds or robust broadband connections. The disconnect between internet performance and real-world streaming quality often lies not in raw speed, but in how that bandwidth is delivered, processed, and prioritized within your home network ecosystem.
Buffering occurs when your smart TV can’t download video data quickly enough to maintain continuous playback. While low internet speed is a common culprit, it’s far from the only one. Modern smart TVs face multiple technical hurdles—from Wi-Fi interference and outdated firmware to ISP throttling and server-side congestion—that can degrade performance regardless of your advertised connection speed.
This guide dives deep into the hidden causes behind persistent buffering, offering actionable solutions backed by networking principles and real-world testing. Whether you're using a Samsung, LG, Sony, or Roku-powered device, understanding these factors will help you reclaim smooth, uninterrupted viewing.
Understanding the Gap Between Speed and Stability
Internet service providers often advertise “up to” certain speeds, but real-world performance varies due to signal degradation, network congestion, and hardware limitations. More importantly, speed alone doesn’t guarantee stability. A 300 Mbps connection with high latency or packet loss will perform worse than a stable 100 Mbps line.
Streaming services like Netflix, Disney+, and YouTube require consistent throughput rather than peak bursts. For example:
- HD (720–1080p) streaming typically needs 5–8 Mbps
- 4K Ultra HD requires 25 Mbps or more
- High dynamic range (HDR) and Dolby Atmos audio increase data demands
If your smart TV frequently drops below these thresholds—even briefly—it triggers rebuffering. This explains why a 100 Mbps connection might still struggle: intermittent dips caused by network hiccups are enough to disrupt playback.
“Bandwidth is only one part of the equation. Latency, jitter, and packet loss have a greater impact on streaming quality than headline download speeds.” — Raj Patel, Network Engineer at Broadband Insights Group
Common Causes of Smart TV Buffering Despite Fast Internet
1. Wi-Fi Signal Interference and Distance
Most smart TVs connect via Wi-Fi, which is inherently less reliable than Ethernet. Walls, appliances, neighboring networks, and even microwave ovens can interfere with 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. If your router is in another room or blocked by furniture, signal strength diminishes significantly.
Smart TVs often have weaker internal antennas compared to smartphones or laptops, making them more susceptible to poor reception. Even if your phone shows full bars nearby, the TV may be receiving a degraded signal.
2. Network Congestion from Other Devices
Your total bandwidth is shared across all connected devices. Background activities such as cloud backups, software updates, gaming, or multiple video streams can consume significant bandwidth without your awareness.
For instance, a single Windows PC updating in the background can use 50+ Mbps for minutes at a time, starving your smart TV of necessary bandwidth—even on a 200 Mbps plan.
3. Outdated Firmware or App Software
Smart TV manufacturers release firmware updates to improve performance, fix bugs, and enhance app compatibility. An outdated operating system may lack optimizations for current streaming protocols or contain known issues affecting video decoding.
Likewise, individual apps like Netflix or Hulu receive regular updates. If auto-updates are disabled, older versions may not handle adaptive bitrate streaming efficiently, leading to unnecessary buffering.
4. ISP Throttling During Peak Hours
Some Internet Service Providers throttle bandwidth for specific services during high-traffic periods. Though often unadvertised, this practice limits throughput for streaming platforms once a threshold is reached.
You can test for throttling using tools like FCC's Measuring Broadband America or third-party services such as Ookla Speedtest combined with Netflix Open Connect tests.
5. Router QoS Settings and Bandwidth Allocation
Many routers lack Quality of Service (QoS) settings or have them misconfigured. Without QoS, no priority is given to time-sensitive traffic like video streaming. Large downloads or torrent clients can dominate the connection, causing micro-interruptions that trigger buffering.
Troubleshooting Checklist: Fix Buffering Step-by-Step
- ✅ Run a speed test directly on the smart TV (if supported) or a nearby device on the same network
- ✅ Reboot your router and modem
- ✅ Move closer to the router or eliminate physical obstructions
- ✅ Switch from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz Wi-Fi (or vice versa if range is poor)
- ✅ Close unused apps and pause background downloads on other devices
- ✅ Check for and install smart TV firmware updates
- ✅ Update streaming apps individually through the app store
- ✅ Enable QoS settings on your router and prioritize media devices
- ✅ Use an Ethernet cable for a direct, stable connection
- ✅ Contact your ISP to confirm no throttling or line issues exist
Comparing Connection Types: Wi-Fi vs. Wired
| Factor | Wi-Fi (5 GHz) | Ethernet (Wired) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Speed | 50–500 Mbps (varies with distance) | Stable up to 1 Gbps |
| Latency | 15–50 ms | 1–5 ms |
| Jitter (Variability) | Moderate to high | Negligible |
| Interference Risk | High (walls, devices, signals) | None |
| Setup Complexity | Low | Moderate (requires cabling) |
| Best For | Convenience, short distances | 4K/HDR streaming, gaming, reliability |
As shown, Ethernet provides superior consistency. While Wi-Fi has improved over generations (Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6), environmental variables make it unpredictable. For critical applications like 4K streaming, a wired connection remains the gold standard.
Real-World Example: The Case of the Buffering Living Room TV
Consider Mark, a homeowner with a 300 Mbps fiber connection. His living room Samsung QLED TV constantly buffered during evening shows, while his bedroom smart TV worked flawlessly. Both were on the same network.
After investigation, he discovered:
- The living room TV was connected to 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi due to weak 5 GHz signal penetration through two walls
- A nearby wireless speaker caused interference on overlapping channels
- His kids’ tablets were downloading game updates simultaneously
- The TV hadn’t received a firmware update in eight months
Solution steps taken:
- Installed a mesh Wi-Fi extender near the TV
- Switched to 5 GHz band with channel optimization
- Enabled parental controls to limit off-peak downloads
- Manually updated the TV’s firmware
- Set up QoS rules to prioritize streaming devices after 6 PM
Result: Buffering ceased entirely. Streaming stability improved even during family movie nights with multiple devices active.
Advanced Fixes for Persistent Issues
Use a Streaming Media Player Instead of Built-in Apps
Some smart TV platforms—particularly older models—run underpowered processors and limited RAM. Running native apps can strain resources, especially when decoding 4K HDR content.
Replacing your smart TV’s built-in apps with a dedicated streaming device (e.g., Apple TV 4K, Amazon Fire Stick 4K Max, NVIDIA Shield) often results in smoother performance. These devices are optimized for streaming, feature faster chips, better Wi-Fi, and more frequent updates.
Upgrade Your Router or Use Mesh Networking
If your router is more than three years old, it may not support modern standards like Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), MU-MIMO, or beamforming. Upgrading can dramatically improve throughput and device handling.
For larger homes, consider a mesh system (like Eero, Netgear Orbi, or TP-Link Deco). These eliminate dead zones and provide seamless roaming, ensuring your smart TV maintains a strong signal at all times.
Enable DNS Optimization
Changing your router’s DNS settings to faster public resolvers can reduce lookup delays that contribute to initial load times and buffering. Recommended options include:
- Google DNS: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4
- Cloudflare DNS: 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1
- OpenDNS: 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220
To change DNS:
- Access your router’s admin page (usually http://192.168.1.1)
- Log in with admin credentials
- Navigate to Internet or WAN settings
- Replace default DNS fields with preferred addresses
- Save and reboot the router
Frequently Asked Questions
Can my smart TV’s age affect buffering?
Yes. Older smart TVs may have slower processors, limited memory, and outdated Wi-Fi chipsets. They struggle with modern streaming codecs (like AV1) and higher resolutions. Even with fast internet, hardware limitations can cause stalling. Consider adding an external streaming stick to bypass internal limitations.
Does restarting my smart TV help with buffering?
Regular restarts clear temporary memory leaks and reset network connections. If your TV has been on for days, accumulated processes can degrade performance. Power cycling weekly helps maintain responsiveness and streaming efficiency.
Why does only one app buffer while others work fine?
Different apps use different servers, compression methods, and adaptive bitrate algorithms. One app might be experiencing server congestion (e.g., HBO Max during a premiere), while another (like YouTube) adjusts smoothly. Try clearing the app cache or reinstalling the problematic app.
Final Recommendations for Buffer-Free Streaming
Buffering on a smart TV with high-speed internet is rarely about bandwidth alone. It’s a symptom of systemic inefficiencies in your home network, device configuration, or service delivery. Addressing these holistically yields lasting improvements.
Start with simple fixes: reboot your equipment, close background tasks, and ensure software is current. Then progress to structural upgrades—wired connections, mesh networks, or external streamers—if needed. Monitor changes with repeat speed and ping tests to validate improvements.
Remember, optimal streaming isn't just about speed—it's about consistency, prioritization, and minimizing latency at every link in the chain.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?