If your internet speeds are strong during the day but crawl to a halt every evening, you're not imagining things. Many households experience a noticeable drop in WiFi performance at night — just when streaming, gaming, and video calls are most in demand. This isn’t random; it’s typically the result of network congestion, interference, or device overload. The good news is that with targeted troubleshooting, you can significantly improve your nighttime connectivity without upgrading your plan.
Understanding Why Nighttime WiFi Slows Down
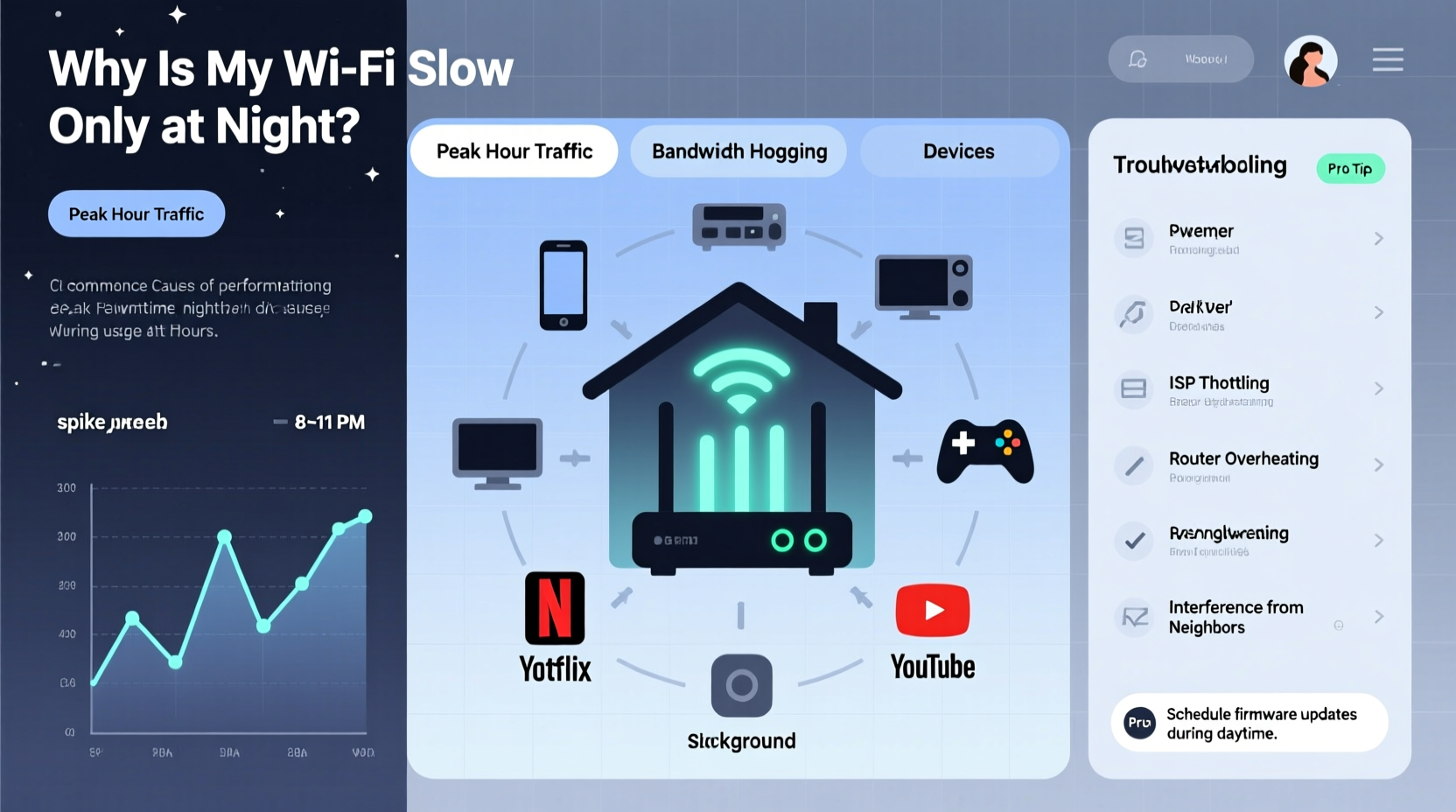
Nighttime internet slowdowns are often caused by increased network demand. During the day, neighbors may be at work or school, using fewer devices. But once everyone returns home, multiple households begin streaming 4K video, downloading large files, and connecting smart devices simultaneously. This surge in local network traffic affects both your home setup and your Internet Service Provider's (ISP) infrastructure.
In technical terms, this phenomenon is known as \"peak hour congestion.\" According to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), average broadband speeds can drop by up to 30% between 7 PM and 11 PM across major U.S. cities. This isn't just anecdotal — it's measurable, especially in densely populated areas where many users share the same ISP node or wireless spectrum.
Additionally, within your own home, more people tend to go online at night. Kids stream shows, partners join Zoom meetings, and smart TVs download updates. All these activities compete for bandwidth, overwhelming your router if it wasn't designed for high concurrent usage.
Common Causes of Nighttime WiFi Lag
Several factors contribute specifically to poor WiFi performance after dark. Identifying which ones apply to your situation is key to solving the issue.
- Neighbor Network Interference: In apartments or suburban neighborhoods, dozens of WiFi networks operate on the same radio frequencies (especially 2.4 GHz). When more people come home, overlapping signals create interference.
- ISP Throttling or Congestion: Some ISPs manage traffic during peak hours, reducing individual user speeds to maintain overall network stability.
- Bandwidth-Hungry Devices: Smart TVs, gaming consoles, and background software updates often run automatically at night, consuming large amounts of data.
- Router Overload: Older or low-end routers struggle to handle multiple high-demand connections simultaneously.
- Signal Obstruction: Physical barriers like walls and appliances weaken signals, and their impact worsens when signal quality is already strained.
“Peak time slowdowns are one of the most common complaints we receive from urban customers. Often, switching to the 5 GHz band or updating firmware resolves half the cases.” — Jordan Lee, Senior Network Engineer at NetSecure Solutions
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose and Fix Nighttime WiFi Issues
Follow this structured approach to identify and eliminate the root causes of your slow nighttime internet.
- Conduct a Baseline Speed Test
Use a trusted service like Speedtest.net or Fast.com to measure download, upload, and ping at different times. Compare midday results with evening readings. - Check Connected Devices
Log into your router’s admin panel (usually via 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) and view the list of connected devices. Look for unknown or inactive gadgets siphoning bandwidth. - Switch to the 5 GHz Band
If your router supports dual-band WiFi, connect devices capable of using 5 GHz instead of 2.4 GHz. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds and less interference, though with slightly shorter range. - Change Your WiFi Channel
Use a free app like Wi-Fi Analyzer (Android) or AirPort Utility (iOS) to scan nearby networks. Choose a less crowded channel in your router settings — for 2.4 GHz, channels 1, 6, or 11 are standard non-overlapping options. - Update Router Firmware
Manufacturers release updates to fix bugs and improve performance. Access your router dashboard and check for available firmware upgrades. - Reposition Your Router
Place your router centrally, elevated, and away from metal objects, microwaves, and cordless phones. Avoid basements or enclosed cabinets. - Limit Background Activity
Schedule large downloads, cloud backups, and system updates for off-peak hours (e.g., early morning). - Enable QoS (Quality of Service)
This router feature prioritizes critical traffic like video calls or gaming over less urgent tasks like software updates.
Tips and Best Practices for Sustained Performance
Beyond immediate fixes, adopting long-term habits ensures consistent performance even during high-demand periods.
Consider setting up a guest network for visitors and IoT devices (like smart bulbs or thermostats). This reduces load on your primary network and enhances security.
WiFi Optimization Checklist
- ✅ Run speed tests at peak and off-peak times
- ✅ Identify all connected devices
- ✅ Switch compatible devices to 5 GHz
- ✅ Change to a less congested WiFi channel
- ✅ Update router firmware
- ✅ Reposition router for optimal coverage
- ✅ Schedule heavy downloads outside evening hours
- ✅ Enable QoS and prioritize key applications
- ✅ Set up a separate guest network
- ✅ Reboot router regularly (weekly recommended)
When Hardware Limits Are the Real Problem
Sometimes, no amount of tweaking will overcome outdated equipment. Routers older than three to four years often lack support for modern standards like MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output) or beamforming, which help manage multiple devices efficiently.
Similarly, if you have a large home or thick walls, your single router may simply not provide adequate coverage. In such cases, consider upgrading to a mesh WiFi system. These systems use multiple nodes to blanket your space with strong, seamless signal — ideal for multi-story homes or those with dead zones.
| Router Type | Best For | Limits |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Band (2.4 GHz) | Basic browsing, small spaces | High interference, slow speeds |
| Dual-Band (2.4 + 5 GHz) | Moderate households, medium-sized homes | Limited range on 5 GHz |
| Tri-Band Mesh System | Large homes, 15+ devices, heavy streaming/gaming | Higher cost, more complex setup |
If your ISP-provided router is old or underpowered, ask if you can replace it with a newer model — some providers offer free upgrades upon request.
Real Example: The Martinez Family’s Fix
The Martinez family in Austin, Texas, struggled nightly with buffering Netflix streams and dropped Zoom calls. Their kids couldn’t complete homework videos, and movie nights were ruined by constant rebuffering. After testing speeds, they found daytime downloads averaged 85 Mbps, but dropped to 18 Mbps at 8 PM.
They used a WiFi analyzer app and discovered 27 nearby networks, all clustered on channel 6. By switching their router to channel 1 and enabling the 5 GHz band for streaming devices, speeds improved to 45 Mbps at night. They also enabled QoS to prioritize video conferencing and scheduled game updates for 3 AM. Within a week, their evening experience transformed — no more lag, just smooth streaming.
FAQ: Common Questions About Nighttime WiFi Slowdowns
Can my ISP intentionally slow down my internet at night?
Some ISPs implement traffic shaping or throttling during peak hours, particularly if you exceed data caps or use excessive bandwidth. While outright throttling is less common now due to net neutrality guidelines, network congestion management still occurs. Contact your ISP to confirm their policies. You can test for throttling using tools like the Electronic Frontier Foundation’s proxy test.
Should I upgrade my internet plan if WiFi is slow at night?
Not necessarily. Before paying more, try optimizing your current setup. Often, better router placement, band steering, or eliminating interference yields dramatic improvements. However, if you consistently run 10+ devices and stream 4K content, upgrading to a higher-tier plan (e.g., 300+ Mbps) may be justified.
Does turning off WiFi at night help?
Turning off WiFi doesn’t solve slowdowns — it avoids them entirely. Instead, focus on optimization. However, rebooting your router nightly (manually or via a smart plug) can clear temporary issues and refresh the connection each day.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Evening Internet Experience
Slow WiFi at night doesn’t have to be a fact of life. With a methodical approach, you can pinpoint whether the issue stems from neighborhood congestion, internal network clutter, or outdated hardware. Simple changes — like switching to 5 GHz, changing channels, or enabling QoS — often deliver dramatic improvements without any added cost.
Consistent performance starts with awareness and maintenance. Monitor your speeds, manage connected devices, and keep your equipment updated. If needed, invest in a modern mesh system or consult your ISP about potential infrastructure limitations.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?