If your internet speeds drop every evening just when you're trying to stream a movie or join a video call, you're not imagining things. Millions of households experience the same frustrating slowdown during peak hours—typically between 6 PM and 10 PM. This isn’t random; it’s a predictable result of network congestion, device overload, and outdated hardware. The good news? You don’t need a new ISP or expensive equipment to fix it. With a few smart adjustments, you can significantly improve your evening Wi-Fi performance.
Understanding Evening Wi-Fi Slowdowns
The root cause of slow evening internet lies in shared bandwidth. During peak hours, everyone in your neighborhood—and often on your home network—is online at once. Families are streaming shows, kids are gaming, smart devices are syncing, and someone might be downloading large files. This collective demand overwhelms both your router and your Internet Service Provider's (ISP) local infrastructure.
Think of your internet connection like a highway. During off-peak times, traffic flows smoothly. But when rush hour hits, too many cars (data packets) try to use the same lanes (bandwidth), causing bottlenecks. In urban areas or apartment complexes, this effect is amplified because multiple users share the same node or fiber line from the ISP.
“Peak time congestion is one of the most common but misunderstood issues in residential broadband. It’s not always about speed tiers—it’s about how efficiently the network is used.” — Dr. Raj Mehta, Network Optimization Specialist, Broadband Research Institute
Common Causes of Peak Hour Lag
- Network Congestion: Your ISP’s local node becomes overloaded when too many users access the internet simultaneously.
- Home Network Overload: Multiple devices streaming, gaming, or updating at once strain your router’s processing power.
- Outdated Router: Older routers lack modern standards like MU-MIMO or beamforming, which help manage multiple connections efficiently.
- Poor Router Placement: Physical obstructions like walls, metal appliances, or distance reduce signal strength, especially under load.
- Interference from Neighboring Networks: In dense areas, overlapping Wi-Fi channels create signal noise and reduce throughput.
- Background Device Activity: Smart TVs, phones, and laptops often update apps or back up data automatically in the evening.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing Evening Wi-Fi Lag
Follow this proven sequence to diagnose and resolve your peak-hour slowdowns. Most fixes take less than 30 minutes and require no technical expertise.
- Test Your Speed at Different Times
Use a free tool like Fast.com or Speedtest.net to measure your download/upload speeds at noon, 6 PM, and 9 PM. If speeds drop significantly only during evening hours, congestion is likely the culprit. - Restart Your Router and Modem
Unplug both devices for 30 seconds, then power them back on. This clears temporary glitches and resets connection logs that may be slowing performance. - Update Router Firmware
Log into your router’s admin page (usually via 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). Check for firmware updates under \"Administration\" or \"System.\" Updated firmware improves stability and security. - Change Your Wi-Fi Channel
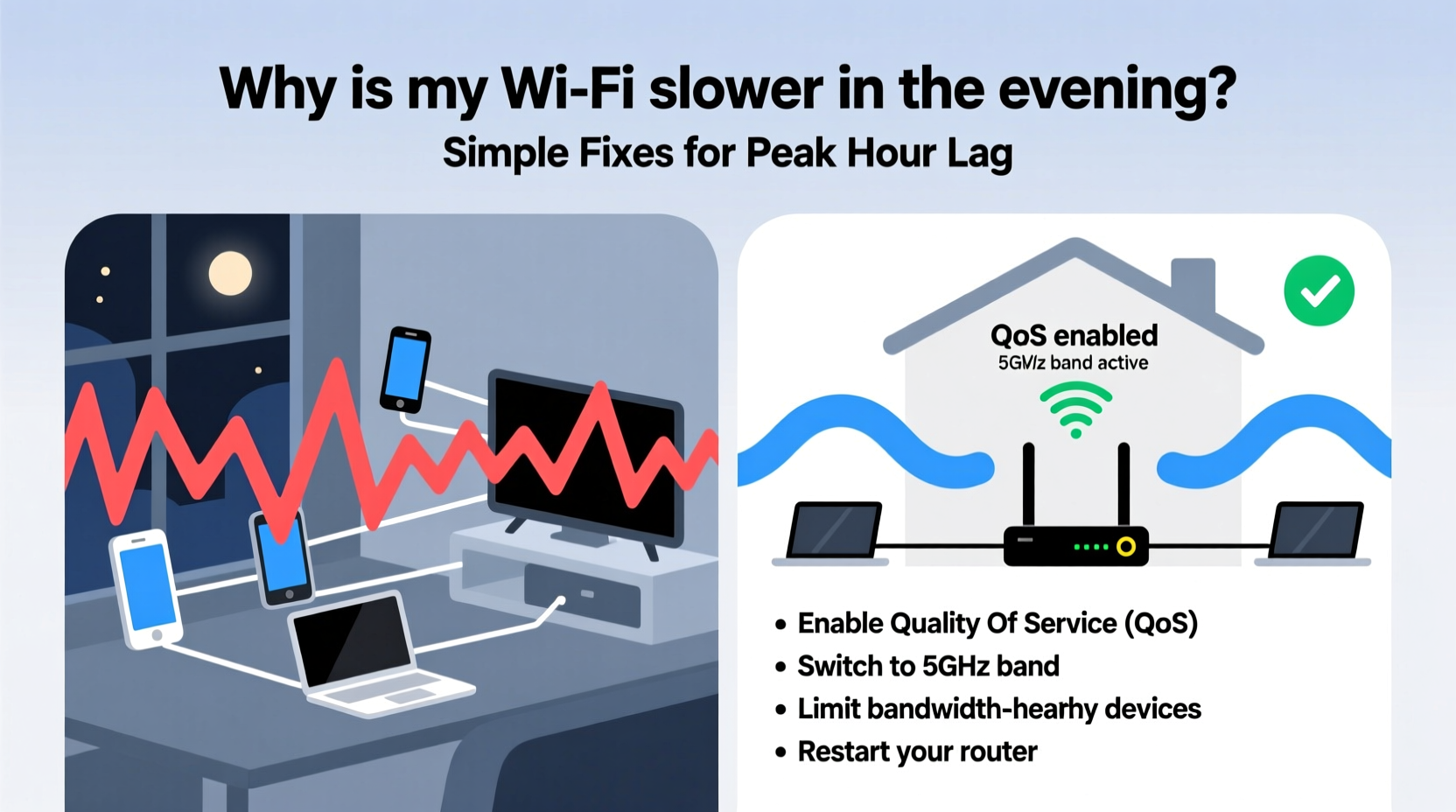
Use a free app like Wi-Fi Analyzer (Android) or NetSpot (Windows/Mac) to see which 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz channels nearby networks are using. Switch your router to the least crowded channel—ideally channel 1, 6, or 11 on 2.4 GHz, or any non-overlapping channel on 5 GHz. - Enable Quality of Service (QoS)
In your router settings, enable QoS and prioritize critical activities like video calls or streaming. This ensures bandwidth is allocated fairly instead of letting one device hog everything. - Limit Background Devices
Temporarily disconnect devices you’re not actively using. You can also set up MAC address filtering or device scheduling to prevent certain gadgets from connecting after 7 PM. - Reposition Your Router
Place your router centrally, elevated, and away from microwaves, cordless phones, and thick walls. Avoid basements or enclosed cabinets.
Do’s and Don’ts: Wi-Fi Optimization Table
| Action | Do | Don't |
|---|---|---|
| Router Placement | Central location, elevated, open space | Near microwave, behind TV, inside drawer |
| Channel Selection | Use 5 GHz or least crowded 2.4 GHz channel | Leave on auto if interference is high |
| Device Management | Turn off unused smart devices | Allow all devices full access 24/7 |
| Firmware | Check updates quarterly | Ignore notifications or skip updates |
| Streaming Priorities | Enable QoS for media devices | Let downloads run during movie time |
Mini Case Study: The Johnson Family’s Streaming Struggles
The Johnsons in suburban Chicago had been frustrated for months. Every night at 7:30 PM, their Netflix would buffer mid-episode. Their plan was 200 Mbps, so they assumed it was a problem with the service. After running speed tests, they discovered their actual throughput dropped to 35 Mbps during peak hours.
They followed the step-by-step guide above: updated their three-year-old router’s firmware, switched from channel 6 to channel 1 on 2.4 GHz, and enabled QoS to prioritize their Apple TV. They also scheduled their Ring doorbell and Nest thermostat to update at 5 AM.
Within two days, their evening speeds stabilized at 150+ Mbps. No more buffering. They avoided paying for a higher-tier plan and extended their router’s life by another two years.
When Hardware Matters: Upgrading Strategically
Sometimes, the issue isn’t usage—it’s aging equipment. Routers older than 3–4 years may not support modern standards like Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), which handle multiple devices far more efficiently.
If you’ve optimized settings and still face lag, consider upgrading. But don’t rush to buy the most expensive model. Instead, match your needs:
- Small apartment, few devices: A modern dual-band router ($60–$100) is sufficient.
- Large home, 10+ devices: Invest in a Wi-Fi 6 mesh system (e.g., TP-Link Deco, Eero) for seamless coverage.
- Gamers or 4K streamers: Look for routers with QoS, low latency modes, and tri-band support.
One key feature to prioritize is MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output), which allows your router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously—not one at a time. This drastically reduces lag during peak usage.
“Upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 router reduced my family’s evening complaints from daily to zero. It handles congestion like nothing I’ve seen before.” — Lisa Tran, Home Network Consultant
Advanced Fixes for Persistent Lag
If basic optimizations haven’t solved the problem, try these deeper interventions:
Use Ethernet Where Possible
Hardwiring your main devices—smart TV, desktop PC, game console—removes them from the Wi-Fi load entirely. Even a single Ethernet connection can free up enough bandwidth to smooth out the rest of the network.
Switch to the 5 GHz Band
Your router broadcasts two signals: 2.4 GHz (longer range, slower, crowded) and 5 GHz (faster, shorter range, less interference). Connect high-demand devices to 5 GHz. Rename your SSIDs (e.g., “Home-WiFi-2G” and “Home-WiFi-5G”) to make switching easier.
Contact Your ISP About Node Congestion
If your speed tests show a consistent 40–60% drop during evenings, contact your ISP. Ask: “Is there known node congestion in my area?” Some providers offer usage-based throttling disclosures or can upgrade your segment priority.
Set Up a Guest Network
Run guest devices (visitors’ phones, IoT gadgets) on a separate network. This isolates traffic and prevents unknown devices from consuming your primary bandwidth.
Checklist: Optimize Your Wi-Fi for Peak Hours
Print or save this checklist to perform a monthly Wi-Fi health check:
- ✅ Run speed tests at peak and off-peak times
- ✅ Restart modem and router
- ✅ Update router firmware
- ✅ Change to the least congested Wi-Fi channel
- ✅ Enable Quality of Service (QoS)
- ✅ Disconnect or schedule inactive devices
- ✅ Reposition router for optimal coverage
- ✅ Use Ethernet for high-bandwidth devices
- ✅ Consider a Wi-Fi 6 upgrade if over 3 years old
- ✅ Contact ISP if slowdowns persist
FAQ: Common Questions About Evening Wi-Fi Lag
Why does my Wi-Fi slow down only at night?
Evening slowdowns occur due to increased demand on both your home network and your ISP’s local infrastructure. More people are home using streaming, gaming, and social media, leading to congestion.
Can my neighbors really affect my Wi-Fi speed?
Yes. In densely populated areas, overlapping Wi-Fi signals on the same channel cause interference. Using a Wi-Fi analyzer app helps you pick the clearest channel.
Will restarting my router help every day?
Restarting clears memory and reestablishes a clean connection. While not a permanent fix, doing it daily—or scheduling automatic reboots via your router settings—can maintain stability during heavy use periods.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Evening Internet
Slow Wi-Fi in the evening doesn’t have to be inevitable. By understanding the causes—network congestion, outdated gear, poor setup—and applying targeted fixes, you can reclaim fast, reliable internet when you need it most. The solutions aren’t complicated or costly. From adjusting settings to smarter device management, each small change adds up to a smoother online experience.
You don’t need to suffer through endless buffering or laggy Zoom calls. Start tonight: reboot your router, check your Wi-Fi channel, and disable background updates. Small actions lead to big improvements. Share your success story or ask questions in the comments—let’s build a community of faster, smarter home networks.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?