Super Micro Computer, Inc. (SMCI) has experienced significant volatility in recent months, with its once-meteoric rise followed by a sharp reversal. After reaching all-time highs in mid-2024 on the back of surging demand for AI infrastructure, the stock has pulled back notably, leaving investors questioning what’s behind the downturn. While long-term fundamentals remain strong for many analysts, several interrelated factors have contributed to the recent decline in SMCI stock.
Market Sentiment Shift in Tech and AI Stocks
The broader technology sector, particularly AI-focused companies, saw a speculative surge in early 2024. Investors poured capital into firms positioned at the forefront of artificial intelligence, and Super Micro was among the biggest beneficiaries. However, by late 2024, sentiment began to shift. Rising interest rates, inflation concerns, and fears of an economic slowdown prompted a reassessment of high-growth, high-multiple stocks.
SMCI, which traded at price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios far above historical averages, became vulnerable to profit-taking. As institutional investors rebalanced portfolios toward more defensive positions, momentum-driven traders exited their positions, accelerating the sell-off.
Supply Chain and Production Challenges
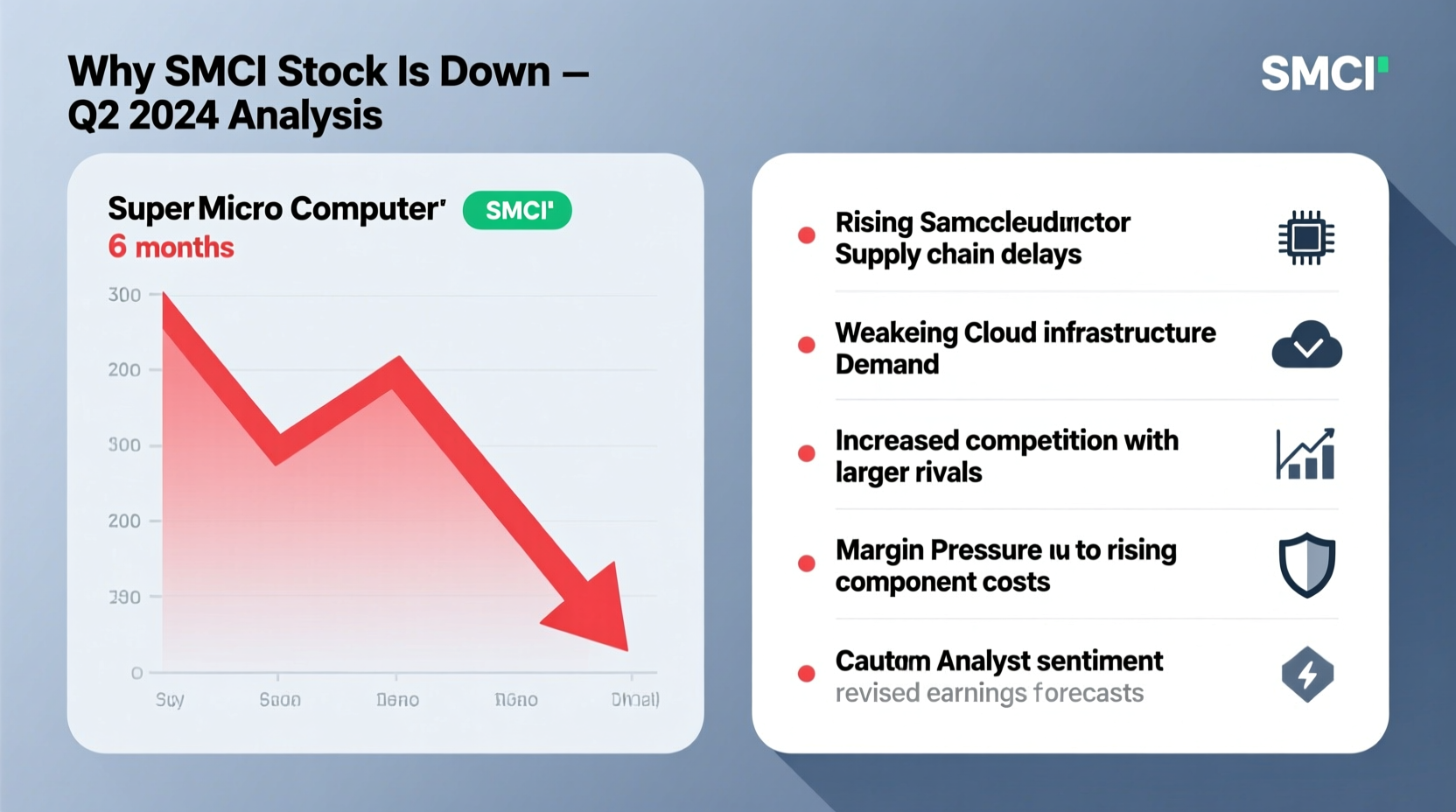
Despite strong demand for AI servers, Super Micro has faced operational headwinds. In Q3 2024, the company issued a statement citing temporary delays in component sourcing, particularly advanced GPUs and networking chips. These bottlenecks limited its ability to fulfill orders on time, leading some clients to explore alternative vendors or delay deployments.
While the company emphasized that these were short-term issues tied to global semiconductor shortages, the market reacted negatively. Revenue growth projections were revised slightly downward, and margins were pressured due to increased logistics costs and expedited shipping fees.
Additionally, Super Micro’s reliance on third-party suppliers for critical components exposes it to geopolitical risks—especially given ongoing tensions affecting Taiwan and South Korea-based manufacturers.
Increased Competition in the AI Server Market
Super Micro’s niche in custom, energy-efficient AI-optimized servers gave it a first-mover advantage. But that lead is narrowing. Major players like Dell, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), and Lenovo have accelerated their AI server offerings, leveraging stronger balance sheets and established enterprise relationships.
Moreover, cloud giants such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are increasingly designing in-house server solutions, reducing reliance on external OEMs like Super Micro. This trend threatens long-term market share, especially in large-scale data center contracts.
Analysts note that while Super Micro maintains technological differentiation, its smaller scale compared to industry giants makes customer retention more challenging during pricing wars or extended delivery timelines.
“Super Micro built a compelling story around AI infrastructure, but scalability and execution risk remain key concerns.” — Rajiv Mehta, Senior Analyst at TechEquity Research
Valuation Concerns and Profit-Taking
At its peak in June 2024, SMCI traded at over 70 times forward earnings—a valuation typically reserved for hyper-growth tech leaders with dominant market positions. With revenue growing rapidly but profitability still maturing, some investors questioned whether the stock had outpaced its fundamentals.
The pullback allowed for a re-rating more aligned with sustainable growth expectations. A correction from extreme multiples brought SMCI closer to peers like NVIDIA and AMD on a growth-adjusted basis, though it remains relatively expensive.
| Company | Forward P/E (Peak 2024) | Current P/E (Late 2024) | Revenue Growth (YoY) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Super Micro (SMCI) | 72x | 48x | 85% |
| NVIDIA (NVDA) | 65x | 42x | 120% |
| HPE (HPE) | 10x | 9x | 7% |
The table illustrates how SMCI’s valuation, while still elevated, has adjusted to reflect tempered expectations. The decline wasn’t solely due to weak performance but rather a recalibration of investor appetite for risk.
Macro and Regulatory Factors
Beyond company-specific issues, macroeconomic conditions played a role. The Federal Reserve maintained higher-for-longer interest rate policies into late 2024, increasing borrowing costs and reducing the present value of future earnings—particularly impactful for growth stocks.
Additionally, new U.S. export controls on advanced computing chips to certain countries created uncertainty for companies involved in global AI infrastructure. While Super Micro complies with all regulations, the complexity of compliance and potential delays in international shipments added operational friction.
Currency fluctuations also affected margins, as a stronger U.S. dollar made Super Micro’s products more expensive in key overseas markets, including Europe and parts of Asia.
Real Example: Institutional Investor Pullback
In August 2024, a major hedge fund known for its tech investments reduced its stake in SMCI by 40%. Internal communications cited “valuation disconnect” and “execution risk amid supply constraints” as primary reasons. The move triggered algorithmic selling across multiple funds using similar risk models, amplifying the downward pressure.
This case highlights how single decisions by large investors can cascade through the market, especially in stocks with lower float and high institutional ownership like SMCI.
Actionable Checklist for SMCI Investors
- Evaluate holding rationale: Are you investing based on long-term AI trends or short-term momentum?
- Review valuation metrics: Compare SMCI’s P/E, PEG ratio, and revenue growth against sector benchmarks.
- Monitor quarterly guidance: Pay close attention to management’s commentary on supply chain improvements and backlog fulfillment.
- Assess competition: Track wins/losses against HPE, Dell, and in-house cloud provider solutions.
- Diversify exposure: Consider balancing SMCI with broader AI or semiconductor ETFs to reduce single-stock risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is SMCI stock fundamentally broken?
No. The core business remains strong, with robust demand for AI-optimized servers. The decline reflects valuation corrections and near-term challenges, not a collapse in fundamentals.
Could SMCI recover in 2025?
Yes. If supply chain issues ease, margins stabilize, and AI adoption continues growing, SMCI could regain investor confidence. Many analysts maintain “buy” ratings with target prices above current levels.
Should I buy the dip?
That depends on your risk tolerance and investment horizon. Long-term investors may see this as an entry opportunity, but volatility is likely to persist. Dollar-cost averaging can help mitigate timing risk.
Conclusion: Navigating Volatility with Clarity
The decline in SMCI stock is not the result of a single failure but a confluence of market dynamics, competitive pressures, and valuation realities. While the AI wave remains powerful, investor expectations have shifted from unbridled optimism to a more cautious assessment of execution and sustainability.
For shareholders, this period offers a chance to reassess positioning and strategy. For prospective investors, the pullback provides a more reasonable entry point—if accompanied by thorough due diligence.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?