Flaxseed oil, derived from the seeds of the flax plant (*Linum usitatissimum*), has been used for centuries in traditional medicine and culinary practices. Today, it stands out as one of the richest plant-based sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an essential omega-3 fatty acid. Unlike fish oils, which provide EPA and DHA directly, flaxseed oil offers a vegan-friendly alternative that supports cardiovascular, cognitive, and inflammatory health when consumed consistently. With growing interest in natural supplements and plant-powered nutrition, understanding why use flaxseed oil—and how to use it effectively—has never been more relevant.
The Nutritional Powerhouse Behind Flaxseed Oil
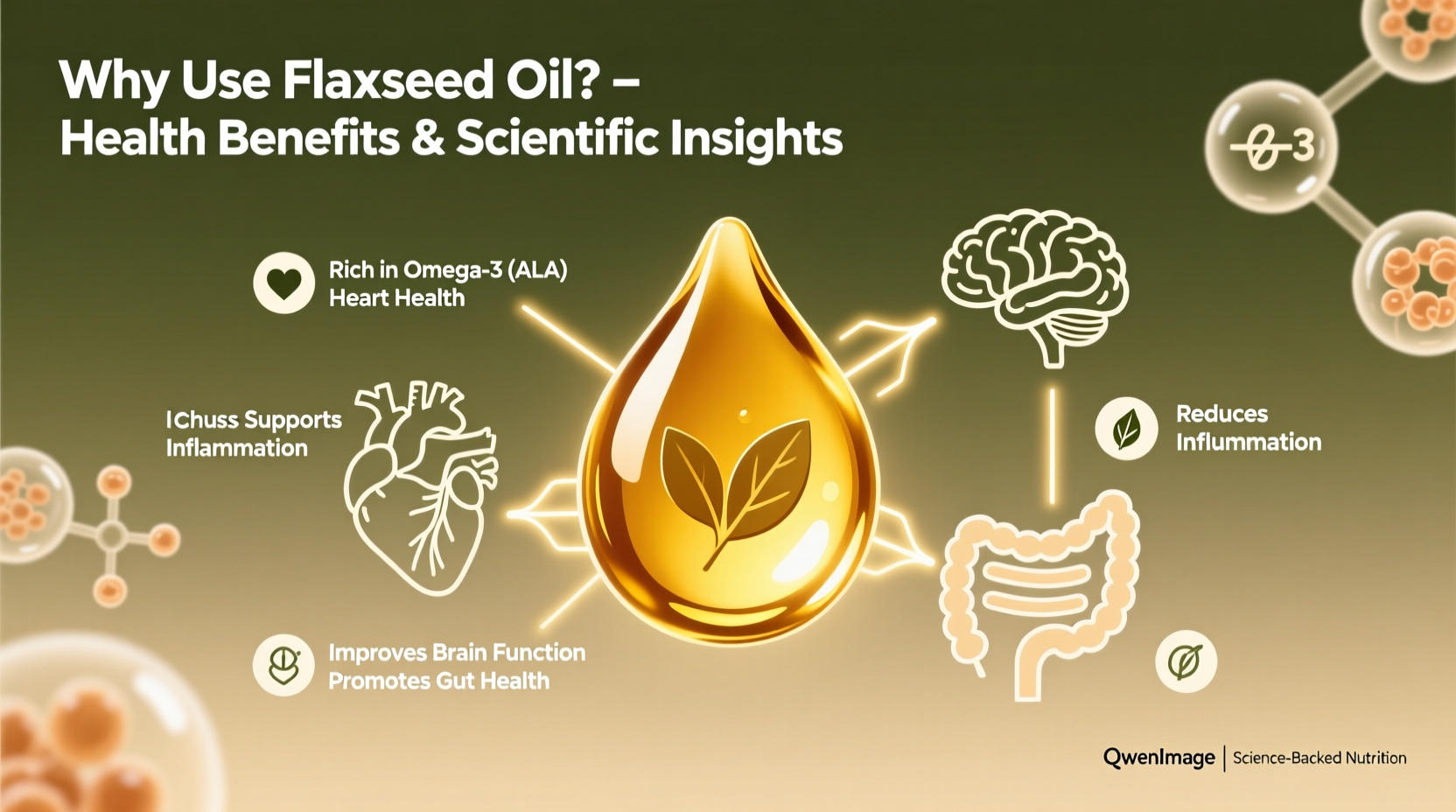
Flaxseed oil is not just another dietary supplement—it’s a concentrated source of polyunsaturated fats, particularly ALA, which the body cannot produce on its own. A single tablespoon (14 grams) contains approximately 7,200 mg of ALA, meeting and often exceeding daily recommended intakes for omega-3s. It also contains lignans (though in lower amounts than whole flaxseeds), vitamin E, and phytosterols, all contributing to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity.
What sets flaxseed oil apart is its exceptional omega-3 to omega-6 ratio. While modern diets tend to be overloaded with omega-6 fats (pro-inflammatory), flaxseed oil helps restore balance by boosting intake of anti-inflammatory omega-3s. This shift can influence everything from joint comfort to mood regulation.
Science-Backed Health Benefits of Flaxseed Oil
Modern research supports many of the traditional claims surrounding flaxseed oil, particularly regarding chronic disease prevention and metabolic support.
Cardiovascular Protection
Omega-3 fatty acids are well known for their role in heart health. Studies show that regular consumption of flaxseed oil can help reduce total cholesterol, LDL (\"bad\") cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Its anti-inflammatory properties may also prevent arterial plaque buildup and improve endothelial function.
“Replacing saturated fats with plant-based omega-3s like those in flaxseed oil is a simple yet powerful step toward long-term cardiovascular resilience.” — Dr. Lena Patel, Integrative Cardiologist
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation underlies conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and even certain cancers. ALA converts in the body to compounds that modulate inflammatory pathways. Clinical trials have shown reductions in C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) markers after flaxseed oil supplementation, especially in individuals with elevated baseline inflammation.
Brain and Cognitive Support
Although flaxseed oil does not contain DHA directly, some ALA is converted into DHA in small amounts—particularly in women due to hormonal influences on enzyme activity. Regular intake supports neuronal membrane fluidity and may slow age-related cognitive decline. Some preliminary evidence suggests benefits in mood disorders like depression, though more human trials are needed.
Metabolic and Hormonal Balance
Preliminary studies indicate flaxseed oil may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fasting blood glucose in people with type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the lignans present (more abundant in ground seeds but still traceable in oil) exhibit weak phytoestrogenic activity, potentially easing menopausal symptoms and supporting hormonal equilibrium without disrupting endocrine function.
Practical Uses: How to Incorporate Flaxseed Oil Into Your Diet
Due to its low smoke point (around 225°F or 107°C), flaxseed oil should never be heated or used for cooking. Instead, integrate it into meals where heat isn’t applied.
- Add 1–2 tablespoons to smoothies or protein shakes.
- Drizzle over salads, steamed vegetables, or grain bowls.
- Mix into yogurt, oatmeal, or chia pudding.
- Blend into homemade dressings with lemon juice, garlic, and herbs.
For best results, consume flaxseed oil within 4–6 weeks of opening and store it in the refrigerator to prevent oxidation. Rancid oil develops a bitter smell and loses nutritional value.
Step-by-Step Guide: Building a Daily Flaxseed Oil Habit
- Choose quality: Select unrefined, cold-pressed, opaque-bottled oil from reputable brands.
- Start slow: Begin with ½ tablespoon per day to assess tolerance.
- Incorporate cold: Use only in raw applications to preserve ALA content.
- Pair wisely: Combine with vitamin E-rich foods (like nuts or spinach) to enhance stability.
- Track effects: Monitor changes in skin texture, joint comfort, or digestion over 4–8 weeks.
Flaxseed Oil vs. Other Omega-3 Sources: A Comparison
| Source | Omega-3 Type | ALA Content (per tbsp) | DHA/EPA? | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flaxseed Oil | ALA | ~7,200 mg | No | Vegans, heart health, inflammation |
| Fish Oil | EPA/DHA | Negligible | Yes | Brain function, prenatal health |
| Chia Seeds | ALA | ~5,000 mg | No | Fiber + omega combo |
| Walnuts | ALA | ~2,500 mg | No | Snacking, general nutrition |
| Algal Oil | DHA/EPA (from algae) | N/A | Yes | Vegan DHA needs (e.g., pregnancy) |
While flaxseed oil leads in ALA concentration, those seeking direct DHA (especially during pregnancy or aging) may benefit from combining it with algal oil. However, for general wellness and preventive care, flaxseed oil remains a cost-effective, sustainable choice.
Real-Life Example: Managing Joint Discomfort Naturally
Sarah, a 52-year-old office worker with early osteoarthritis, struggled with morning stiffness in her hands and knees. After reading about plant-based anti-inflammatories, she began adding one tablespoon of refrigerated flaxseed oil to her daily green smoothie. Within six weeks, she noticed reduced joint pain and improved mobility. Her CRP levels, measured during a routine check-up, dropped from 4.1 mg/L to 2.3 mg/L—still within normal range but reflecting decreased systemic inflammation. Though not a cure, flaxseed oil became part of her proactive health strategy alongside gentle exercise and hydration.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I take flaxseed oil if I’m on blood thinners?
Consult your doctor before combining flaxseed oil with anticoagulant medications like warfarin. High doses of omega-3s may increase bleeding risk due to mild platelet inhibition.
How much flaxseed oil should I take daily?
Most adults benefit from 1–2 tablespoons (14–28 g) per day. This provides 7,000–14,000 mg of ALA, aligning with recommendations for omega-3 intake from plant sources.
Is flaxseed oil safe for children?
Yes, in moderate amounts. Children over age 4 can consume ½ to 1 teaspoon daily, especially if they don’t eat fish. Always introduce gradually and monitor for digestive reactions.
Checklist: Getting the Most From Your Flaxseed Oil
- ☑ Buy cold-pressed, organic oil in dark glass packaging
- ☑ Store in the refrigerator and use within 6 weeks of opening
- ☑ Avoid heating or frying with the oil
- ☑ Consume daily with food to enhance absorption
- ☑ Pair with antioxidants (vitamin E, C) to prevent oxidation
- ☑ Track physical changes over time (skin, energy, joint comfort)
Final Thoughts: Why Make Flaxseed Oil Part of Your Routine?
Choosing flaxseed oil isn't just about filling a nutrient gap—it's about making a deliberate move toward preventive, plant-centered wellness. Whether you're aiming to support heart function, reduce inflammation, or simply diversify your fat intake with cleaner options, this golden oil offers measurable benefits backed by both tradition and science. It fits seamlessly into plant-based diets and complements omnivorous lifestyles alike.
The key lies in consistency and proper handling. When stored correctly and used intelligently, flaxseed oil becomes more than a supplement—it becomes a daily act of self-care rooted in nature’s design.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?