Wireless mice offer freedom from cables and clutter, but when they start lagging, the experience can be more frustrating than functional. Whether you're navigating spreadsheets, editing photos, or immersed in a fast-paced game, even minor delays between movement and cursor response break productivity and immersion. The good news is that most cases of wireless mouse lag are fixable—often with simple adjustments. Understanding the root causes and knowing how to respond quickly can save time and prevent unnecessary replacements.
Common Causes of Wireless Mouse Lag
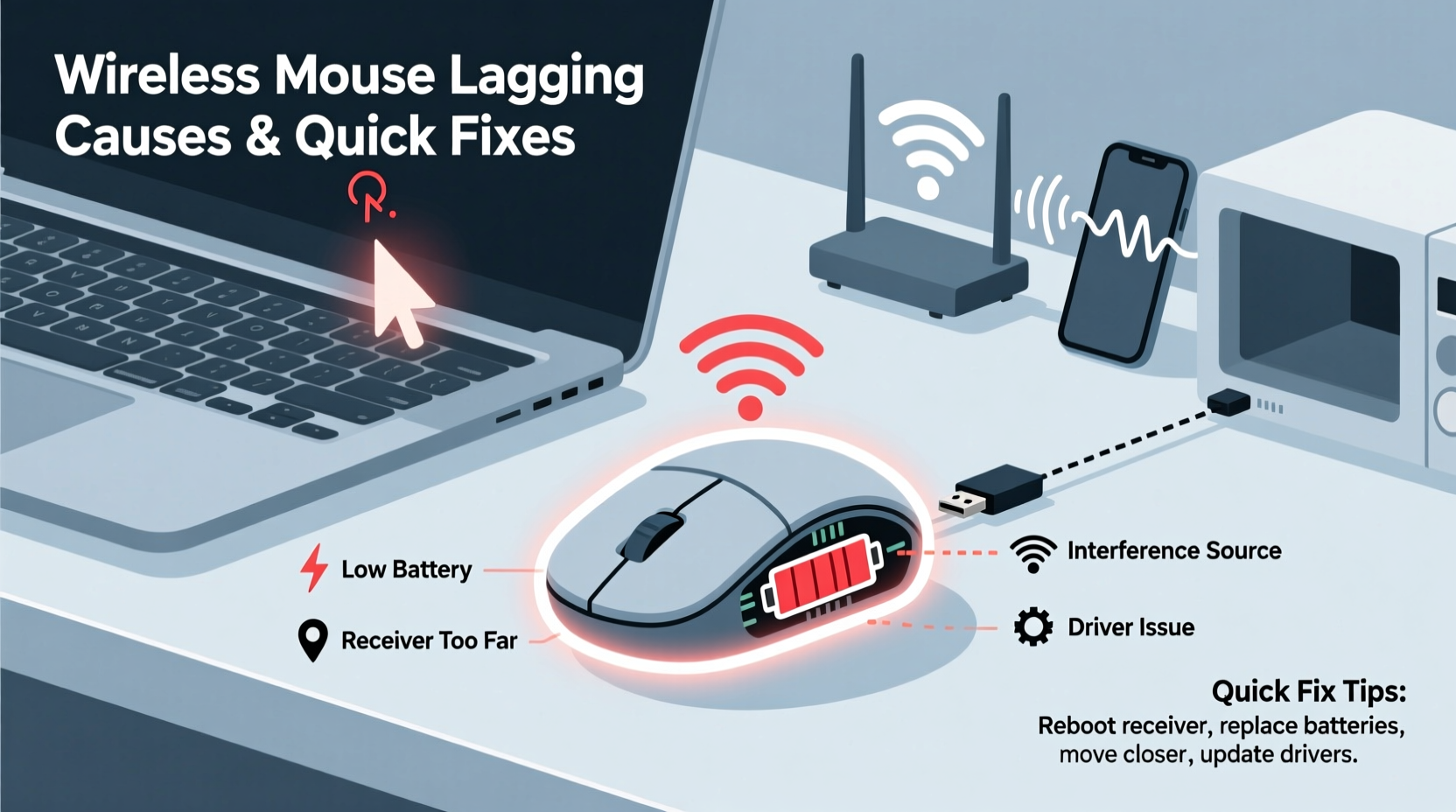
Lag in a wireless mouse isn’t always due to hardware failure. More often, it stems from environmental interference, outdated drivers, or improper setup. Identifying the cause is the first step toward resolution.
- Interference from other devices: Bluetooth and radio frequency (RF) signals can be disrupted by nearby electronics like microwaves, cordless phones, or Wi-Fi routers.
- Low battery power: As batteries deplete, signal strength weakens, leading to inconsistent responsiveness.
- USB receiver placement: If the receiver is blocked or placed behind a metal object, signal transmission suffers.
- Outdated or corrupted drivers: Operating systems require updated drivers to communicate efficiently with peripheral devices.
- Distance from the receiver: Most wireless mice operate optimally within 6–10 feet of the USB dongle.
- High system resource usage: When your computer is overloaded, input device polling may be delayed.
- Dongle conflicts: Multiple wireless devices using similar frequencies on the same USB hub can interfere with each other.
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose and Fix Lag
Follow this logical sequence to systematically eliminate potential sources of lag:
- Check battery level: Replace old batteries with fresh ones—even if the low-battery indicator hasn't activated.
- Reposition the USB receiver: Use an extension cable or move the receiver closer to the mouse, ideally at desk level and unobstructed.
- Reduce wireless interference: Turn off nearby Bluetooth speakers, phones, or microwave ovens temporarily to test improvement.
- Test on another computer: Plug the mouse into a different machine to determine if the issue lies with the device or your system. <5> Update mouse drivers: Visit the manufacturer’s website (Logitech, Microsoft, Razer, etc.) and download the latest firmware and software suite.
- Adjust pointer settings: In Windows, go to Settings > Devices > Mouse > Additional mouse options, then disable \"Enhance pointer precision\" and reduce pointer speed to minimize processing overhead.
- Close background applications: High CPU or disk usage can delay input polling. Use Task Manager to identify and close resource-heavy apps.
Do’s and Don’ts: Best Practices for Wireless Mouse Performance
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Use high-quality alkaline or rechargeable batteries with stable voltage output. | Use cheap or mixed batteries—one weak cell can destabilize the entire connection. |
| Keep the USB receiver elevated and clear of obstructions. | Plug the receiver into a USB hub buried behind your PC tower. |
| Regularly update your operating system and peripheral drivers. | Ignore firmware update notifications from your mouse manufacturer. |
| Limit the number of active Bluetooth devices near your workspace. | Surround your desk with multiple wireless gadgets without testing for interference. |
| Use a dedicated USB port, not shared through a hub. | Run power-intensive tasks and expect flawless mouse tracking simultaneously. |
Real Example: Solving Lag in a Home Office Setup
Sarah, a freelance graphic designer, began noticing her Logitech MX Master 3 would freeze intermittently during client Zoom calls and Photoshop sessions. She initially assumed the mouse was failing. After testing it on her partner’s laptop—with no issues—she realized the problem was local to her desktop. Her PC sat under a metal desk, and the USB receiver was plugged into a rear port, blocked by the chassis. She used a 1-foot USB extension cable to bring the receiver to the front edge of the desk, away from metal shielding. She also replaced aging AA batteries with new lithium ones. The lag disappeared immediately. Later, she updated the Logi Options+ software and disabled pointer acceleration, achieving buttery-smooth tracking essential for precision design work.
Expert Insight on Wireless Peripheral Reliability
“Signal stability in wireless mice depends more on environment and configuration than on the mouse itself. A well-placed receiver and clean power supply solve 80% of reported lag issues.” — David Lin, Senior Hardware Engineer at Peripheral Dynamics Lab
Quick Fixes Checklist
Use this checklist for rapid troubleshooting when your wireless mouse starts lagging:
- ✅ Replace or recharge batteries
- ✅ Reposition USB receiver to an open, unobstructed port
- ✅ Move away from sources of electromagnetic interference
- ✅ Update mouse drivers and firmware via manufacturer software
- ✅ Test the mouse on another computer
- ✅ Disable mouse acceleration and adjust pointer speed
- ✅ Restart your computer to clear temporary system glitches
- ✅ Avoid using USB hubs; connect directly to the motherboard
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Wi-Fi networks affect my wireless mouse?
Yes. Many wireless mice use the 2.4 GHz band, which is shared with Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, and other peripherals. If multiple devices operate on this frequency in close proximity, interference can occur. To reduce conflict, consider switching your router to 5 GHz where possible, or use a wired mouse in high-interference environments.
Is Bluetooth better than RF for reducing lag?
Not necessarily. While modern Bluetooth 5.0+ offers improved latency and range, RF connections via a dedicated USB dongle typically provide lower latency and more consistent performance. RF mice often support higher polling rates (up to 1000 Hz), making them preferable for gaming and real-time tasks.
Why does my mouse lag only during certain applications?
This usually indicates software-related strain. Video games, video editors, or virtual machines can consume significant CPU resources, delaying how quickly the system polls input devices. Monitor your system performance during these tasks. Closing unused programs or upgrading your RAM and SSD can alleviate bottlenecks affecting mouse responsiveness.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Wireless Experience
Wireless mouse lag is rarely a permanent flaw—it’s usually a solvable mismatch between technology and environment. By methodically addressing power, positioning, interference, and software, most users can restore seamless operation in minutes. Don’t rush to replace a functioning device when a few smart tweaks can revive its performance. Pay attention to your workspace setup, stay current with updates, and treat your peripherals as part of a larger ecosystem. With the right care, your wireless mouse can deliver responsive, reliable control day after day.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?