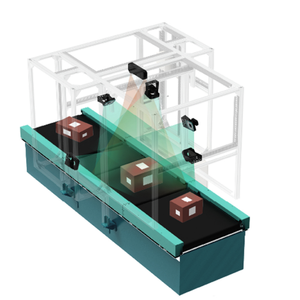
Automated Scans







 1/15
1/15












 1/25
1/25



















 1/3
1/3




 1/2
1/2





 1/3
1/3

 CN
CN






 1/7
1/7

 CN
CN








 1/3
1/3






 1/18
1/18




 1/3
1/3



 1/2
1/2











 1/16
1/16




 1/3
1/3







 1/27
1/27









 1/17
1/17














 1/28
1/28
About automated scans
Where to Find Automated Scans Suppliers?
No active suppliers were identified in the current dataset for automated scans manufacturing. This may indicate limited public visibility of production hubs, specialized niche development within closed industrial ecosystems, or classification under alternative product categories such as industrial automation systems or non-destructive testing (NDT) equipment. In global markets, regions with advanced capabilities in precision instrumentation—such as Guangdong and Jiangsu provinces in China, Baden-Württemberg in Germany, and Aichi Prefecture in Japan—typically serve as core centers for high-tech scanning technologies.
These regions support integrated supply chains combining optical engineering, sensor fabrication, and software integration, enabling end-to-end development of automated scanning solutions. Facilities in these clusters often feature cleanrooms, calibration labs, and AI-driven data processing units, supporting compliance with ISO 17025 for testing and calibration laboratories. Buyers seeking scalable partnerships should focus on suppliers embedded within technology parks or research-industry consortia that facilitate rapid prototyping and regulatory alignment for medical, aerospace, or automotive applications.
How to Choose Automated Scans Suppliers?
In absence of verifiable supplier data, procurement strategies must emphasize rigorous technical and operational due diligence:
Technical Compliance
Require documented adherence to relevant quality and safety standards based on application: ISO 13485 for medical imaging devices, IEC 61326-1 for electromagnetic compatibility in industrial environments, and CE marking for EU market access. For laser-based systems, confirm compliance with IEC 60825 for laser radiation safety. Verify calibration certificates traceable to national measurement institutes (e.g., NIST, PTB).
Production Capability Audits
Evaluate suppliers against critical infrastructure benchmarks:
- Minimum 3,000m² facility with dedicated R&D and testing zones
- In-house expertise in optoelectronics, machine vision algorithms, and motion control systems
- Investment in metrology-grade positioning stages and environmental test chambers
Confirm integration of statistical process control (SPC) in assembly workflows and version-controlled firmware deployment.
Transaction Safeguards
Insist on third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, TÜV) prior to shipment, particularly for first-time engagements. Utilize secure payment mechanisms such as irrevocable letters of credit or escrow arrangements tied to performance milestones. Request sample validation under real-world operating conditions, assessing scan accuracy (±0.01mm tolerance), repeatability, and software interface stability before volume ordering.
What Are the Best Automated Scans Suppliers?
No supplier profiles are available in the current dataset. As a result, no comparative analysis can be conducted regarding factory size, delivery performance, response times, or customer retention metrics. Procurement teams should proactively engage potential manufacturers through industry trade shows (e.g., CONTROL, AUTOMATE), technical publications, or government-certified innovation registries to identify qualified candidates. Prioritize firms demonstrating long-term investment in R&D, patent portfolios in imaging technology, and export experience in regulated sectors.
Performance Analysis
Without empirical data, supplier evaluation relies entirely on verified technical documentation, site audits, and reference client interviews. Emerging players may offer competitive pricing but pose risks related to after-sales support and spare parts availability. Established enterprises typically provide higher system reliability and comprehensive service networks, albeit at premium cost structures. Emphasis should be placed on suppliers offering modular architectures that allow future upgrades in resolution, speed, or analytical software features.
FAQs
How to verify automated scans supplier reliability?
Validate certifications through official databases maintained by accreditation bodies. Request audit trails covering design history files (DHF), risk assessments (per ISO 14971), and corrective action reports. Conduct virtual or on-site facility walkthroughs focusing on cleanroom protocols, component traceability, and employee training records.
What is the average sampling timeline?
Custom automated scanning systems require 30–60 days for prototype development, depending on complexity. Standardized benchtop models may be available in 15–25 days. Add 10–14 days for international air freight and customs clearance. Expedited builds with priority engineering resources can reduce timelines by up to 30%, subject to additional fees.
Can suppliers ship automated scans worldwide?
Yes, experienced exporters manage global logistics via air or sea freight, with proper crating and climate control for sensitive components. Confirm Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP) during contracting and ensure import compliance with destination regulations, including electrical safety, radio frequency emissions, and medical device registration where applicable.
Do manufacturers provide free samples?
Samples are rarely offered free of charge due to high unit costs and customization levels. Some suppliers apply sample fees toward subsequent orders exceeding predefined thresholds (e.g., $50,000). Evaluation units may be provided under loan agreements requiring return within 60 days.
How to initiate customization requests?
Submit detailed technical requirements including scanning method (laser triangulation, structured light, CT-based), field of view (FOV), resolution (µm-level), object dimensions, and integration needs (PLC communication, MES connectivity). Reputable suppliers respond with feasibility studies, 3D mechanical layouts, and software API specifications within 5–7 business days.