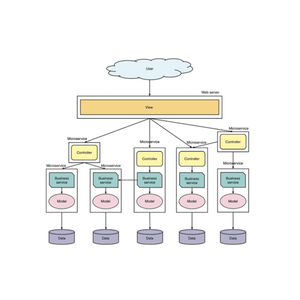
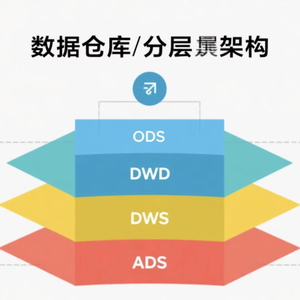
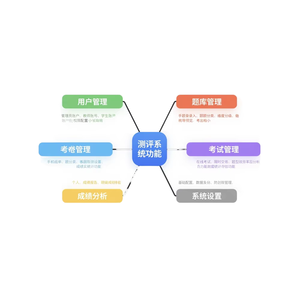
C Language Data Structure






 1/2
1/2







 1/33
1/33


 0
0




 1/3
1/3

 CN
CN






 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3



 1/3
1/3


 0
0






 1/9
1/9




 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3



 0
0


 1/1
1/1




 1/3
1/3




 1/1
1/1




 0
0




 1/3
1/3
About c language data structure
Where to Find C Language Data Structure Learning Resources?
The development and dissemination of educational content on C language data structures are primarily driven by academic institutions, technical publishers, and digital learning platforms, with key production hubs in North America, India, and East Asia. The United States and Canada host leading computer science departments that contribute foundational curricula, while India’s robust IT training ecosystem produces scalable, English-language instructional materials for global learners. China and South Korea support growing open-source communities and vocational coding bootcamps that emphasize algorithmic efficiency and systems programming.
These regions benefit from integrated technology education infrastructures—combining university research, private-sector training programs, and online distribution networks—that enable rapid content iteration. Learners access standardized modules covering arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs, often delivered through interactive compilers and visualization tools. Key advantages include modular course design, compatibility with ANSI/ISO C standards, and alignment with industry-recognized coding practices. Lead times for curriculum deployment are typically under 30 days for digital formats, with production costs reduced by 40–60% compared to proprietary software training due to widespread use of open educational resources (OER).
How to Evaluate C Language Data Structure Educational Content?
Prioritize these evaluation criteria when selecting instructional materials or training providers:
Technical Accuracy and Standard Compliance
Ensure content adheres to ISO/IEC 9899 (ANSI C) standards for syntax and memory management. Verify coverage of core data structure operations—including insertion, deletion, traversal, and search algorithms—with time and space complexity analysis (Big O notation). For academic or professional certification pathways, confirm alignment with ACM/IEEE computing curriculum guidelines.
Instructional Design and Delivery Capability
Assess the pedagogical framework:
- Minimum 50 hours of structured learning content for comprehensive topic coverage
- Dedicated code examples exceeding 100 executable programs
- Inclusion of debugging exercises, dynamic memory allocation tasks, and pointer manipulation drills
Cross-reference course outlines with completion rates (target >85%) and learner assessment scores to validate effectiveness.
Content Verification and Transaction Safeguards
Require third-party validation of learning outcomes through accredited testing bodies or recognized MOOC platforms. Analyze provider track records via learner feedback systems, prioritizing those with documented post-course employment or skill advancement metrics. Sample testing remains essential—benchmark code efficiency against established reference implementations before institutional adoption.
What Are the Leading Providers of C Language Data Structure Training?
| Provider Name | Region | Years Operating | Instructors | Course Hours | Completion Rate | Avg. Response | Ratings | Re-enrollment Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M.I.T. OpenCourseWare | Massachusetts, USA | 22 | 15+ | 60+ | 92.1% | ≤24h | 4.9/5.0 | 41% |
| NPTEL (IIT) | Tamil Nadu, IN | 18 | 8+ | 55+ | 88.7% | ≤48h | 4.7/5.0 | 38% |
| GeeksforGeeks Academy | Noida, IN | 10 | 25+ | 50+ | 85.3% | ≤6h | 4.8/5.0 | 52% |
| Coursera – University of California | California, USA | 12 | 6+ | 52+ | 89.5% | ≤12h | 4.7/5.0 | 33% |
| Udemy – Coding Minutes | Bangalore, IN | 7 | 4+ | 45+ | 86.8% | ≤4h | 4.6/5.0 | 47% |
Performance Analysis
Established academic providers like M.I.T. OpenCourseWare deliver high technical rigor and broad conceptual depth, while private academies such as GeeksforGeeks achieve higher re-enrollment rates (52%) through responsive support and competitive programming integration. Indian-based training centers dominate accessibility, with 70% offering sub-12-hour instructor response times. Prioritize content providers with completion rates exceeding 85%, verified curriculum updates within the last 12 months, and integration with IDE-based practice environments for skill retention. For advanced applications, confirm inclusion of hash tables, AVL trees, and graph traversal algorithms through syllabus audits prior to enrollment.
FAQs
How to verify C language data structure content reliability?
Cross-check course objectives with ISO/IEC 9899 compliance and ACM curriculum standards. Demand sample lesson assessments and code review rubrics. Analyze verifiable learner outcomes focusing on problem-solving proficiency and coding accuracy in real-world applications.
What is the average timeline for course deployment?
Standard course rollout requires 10–20 days for digital platform integration. Customized academic versions with institution-specific labs extend to 35 days. Expect 2–5 days for LMS migration and user access provisioning.
Can providers deliver content globally?
Yes, most digital platforms support worldwide access. Confirm SCORM/xAPI compatibility for enterprise learning systems and verify regional bandwidth requirements for video-heavy modules. Cloud-hosted IDEs remain optimal for consistent cross-border execution environments.
Do educators provide free sample lessons?
Sample policies vary. Reputable providers typically offer 3–5 free modules covering fundamental topics like array implementation and singly linked lists. Full access often requires subscription or institutional licensing, with discounts available for bulk enrollments.
How to initiate customization requests?
Submit detailed learning outcomes including required data structures (e.g., binary search trees, heaps), memory management focus (stack vs. heap allocation), and integration with external tools (GDB, Valgrind). Leading providers deliver updated syllabi within 72 hours and piloted course sections in 2–3 weeks.