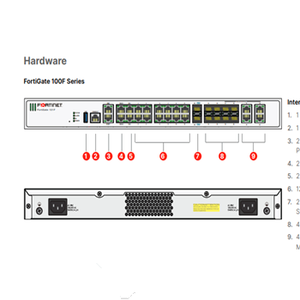
Computer Network And Network Security



 0
0




 0
0







 1/14
1/14



 0
0





 1/3
1/3







 0
0






 1/2
1/2





 CN
CN





 1/1
1/1


 0
0



 1/2
1/2




 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3






 1/1
1/1



 0
0



 1/3
1/3



 1/3
1/3


 0
0






 1/2
1/2
About computer network and network security
Where to Find Computer Network and Network Security Suppliers?
The global supply base for computer network and network security equipment is highly concentrated in East Asia, with China, Taiwan, and South Korea serving as primary manufacturing hubs. Within China, industrial clusters in Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Shanghai dominate production, leveraging advanced electronics manufacturing ecosystems and proximity to semiconductor suppliers. Guangdong—particularly the Shenzhen-Dongguan corridor—hosts over 70% of China’s networking hardware manufacturers, supported by integrated PCB fabrication, SMT assembly lines, and firmware development centers.
These regions offer vertically aligned supply chains enabling rapid prototyping and scalable production. Component availability, automated testing infrastructure, and compliance-ready design frameworks reduce time-to-market by 30–40% compared to Western counterparts. Buyers benefit from co-located EMS providers, certification labs (e.g., CCC, CE, FCC), and logistics gateways that support air and sea freight consolidation. Typical advantages include 25–35% lower unit costs, lead times of 15–30 days for standard orders, and flexibility for OEM/ODM configurations across routers, switches, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
How to Choose Computer Network and Network Security Suppliers?
Adopt rigorous evaluation criteria to ensure technical reliability and supply chain integrity:
Quality & Compliance Verification
Require ISO 9001 certification for quality management and ISO/IEC 27001 for information security practices. For international deployment, confirm product-level compliance with FCC Part 15 (USA), CE-RED (EU), RoHS, and UL standards where applicable. Validate electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) test reports and cybersecurity certifications such as Common Criteria or FIPS 140-2 for encryption modules.
Technical & Production Capacity Assessment
Evaluate supplier capabilities through the following benchmarks:
- Minimum 3,000m² production area with ESD-protected SMT and assembly zones
- In-house R&D team comprising ≥15% of technical staff, specializing in firmware, network protocols (e.g., SNMP, VLAN, OSPF), and threat mitigation algorithms
- Automated optical inspection (AOI) and burn-in testing capacity for 72-hour stress validation
Cross-reference facility size and testing throughput with on-time delivery performance (target ≥97%) to assess scalability and consistency.
Procurement Risk Mitigation
Implement transaction safeguards including third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, BV) prior to shipment. Utilize secure payment structures such as irrevocable LC at sight or escrow arrangements for initial orders. Conduct pre-shipment sample validation against IETF, IEEE 802.3, or NIST SP 800-41 standards depending on application. Prioritize suppliers with documented export experience to North America, EU, and ASEAN markets to ensure customs compliance and after-sales support readiness.
What Are the Best Computer Network and Network Security Suppliers?
| Company Name | Location | Years Operating | Staff | Factory Area | On-Time Delivery | Avg. Response | Ratings | Reorder Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier data currently unavailable | ||||||||
Performance Analysis
In absence of specific supplier data, procurement decisions should focus on operational maturity indicators: companies with over five years in operation typically demonstrate stable firmware update cycles and established QA processes. High reorder rates (>30%) correlate with reliable post-deployment support and interoperability assurance. Prioritize suppliers offering detailed datasheets, CLI/API access documentation, and vulnerability disclosure policies. For mission-critical deployments, verify participation in industry forums such as the Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) or Trusted Computing Group (TCG).
FAQs
How to verify computer network and network security supplier reliability?
Validate certifications through official registries and request audit trails for design validation and batch testing. Assess firmware security by reviewing signed updates, default credential policies, and patch release frequency. Analyze customer references focusing on mean time between failures (MTBF), technical support responsiveness, and field upgrade success rates.
What is the average sampling timeline?
Standard network device samples take 10–20 days for configuration and testing. Security-hardened units requiring cryptographic validation may require 25–35 days. Air freight adds 5–8 days for international delivery. Expect partial cost recovery unless MOQ thresholds (typically 50+ units) are met.
Can suppliers ship globally?
Yes, experienced manufacturers manage worldwide distribution via FOB, CIF, or DDP terms. Confirm inclusion of import-compliant labeling, power adapters, and regulatory documentation. Sea freight is optimal for containerized orders; air freight suits urgent, low-volume procurements.
Do manufacturers provide free samples?
Free samples are rare for high-value networking gear. Most suppliers charge 40–60% of unit cost for evaluation units, refundable upon order confirmation exceeding defined volumes. Exceptions may apply for long-term ODM partnerships.
How to initiate customization requests?
Submit detailed requirements including port density, PoE budget, routing protocols, firewall rule sets, and management interface preferences (CLI, SNMP, cloud). Reputable suppliers respond with system architecture proposals within 5 business days and deliver functional prototypes in 4–6 weeks.