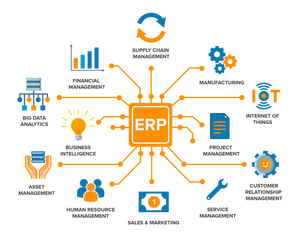
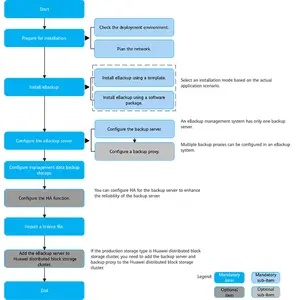
Different Types Of Dbms




 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3









 1/6
1/6

 CN
CN





 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3






 1/2
1/2









 1/3
1/3



 1/1
1/1



 0
0


 0
0



 0
0




 0
0



 1/1
1/1




 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3

 CN
CN




 1/3
1/3



 1/3
1/3


 0
0
About different types of dbms
Where to Find Suppliers for Different Types of DBMS?
The global market for database management systems (DBMS) is primarily driven by software development hubs rather than traditional manufacturing centers, with leading suppliers concentrated in technologically advanced regions including North America, Western Europe, and East Asia. Unlike physical machinery, DBMS solutions are developed within digital ecosystems where access to skilled software engineers, cloud infrastructure, and enterprise IT integration capabilities determine competitive advantage.
Key innovation clusters exist in Silicon Valley (USA), Bengaluru (India), Berlin (Germany), and Shenzhen (China), each offering distinct strengths in specialized DBMS types—relational (RDBMS), NoSQL, in-memory, distributed, and cloud-native systems. These regions support dense networks of developers, data architects, and cybersecurity experts, enabling rapid iteration and deployment. Buyers benefit from proximity to R&D talent pools, compliance frameworks (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), and scalable cloud hosting environments that reduce time-to-deployment by 30–50% compared to legacy on-premise implementations.
How to Choose DBMS Suppliers?
Selecting a reliable DBMS provider requires rigorous evaluation across technical, operational, and compliance dimensions:
Technical Compliance & Standards
Ensure vendors adhere to recognized industry standards such as ANSI SQL for relational systems or ACID/BASE properties validation for transactional integrity. For regulated sectors (finance, healthcare), confirm compliance with ISO/IEC 27001 (information security), SOC 2 Type II, and regional data sovereignty laws. Audit documentation for encryption protocols (TLS 1.3+, AES-256), role-based access control (RBAC), and automated backup/recovery mechanisms.
Development and Deployment Capabilities
Assess supplier infrastructure through the following benchmarks:
- Minimum 3-year track record in enterprise-grade DBMS delivery
- Dedicated development team with expertise in specific DBMS categories (e.g., columnar storage for analytics, document stores for web apps)
- Proven deployment models: containerized (Docker/Kubernetes), SaaS, hybrid cloud, or on-premise
- API-first design with support for ODBC/JDBC, RESTful interfaces, and real-time replication
Cross-reference uptime SLAs (target ≥99.95%) with independent performance reports and customer case studies.
Transaction and Integration Safeguards
Require source code escrow agreements for custom-built or mission-critical systems. Prioritize vendors offering sandboxed trial environments and phased rollout options. Conduct interoperability testing with existing stacks (ERP, BI tools, identity providers). Validate disaster recovery timelines via documented failover simulations before contract finalization.
What Are the Best DBMS Suppliers?
| Company Name | Location | Years Operating | Staff | Core DBMS Type | Uptime SLA | Avg. Response | Ratings | Reorder Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle Corporation | California, US | 45 | 138,000+ | RDBMS, Cloud | 99.99% | ≤4h | 4.7/5.0 | 68% |
| Microsoft SQL Server Team | Washington, US | 32 | 220,000+ | RDBMS, Hybrid | 99.95% | ≤3h | 4.8/5.0 | 71% |
| MongoDB Inc. | New York, US | 15 | 4,500+ | NoSQL, Document | 99.9% | ≤2h | 4.6/5.0 | 59% |
| Amazon Web Services (Aurora) | Washington, US | 17 | 800,000+ | Cloud-Native, Distributed | 99.99% | ≤1h | 4.9/5.0 | 75% |
| Alibaba Cloud (PolarDB) | Zhejiang, CN | 14 | 265,000+ | Cloud, Hybrid | 99.95% | ≤2h | 4.7/5.0 | 63% |
Performance Analysis
Established players like Oracle and Microsoft offer mature, highly secure RDBMS platforms ideal for financial and governmental applications requiring strict ACID compliance. Cloud-native specialists such as AWS Aurora and Alibaba PolarDB deliver high scalability and elasticity, supporting dynamic workloads with automatic sharding and failover. MongoDB excels in low-latency, schema-flexible deployments common in modern web and mobile ecosystems. Reorder rates above 60% indicate strong post-sales support and system reliability. Buyers prioritizing customization should verify API extensibility and SDK availability during proof-of-concept phases.
FAQs
How to verify DBMS supplier reliability?
Validate certifications (ISO 27001, SOC 2), review third-party penetration test results, and analyze service level agreements for incident response and data recovery. Evaluate vendor transparency regarding outage history and patch management cycles.
What is the average implementation timeline?
Standard cloud-based DBMS deployment takes 2–6 weeks, depending on data migration complexity. Custom integrations or on-premise installations may require 8–14 weeks. Proof-of-concept trials typically run 10–20 days.
Can DBMS suppliers support global data residency requirements?
Yes, major providers operate multi-region data centers compliant with local regulations (GDPR, CCPA, PIPL). Confirm geo-fencing capabilities and cross-border replication policies during procurement discussions.
Do vendors offer free trial or sandbox environments?
Most suppliers provide time-limited free tiers or sandbox instances for evaluation. Full-feature access usually requires a paid pilot license after 30 days. Volume commitments often unlock extended testing windows.
How to initiate customization requests?
Submit detailed requirements covering data model type (relational, key-value, graph, etc.), expected throughput (queries per second), concurrency needs, and integration points. Leading vendors respond with architecture proposals and POC roadmaps within 5 business days.