Multiply Binary Numbers





 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3











 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3






 1/6
1/6




 1/3
1/3


 0
0




 1/3
1/3





 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3



 1/1
1/1









 1/3
1/3






 1/11
1/11




 1/1
1/1




 1/3
1/3



 0
0





 1/3
1/3



 0
0
About multiply binary numbers
Where to Find Multiply Binary Numbers Suppliers?
The concept of "multiplying binary numbers" refers to a computational operation rather than a physical product, and as such, there are no tangible goods or industrial manufacturers associated with this function. Binary multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic process executed within digital systems, including microprocessors, FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays), and embedded computing modules. As a result, the "suppliers" for this capability are not equipment producers but providers of integrated circuits, semiconductor components, or programmable logic devices that perform binary arithmetic.
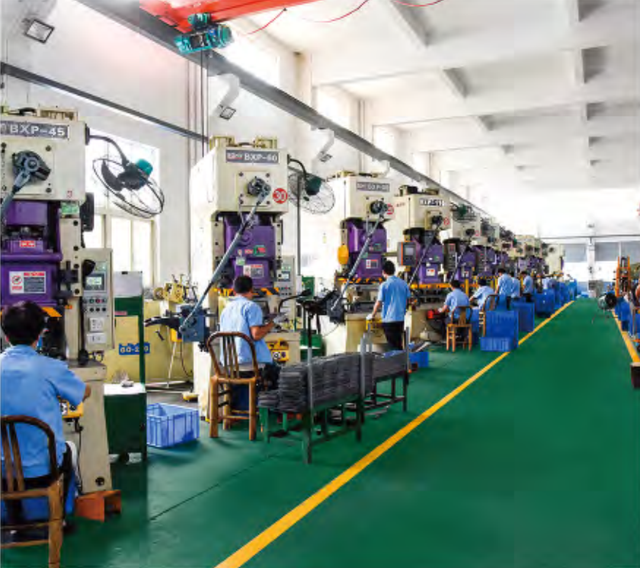
Global semiconductor manufacturing is concentrated in East Asia, particularly in China, Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan, where advanced fabrication plants (fabs) produce logic chips capable of executing binary operations at high speeds. Within China, industrial clusters in Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Beijing host design houses and packaging facilities specializing in digital signal processing units and arithmetic logic units (ALUs). These ecosystems support scalable production of ICs optimized for binary computation, leveraging localized testing infrastructure and mature supply chains for silicon wafers and substrates.
Buyers seeking to integrate binary multiplication functionality should focus on sourcing semiconductor solutions—such as microcontrollers, GPUs, or dedicated ALU chips—from established electronics manufacturers. These components enable binary arithmetic through built-in instruction sets and can be customized via firmware or hardware configuration for specific computational throughput requirements.
How to Choose Multiply Binary Numbers Solution Providers?
Since binary multiplication is implemented via electronic components rather than standalone machinery, selection criteria must center on technical specifications and component reliability:
Functional Compliance
Verify that the selected IC or processor supports binary arithmetic operations natively. Check datasheets for instruction set architecture (ISA) compatibility—ARM, RISC-V, or x86—and confirm inclusion of multiply instructions for unsigned/signed binary integers. For real-time applications, assess clock speed, latency per operation, and power efficiency metrics (e.g., GOPS/W).
Manufacturing & Quality Assurance
Prioritize suppliers adhering to international quality standards:
- ISO 9001-certified design and production processes
- Automotive-grade AEC-Q100 qualification for harsh environments
- RoHS and REACH compliance for material safety
Confirm traceability of wafer lots and packaging batches, especially for high-volume deployments requiring long-term consistency.
Supply Chain Resilience
Evaluate lead times and inventory availability through authorized distributors. Components with extended lifecycle status (>10 years) reduce obsolescence risks. Cross-reference supplier stock levels across global channels and verify dual-sourcing options to mitigate disruption risks. For custom ASIC development, require prototype validation timelines and mask tooling cost disclosures before commitment.
What Are the Best Multiply Binary Numbers Solution Providers?
Due to the nature of the query and absence of direct suppliers related to the phrase “multiply binary numbers” as a product category, no specific companies can be listed based on available supplier data. However, leading semiconductor firms known for producing digital logic components capable of efficient binary multiplication include global IDMs (Integrated Device Manufacturers) and fabless designers with proven track records in computing hardware.
Performance Analysis
In the absence of supplier data, procurement decisions should rely on benchmarked performance parameters: computational accuracy, error rates under thermal stress, and sustained operation life. Engineers should prioritize vendors offering comprehensive SDKs, simulation models, and RTL-level documentation to validate binary multiplication behavior pre-deployment. Engagement with application engineers for use-case-specific optimization remains critical, particularly in edge computing, cryptography, and DSP applications where binary math performance directly impacts system efficiency.
FAQs
How to verify binary multiplication functionality in a component?
Review the device’s technical reference manual for arithmetic instruction support. Use manufacturer-provided simulation tools (e.g., SPICE models, FPGA synthesis suites) to test binary multiply routines. Conduct lab validation using known input pairs (e.g., 101 × 11 = 1111) and compare outputs against expected results.
What is the average lead time for digital logic ICs?
Standard catalog components typically ship within 4–8 weeks. Backordered or end-of-life parts may extend to 16+ weeks. Custom ASIC development requires 6–12 months from design to first article, including tape-out and packaging cycles.
Can suppliers customize binary arithmetic performance?
Yes, through configurable IP cores (e.g., Xilinx LogiCORE, Intel Quartus Megafunctions), buyers can optimize multiplier width (8-bit to 512-bit), pipelining depth, and resource utilization on FPGAs. Full customization via ASIC design allows maximum efficiency but incurs higher NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs.
Do manufacturers provide free samples?
Most semiconductor suppliers offer free evaluation samples for qualified engineering teams. Registration on the manufacturer’s portal, company verification, and stated project details are typically required. Sample limits apply per customer and device type.
How to initiate integration support requests?
Contact the supplier’s field application engineering (FAE) team with board schematics, timing requirements, and use-case descriptions. Reputable vendors provide reference designs, IBIS models, and layout guidelines within 5–7 business days to accelerate prototyping.