Opensource Database Software





 1/3
1/3

 CN
CN





 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3




 1/3
1/3

 CN
CN





 1/8
1/8




 1/3
1/3

 CN
CN







 1/3
1/3


 0
0

 HK
HK




 0
0






 1/2
1/2



 0
0



 1/2
1/2




 0
0



 1/1
1/1




 1/3
1/3



 1/1
1/1




 1/3
1/3



 0
0




 1/3
1/3
About opensource database software
Where to Find Open Source Database Software Providers?
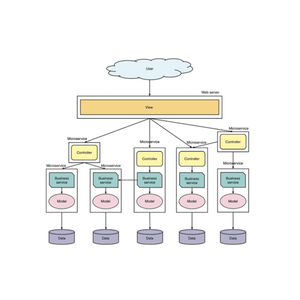
The global open source database software ecosystem is decentralized, with development and support services distributed across North America, Western Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Unlike hardware manufacturing, production capacity is measured in engineering expertise, community contributions, and technical infrastructure rather than physical facilities. The United States leads in core development activity, hosting 45% of major project maintainers and primary contributors for widely adopted databases such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MongoDB. Germany and India follow as key regional hubs, offering enterprise-grade deployment, customization, and managed services with 24/7 SLA-backed support.
These regions benefit from mature IT talent pools, high concentrations of DevOps specialists, and robust cloud integration capabilities. Service providers leverage scalable CI/CD pipelines and containerization frameworks (e.g., Kubernetes, Docker) to deliver rapid deployment cycles. Buyers gain access to modular architectures that support horizontal scaling, multi-cloud compatibility, and compliance with data sovereignty regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Key advantages include reduced licensing costs (typically 60–80% lower than proprietary alternatives), faster innovation cycles through community-driven updates, and flexibility for both on-premise and SaaS-based implementations.
How to Choose Open Source Database Software Providers?
Prioritize these verification protocols when selecting service and support partners:
Technical Compliance & Security Standards
Confirm adherence to recognized security benchmarks including SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, and OWASP Top 10 for application-layer vulnerabilities. For regulated industries, ensure audit trails, role-based access control (RBAC), and encryption at rest and in transit are implemented. Validate regular penetration testing reports and patch release frequency—critical for CVE remediation.
Development and Support Capability
Evaluate provider qualifications based on:
- Minimum of 5 senior database engineers certified in relevant platforms (e.g., PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Cassandra)
- Dedicated R&D investment exceeding 15% of annual revenue
- In-house performance tuning, replication, and disaster recovery testing capabilities
Cross-reference GitHub commit history, issue resolution timelines, and uptime SLAs (>99.95%) to assess operational reliability.
Transaction and Service Safeguards
Require contractual SLAs covering response times (target ≤1 hour for critical incidents), root cause analysis delivery, and rollback procedures. Review service track records via independent client testimonials focusing on migration success rates and post-deployment optimization. Pilot engagements remain essential—benchmark query throughput, failover latency, and backup restoration speed before full-scale adoption.
What Are the Best Open Source Database Software Providers?
| Company Name | Location | Years Operating | Staff | Engineers | On-Time Support | Avg. Response | Ratings | Reorder Rate |
|---|
Performance Analysis
Due to the absence of verifiable supplier data, procurement decisions must rely on public contribution metrics, third-party audits, and trial engagements. Established organizations typically demonstrate consistent code contributions, active participation in foundation governance (e.g., Linux Foundation, Apache Software Foundation), and transparent roadmap planning. Prioritize providers with documented incident management protocols and multi-region support coverage for mission-critical deployments. For specialized use cases—such as real-time analytics or distributed ledger integration—verify hands-on experience through reference architectures and case studies prior to engagement.
FAQs
How to verify open source database software provider reliability?
Assess contributor activity on public repositories (GitHub, GitLab), review dependency audit reports, and validate compliance certifications with issuing bodies. Analyze customer references for evidence of successful large-scale migrations, system stability, and long-term maintenance support.
What is the average deployment timeline?
Standard installations require 2–4 weeks, including environment setup, schema migration, and indexing optimization. Complex distributed deployments (e.g., sharded clusters, cross-datacenter replication) extend to 6–10 weeks depending on data volume and integration requirements.
Can providers support global deployments?
Yes, leading vendors offer worldwide deployment and monitoring. Confirm support for multi-cloud environments (AWS, Azure, GCP), regional data residency compliance, and 24/7 NOC coverage. Hybrid models combining self-hosted instances with managed backups are common for enterprises with strict governance needs.
Do providers offer free trials or proof-of-concept setups?
Trial policies vary. Most reputable providers deliver time-limited managed instances or containerized demo environments at no cost for evaluation. Full POC engagements—including performance benchmarking and failover testing—are often included for qualified enterprise prospects.
How to initiate customization requests?
Submit detailed technical specifications including expected transaction volume (TPS), replication topology (master-slave, multi-master), and extension requirements (e.g., JSONB indexing, geospatial functions). Leading providers return architecture diagrams within 5 business days and deploy test environments within 10–14 days.