Finding the right photo online can make or break a project—whether it’s for a blog post, presentation, social media update, or personal use. While Google Images is one of the most powerful visual search tools available, many users only scratch the surface of its capabilities. Knowing how to navigate beyond basic keyword searches unlocks access to higher-quality, more relevant images in less time. This guide walks through the full process of conducting an effective photo search on Google, using precision tools, filters, and best practices that professionals rely on.
1. Start with a Clear Search Intent
Before typing anything into the search bar, define what you’re looking for. Are you searching for a specific person, landmark, or artwork? Or do you need a conceptual image like “team collaboration” or “sustainable energy”? The clarity of your intent shapes every subsequent step.
Vague queries like “nice pictures” yield poor results. Instead, be specific: “woman working remotely from a mountain cabin” gives Google much more context to deliver accurate visuals.
Refine Keywords Strategically
- Synonyms: Try variations like “portrait,” “headshot,” or “selfie” depending on formality.
- Color terms: Add colors (“red dress,” “blue sky”) to narrow results visually.
- Timeframe: Include decades (“1980s fashion”) or eras (“Victorian architecture”) when relevant.
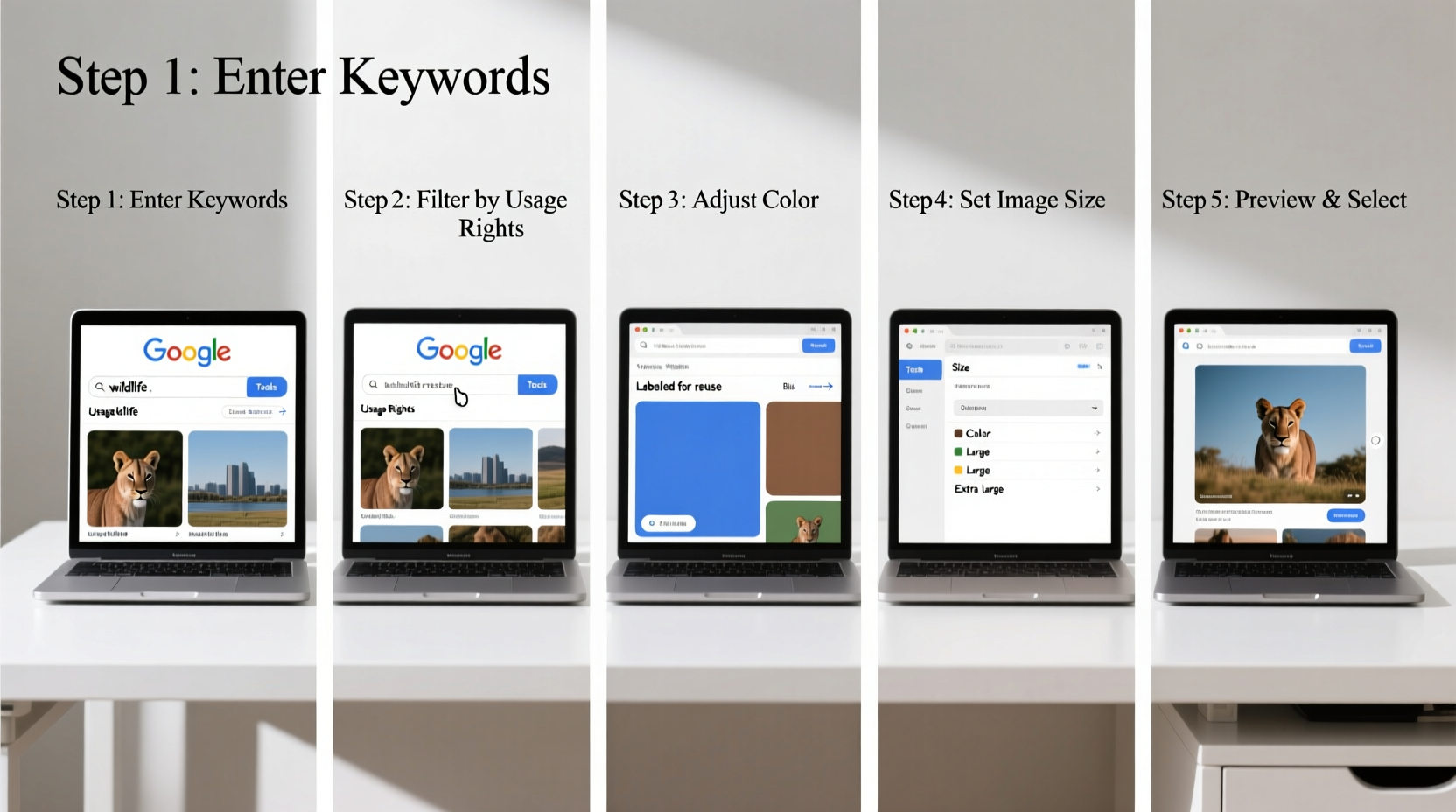
2. Use Google Images with Precision Tools
Navigate to images.google.com and enter your refined search term. Once results appear, don’t just scroll—use the built-in tools above the image grid to filter and refine.
Key Filter Options Explained
| Filter | Best For | Limits To Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Size | High-resolution needs (print, banners) | Overusing “Large” may reduce variety |
| Type | Finding clipart, faces, photos, or drawings | Mislabeling; double-check accuracy |
| Color | Matching brand palettes or themes | May exclude excellent B&W or sepia images |
| Time | Recent events or trending visuals | Older but still relevant content |
| Usage Rights | Safe reuse without copyright issues | Smaller pool; not all labeled correctly |
“Most people miss the value of the ‘Usage Rights’ filter. It’s the fastest way to avoid legal risks when sourcing images.” — Daniel Park, Digital Media Law Consultant
3. Apply Advanced Search Techniques
Beyond dropdown filters, Google supports advanced search operators that give granular control over results. These are typed directly into the search box.
Common Search Operators
filetype:jpg– Limits results to JPEG files (also works with png, gif, svg).site:.govorsite:.edu– Finds images hosted on government or educational sites, often high quality and public domain.inurl:gallery– Targets pages specifically designed as image galleries.intitle:\"sunset beach\"– Finds pages where the title includes your phrase, increasing relevance.\"exact phrase\"– Searches for the exact sequence of words, reducing unrelated matches.
Example: Searching for \"golden retriever puppy\" filetype:jpg site:.org returns high-quality photos of golden retriever puppies from nonprofit organizations, often used for adoption campaigns.
\"urban garden\" filetype:png size:large usage rights:free to use.
4. Reverse Image Search for Discovery and Verification
Sometimes you already have a photo in mind—or even a partial screenshot—but don’t know its source. Google’s reverse image search helps identify origins, find higher-resolution versions, or discover similar styles.
How to Perform a Reverse Image Search
- Go to Google Images.
- Click the camera icon in the search bar.
- Upload an image file or paste an image URL.
- Analyze the results: look for “Pages that include matching images” and “Visually similar images.”
This method is invaluable for fact-checking, identifying unknown locations, or finding design inspiration based on a single visual cue.
Mini Case Study: Finding the Source of a Viral Nature Photo
A travel blogger came across a stunning photo of a turquoise lake surrounded by snow-capped peaks on a social media post with no credit. Wanting to feature it ethically, she used reverse image search. Uploading the image revealed it originated from a national park’s official website, taken by a ranger during summer patrol. She contacted the photographer, obtained permission, and properly credited the image in her article—avoiding copyright infringement while building trust with her audience.
5. Evaluate and Verify Before Downloading
Just because an image appears in search results doesn’t mean it’s free to use. Always verify licensing and source credibility before downloading or publishing.
Checklist: Safe Image Sourcing
- ✅ Confirm the intended usage (personal, commercial, modification).
- ✅ Look for clear licensing info (Creative Commons, public domain, royalty-free).
- ✅ Check the host website’s reputation (official institutions, established stock platforms).
- ✅ When in doubt, link back to the original page or seek permission.
- ✅ Avoid sites that republish copyrighted content without authorization.
Remember: “Free to view” does not mean “free to use.” Always assume copyright applies unless explicitly stated otherwise.
FAQ: Common Questions About Google Image Search
Can I use any image from Google Images for my business website?
No. Most images are protected by copyright. Only use those labeled with appropriate usage rights (e.g., “labeled for reuse”), or obtain a license through platforms like Unsplash, Shutterstock, or via direct permission from the creator.
Why do some filters disappear after I search?
Google dynamically shows filters based on search volume and result type. If “Color” or “Type” options vanish, try broadening your query slightly or adding more common keywords to trigger richer filtering options.
Is reverse image search private?
Yes. When you upload an image for reverse search, Google does not store or associate it with your account if you're not signed in. However, avoid uploading sensitive or private photos to any online tool.
Conclusion: Master Visual Search Like a Pro
Searching for photos on Google isn’t about luck—it’s about strategy. From crafting precise queries to leveraging filters, advanced operators, and reverse lookup tools, each step increases your chances of finding exactly what you need, quickly and legally. The ability to locate high-quality, rights-cleared images efficiently is a skill that saves time, enhances creativity, and protects against legal pitfalls.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?