Understanding percentages is essential in everyday decision-making, whether you're analyzing sales data, calculating a tip, or comparing test scores. While the concept may seem basic, many people struggle when asked to determine the percentage change or relationship between two numbers. This guide breaks down the process into simple, actionable steps so you can confidently calculate any percentage scenario—accurately and efficiently.
Understanding What Percentage Means
A percentage represents a part per hundred. It's a way to express a fraction or ratio where 100 is the whole. For example, 25% means 25 out of 100, or one-quarter. When comparing two numbers, percentage calculations help reveal relative differences, growth, or reductions in value.
There are three main types of percentage problems involving two numbers:
- Finding what percent one number is of another (e.g., “What percent is 40 of 80?”)
- Calculating the percentage increase or decrease between two values (e.g., “Sales rose from $200 to $250—what’s the percentage increase?”)
- Determining a number based on a percentage of another (e.g., “What is 30% of 150?”)
This guide focuses primarily on the first two: determining percentage relationships and changes between two numbers.
Step-by-Step: How to Find What Percent One Number Is of Another
To find what percent one number (the part) is of another (the whole), use this formula:
(Part ÷ Whole) × 100 = Percentage
Step 1: Identify the Part and the Whole
The “part” is the number you want to compare. The “whole” is the total or reference value. For example, if you scored 45 on a test out of 60, 45 is the part, and 60 is the whole.
Step 2: Divide the Part by the Whole
Calculate 45 ÷ 60 = 0.75
Step 3: Multiply by 100
0.75 × 100 = 75%
You scored 75% on the test.
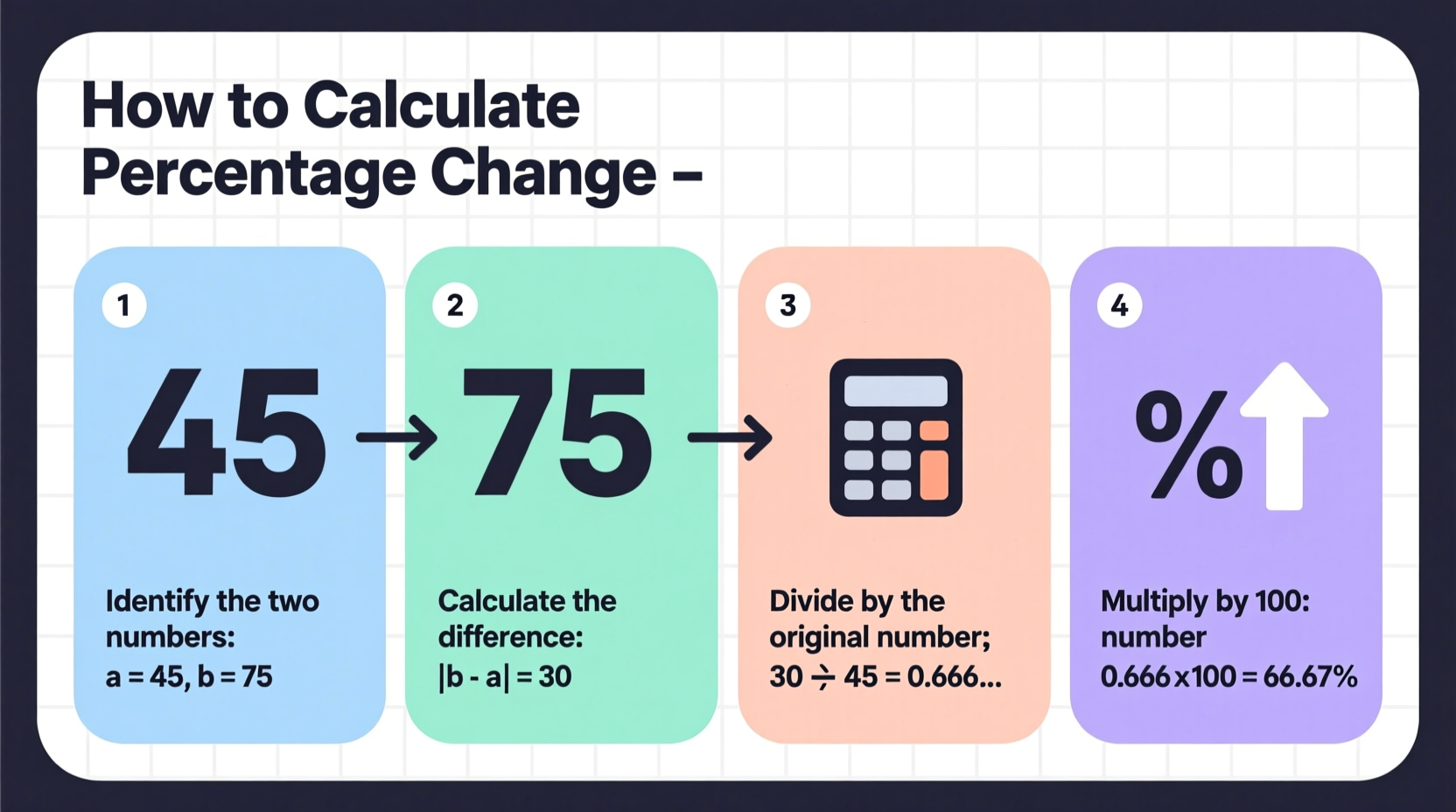
Calculating Percentage Increase or Decrease
When values change over time—such as prices, populations, or profits—you often need to know the percentage change. This shows how much a value has grown or shrunk relative to its original amount.
Percentage Change = [(New Value – Original Value) ÷ Original Value] × 100
Step 1: Subtract the Original Value from the New Value
This gives you the absolute change. If the result is positive, it’s an increase; if negative, it’s a decrease.
Step 2: Divide the Change by the Original Value
This normalizes the change relative to the starting point.
Step 3: Multiply by 100
Convert the decimal to a percentage.
Example Calculation: Price Increase
A smartphone originally priced at $400 now costs $480. What’s the percentage increase?
- Change: 480 – 400 = 80
- Divide: 80 ÷ 400 = 0.2
- Multiply: 0.2 × 100 = 20%
The price increased by 20%.
Example: Sales Decline
Last month, a store sold 500 units. This month, it sold 425. What’s the percentage decrease?
- Change: 425 – 500 = -75
- Divide: -75 ÷ 500 = -0.15
- Multiply: -0.15 × 100 = -15%
Sales decreased by 15%.
“Percentage change is more informative than raw numbers because it puts fluctuations into context. A $10 increase on a $2 item is massive—500%—but the same dollar change on a $1000 product is negligible.” — Dr. Alan Reeves, Data Literacy Educator
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even simple percentage calculations can go wrong if you misapply the formula or confuse the variables. Here are frequent errors and how to prevent them:
| Mistake | Why It’s Wrong | How to Fix It |
|---|---|---|
| Using the new value as the denominator | Skews results; the base should always be the original value | Always divide by the original, not the new, value |
| Forgetting to multiply by 100 | Leaves answer as a decimal, not a percentage | Always convert decimals to percentages |
| Confusing increase and decrease signs | Negative percentages indicate reduction, but people often ignore the sign | Pay attention to positive vs. negative outcomes |
| Reversing part and whole in proportion questions | Results in percentages over 100% when they shouldn’t be | Ask: “What am I comparing to what?” |
Mini Case Study: Budget Planning for a Small Business
Julia runs a small bakery. Last year, her ingredient costs totaled $12,000. This year, due to inflation, they rose to $14,500. She needs to calculate the percentage increase to adjust her pricing strategy.
Using the formula:
- Difference: 14,500 – 12,000 = 2,500
- Divide: 2,500 ÷ 12,000 ≈ 0.2083
- Multiply: 0.2083 × 100 ≈ 20.83%
Ingredient costs increased by nearly 21%. Julia decides to raise her average pastry price from $3.50 to $4.00—a 14.3% increase—to offset some of the cost while remaining competitive. By using percentage analysis, she makes informed financial decisions without overpricing her products.
Practical Tips for Accurate Percentage Calculations
Quick Checklist: Verify Your Percentage Calculation
- ✅ Identified which number is the part and which is the whole
- ✅ Used the correct formula for the type of problem (proportion vs. change)
- ✅ Subtracted in the right order for change calculations
- ✅ Divided by the original value, not the new one
- ✅ Multiplied by 100 to convert to percentage form
- ✅ Checked the sign (positive/negative) for increases or decreases
- ✅ Verified the result makes logical sense (e.g., a part can't be 150% of a whole unless it truly exceeds it)
FAQ
Can a percentage be more than 100%?
Yes. If the “part” is larger than the “whole,” the percentage will exceed 100%. For example, if you made $150 in profit from a $100 investment, that’s a 150% return.
What if the original value is zero?
You cannot calculate a percentage change when the original value is zero because division by zero is undefined. In such cases, describe the change in absolute terms instead (e.g., “Sales went from 0 to 50 units” rather than stating a percentage).
How do I reverse a percentage to find the original number?
If you know a value after a percentage increase, divide it by (1 + the percentage as a decimal). For example, if a price of $110 includes a 10% increase, the original was 110 ÷ 1.10 = $100.
Conclusion: Make Percentages Work for You
Calculating the percentage between two numbers isn’t just a math exercise—it’s a practical skill that empowers better decisions in business, finance, education, and daily life. Whether you're evaluating a discount, tracking progress, or analyzing trends, understanding percentages gives you clarity and confidence. Now that you’ve mastered the formulas, avoided common pitfalls, and seen real-world applications, put this knowledge into action. Practice with real data, double-check your work, and share these methods with others who could benefit.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?