Staying connected is essential in today’s digital world. Whether you're browsing social media, streaming videos, or working remotely, a reliable Wi-Fi connection on your cell phone makes all the difference. While connecting to Wi-Fi may seem straightforward, many users encounter issues ranging from failed connections to weak signals. This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of getting Wi-Fi on any smartphone—Android or iPhone—and includes practical troubleshooting methods to resolve common problems.
Understanding How Wi-Fi Works on Smartphones
Wi-Fi allows your cell phone to connect to the internet using a wireless router instead of cellular data. This not only reduces data usage but often provides faster and more stable speeds. Modern smartphones are equipped with built-in Wi-Fi adapters that automatically detect available networks within range. Once detected, your device can join a network if you have the correct credentials (usually a password).
Most home and public Wi-Fi networks use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption for security. Open networks, like those in cafes or airports, don’t require passwords but come with increased privacy risks. Always be cautious when transmitting sensitive information over public networks.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting Your Phone to Wi-Fi
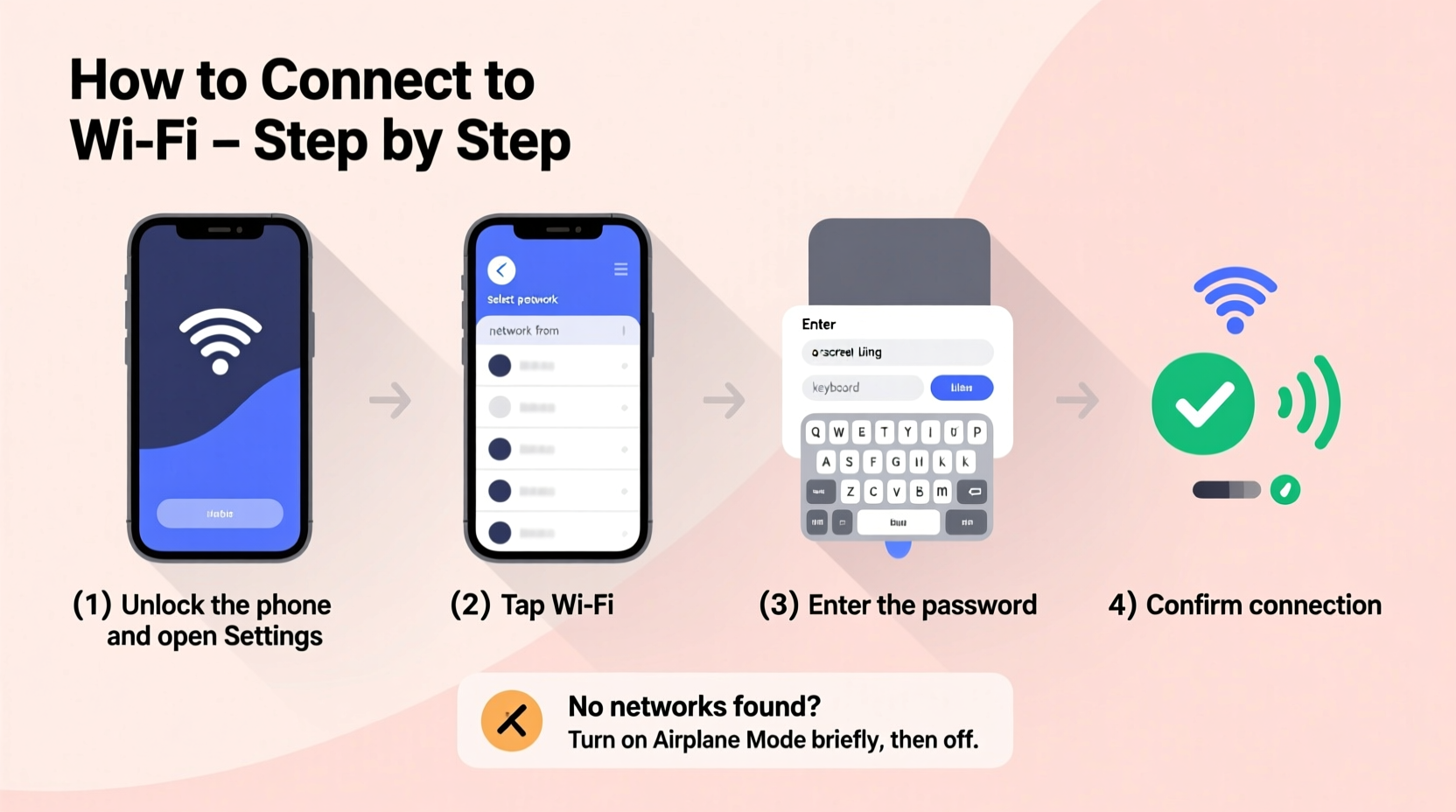
- Unlock your phone and go to the home screen.
- Open Settings — tap the gear icon on Android or iPhone.
- Navigate to Wi-Fi settings:
- On Android: Tap “Network & Internet” > “Wi-Fi”
- On iPhone: Tap “Wi-Fi”
- Turn Wi-Fi on if it isn’t already enabled.
- Wait a few seconds for your phone to scan and display nearby networks.
- Select your desired network from the list.
- Enter the password when prompted. Ensure case sensitivity and special characters are correct.
- Tap Connect. If successful, you’ll see a checkmark (iPhone) or “Connected” status (Android).
Once connected, your phone will typically remember the network and automatically reconnect whenever it's in range. For added convenience, consider labeling your home network so it's easily identifiable among others.
Troubleshooting Common Wi-Fi Connection Issues
Even with the correct steps, Wi-Fi problems can still occur. Here are the most frequent issues and how to fix them:
No Networks Appearing
This usually indicates Wi-Fi is turned off or the radio isn’t functioning. First, toggle Wi-Fi off and back on. Restart your phone if the issue persists. If no networks show up after rebooting, check airplane mode—ensure it’s disabled.
“Saved” but Not Connecting
If your phone says it’s connected but you can’t browse, try forgetting the network and reconnecting. On iPhone: tap the ⓘ next to the network > “Forget This Network.” On Android: long-press the network name > “Forget.” Then re-enter the password.
Weak Signal or Slow Speeds
Distance from the router, physical obstructions (walls, appliances), or interference from other devices can degrade signal quality. Move closer to the router or restart it. Consider upgrading to a mesh Wi-Fi system for larger homes.
Authentication Problems
If you’re entering the right password but still can’t connect, the issue might be with the router settings. Try rebooting the router. Also, ensure your phone’s date and time are set correctly—incorrect settings can interfere with secure network authentication.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Can't find any networks | Wi-Fi disabled or hardware error | Toggle Wi-Fi off/on; restart device |
| Keeps disconnecting | Router instability or IP conflict | Restart router; renew IP address |
| Connected but no internet | Router has no internet access | Check modem lights; contact ISP |
| Password rejected | Incorrect entry or outdated encryption | Verify password; update router firmware |
“We’ve seen a 40% increase in Wi-Fi-related support calls since the rise of remote work. Most issues stem from misconfigured routers or outdated phone software.” — David Lin, Senior Network Technician at NetSecure Solutions
Advanced Tips for Better Wi-Fi Performance
Beyond basic setup, optimizing your phone and network environment enhances performance and reliability.
- Update your phone’s OS: Manufacturers release updates that improve connectivity and patch bugs.
- Use 5 GHz band when possible: Dual-band routers offer both 2.4 GHz (longer range) and 5 GHz (faster speeds). Connect to 5 GHz for streaming or gaming if you’re near the router.
- Limit background apps: Apps refreshing in the background consume bandwidth. Disable auto-sync for non-essential apps in settings.
- Enable Wi-Fi Assist (iPhone) or Adaptive Connectivity (Android): These features seamlessly switch to cellular data when Wi-Fi is weak, preventing disconnections.
Mini Case Study: Fixing Home Office Connectivity
Sarah, a freelance graphic designer, struggled with video call lag despite being connected to her home Wi-Fi. Her laptop worked fine, but her phone kept dropping during client meetings. After testing, she discovered her phone was stuck on the 2.4 GHz band while her router supported 5 GHz. By manually selecting the 5 GHz network (named slightly differently), her connection stabilized instantly. She also updated her phone’s OS, which resolved an underlying bug affecting Wi-Fi handoff.
Essential Wi-Fi Checklist
Follow this checklist to ensure smooth Wi-Fi setup and maintenance:
- ✅ Confirm Wi-Fi is enabled on your phone
- ✅ Verify you’re within range of the network
- ✅ Enter the correct password (check caps lock)
- ✅ Restart your phone if connection fails
- ✅ Reboot the router if multiple devices are affected
- ✅ Forget and re-add the network if stuck on “Obtaining IP Address”
- ✅ Check for software updates on both phone and router
- ✅ Test speed using free tools like Fast.com or Speedtest.net
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my phone say “No Internet” even though I’m connected to Wi-Fi?
This message means your phone has joined the network but the router isn’t providing internet access. The issue likely lies with the router or modem. Check if other devices have internet. If not, restart your modem or contact your internet service provider.
Can I connect to Wi-Fi without a password?
Yes, but only on open networks. Most private networks require a password for security. Some modern routers support WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup), allowing connection via a button press instead of a password—but this feature should be disabled afterward for security reasons.
How do I share my Wi-Fi password with someone securely?
On iPhones, bring two phones close together—one connected to Wi-Fi—and a prompt appears to share the password. On Android, use Google’s QR code sharing feature under Wi-Fi settings. Avoid sending passwords via text or email.
Final Thoughts and Action Steps
Getting Wi-Fi on your cell phone doesn’t have to be complicated. With the right approach, you can establish a strong, stable connection in minutes. Start by ensuring your phone’s settings are properly configured, then methodically troubleshoot any issues using the steps outlined above. Remember, many connectivity problems originate not from your phone, but from the router or internet service itself.
Take action today: test your current Wi-Fi speed, verify your network settings, and perform a quick router restart. Small adjustments can lead to dramatically better performance. Stay proactive about updates and security, and your phone will remain reliably connected wherever you go.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?