YouTube is the second-largest search engine in the world, hosting over 2 billion logged-in users each month. Whether you're an educator, marketer, or content enthusiast, knowing how to properly upload, share, and repurpose videos can significantly expand your reach. However, many users misunderstand the process—especially when it comes to uploading someone else’s video or re-sharing content across platforms. This guide breaks down the correct, legal, and effective methods for uploading your own videos to YouTube, sharing them across channels, and understanding the boundaries of reposting others’ content.
Understanding What “Uploading” Means on YouTube
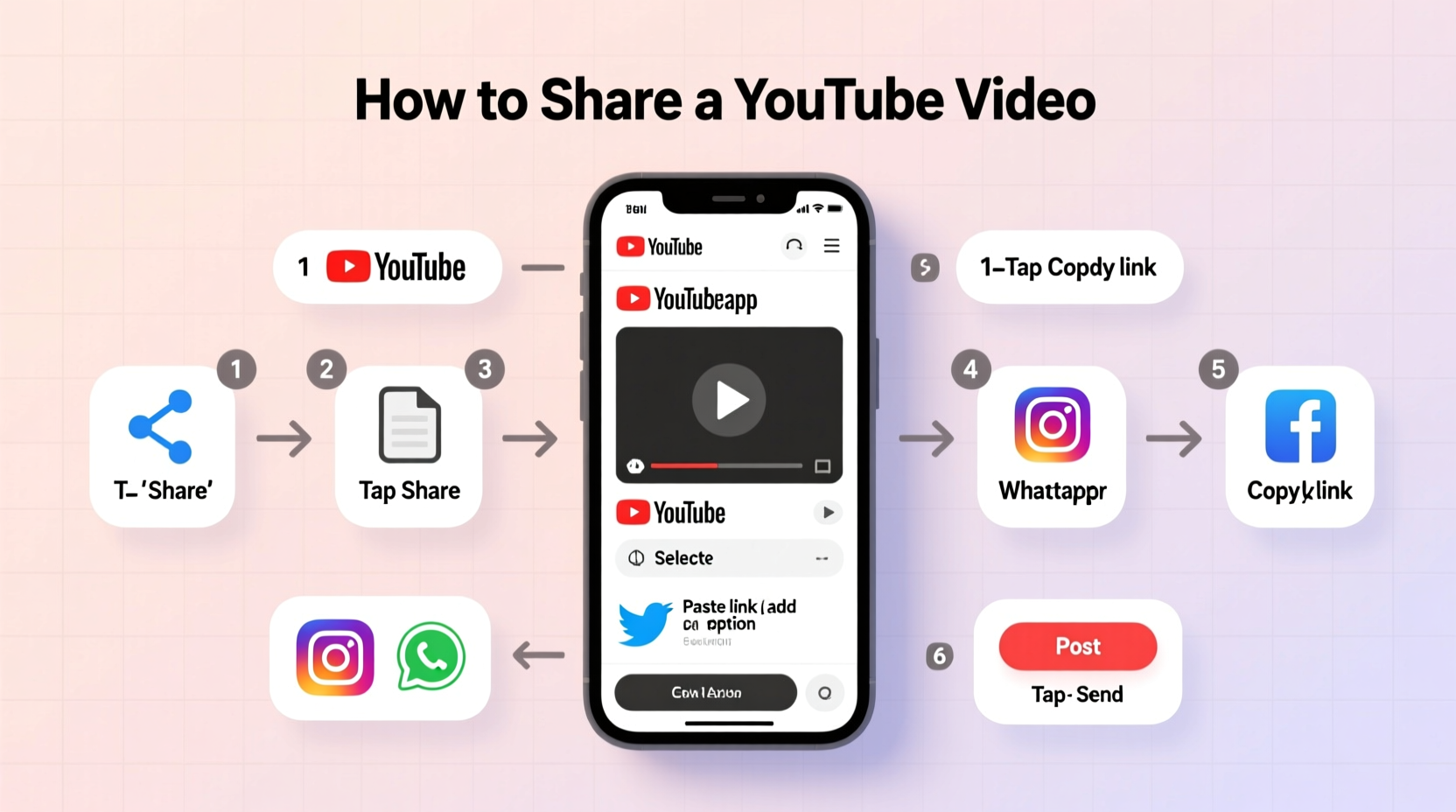
When people ask how to \"upload a video from YouTube,\" they often mean one of two things: either uploading their own original video to the platform, or attempting to download and re-upload someone else’s content. The first is encouraged and straightforward. The second is a violation of YouTube’s Terms of Service unless explicit permission is granted.
Every video on YouTube is protected by copyright law the moment it's created and published. Reposting without consent—even with credit—can lead to content ID claims, strikes, or channel termination. Therefore, this guide focuses on three key areas:
- How to upload your original video to YouTube
- How to legally share or embed existing YouTube videos
- Best practices for repurposing content with permission
Step-by-Step Guide to Uploading Your Own Video to YouTube
If you’ve recorded a video using your phone, camera, or screen recording software, uploading it to YouTube is simple. Follow these steps carefully to ensure optimal visibility and quality.
- Sign in to YouTube: Use your Google account to log in at youtube.com.
- Click the Create button: Located in the top-right corner, represented by a camera icon. Select “Upload video.”
- Select your file: Drag and drop your video file or browse your device to locate it. Supported formats include MP4, MOV, AVI, and WMV.
- Add details while it uploads:
- Title: Clear, engaging, and under 60 characters.
- Description: At least 150–200 words with relevant keywords.
- Thumbnail: Upload a custom image (1280x720 pixels recommended).
- Tags: Include 5–10 relevant keywords to improve discoverability.
- Set visibility: Choose between Public, Unlisted, or Private based on your sharing goals.
- Age restriction and monetization: Confirm whether your content contains mature themes and if you want to enable ads.
- Publish: Click “Next” until you see “Publish” and confirm.
Sharing vs. Reposting: What’s the Difference?
Many users conflate sharing with reposting. Understanding the distinction is crucial for maintaining credibility and compliance.
| Action | Definition | Legal Status | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharing | Distributing a link, embedding a video, or posting it in a story | Fully allowed | Social media, blogs, newsletters |
| Reposting | Re-uploading someone else’s video to your own channel | Prohibited without permission | Only with written consent or under fair use (rare) |
| Remixing/Editing | Using clips under transformative intent (e.g., commentary, critique) | Conditionally allowed under fair use | Educational or critical content |
YouTube encourages sharing through built-in tools like the Share button beneath every video. You can copy the link, generate embed codes, or directly post to Facebook, Twitter, or WhatsApp.
How to Embed a YouTube Video on Your Website
Embedding keeps viewers on your site while giving proper attribution to the creator. To do so:
- Open the YouTube video you want to share.
- Click “Share” below the player, then select “Embed.”
- Copy the HTML code provided.
- Paste it into your website’s HTML editor where you want the video to appear.
You can customize the size, autoplay settings, and privacy-enhanced mode in the embed options.
When and How to Legally Repost Someone Else’s Content
There are limited scenarios where reposting another creator’s video is acceptable:
- You have written permission from the copyright holder.
- The video is licensed under Creative Commons (CC BY).
- Your use qualifies as “fair use” (e.g., for criticism, education, or news reporting).
To check if a video is CC-licensed, go to the video’s description and look for “Creative Commons – Attribution license.” If present, you may re-upload it as long as you credit the original creator and don’t claim ownership.
“Reposting without permission undermines creators’ livelihoods. Always seek consent before redistributing content.” — Sarah Lin, Digital Media Attorney
Mini Case Study: A Blogger’s Mistake and Recovery
Jamal, a fitness blogger, wanted to feature a popular yoga tutorial on his website. Instead of embedding the video, he downloaded it using third-party tools and uploaded it to his YouTube channel titled “Best Yoga Routines.” Within 48 hours, he received a copyright strike.
After removing the video and reaching out to the original creator, he negotiated permission to feature the content with proper credit. The creator agreed, provided Jamal embedded the video and linked to their channel. Not only did Jamal resolve the issue, but he also built a collaborative relationship that led to future guest appearances.
This case underscores the importance of respecting intellectual property while still leveraging valuable content ethically.
Checklist: Safe and Effective Video Sharing Practices
- ✅ Is the video mine? If yes, upload directly via YouTube Studio.
- ✅ If not mine, am I embedding or linking—not re-uploading?
- ✅ Does the video have a Creative Commons license?
- ✅ Have I contacted the creator for written permission?
- ✅ Am I providing clear attribution (name, channel, link)?
- ✅ Am I adding value through commentary, analysis, or context?
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I download a YouTube video and upload it to my channel?
No, downloading and re-uploading someone else’s video violates YouTube’s Community Guidelines and copyright laws, even if you give credit. Use the Share or Embed features instead.
What happens if I repost a video without permission?
You risk receiving a copyright strike. Three strikes result in permanent channel termination. Additionally, the copyright owner may issue a takedown request or pursue legal action.
Is it okay to use short clips from other videos?
Short clips may fall under “fair use” if used for commentary, criticism, teaching, or parody. However, there’s no guaranteed length that makes it safe. Always minimize usage and add significant original context.
Conclusion: Share Smart, Respect Creators, Grow Authentically
Uploading your own videos to YouTube is a powerful way to express ideas, build an audience, and contribute to the digital ecosystem. When it comes to sharing others’ content, the path forward isn’t through duplication—it’s through collaboration, attribution, and smart distribution.
By mastering the upload process, leveraging sharing tools responsibly, and honoring copyright, you position yourself as a trustworthy and ethical participant in the online community. Whether you’re launching a personal vlog or managing a brand channel, these practices lay the foundation for sustainable growth.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?