Temperature affects nearly every aspect of daily life—from checking the weather forecast to cooking meals and monitoring health. Yet for many, especially those moving between countries or reading international data, one challenge persists: converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius. While it may seem like a minor mathematical task, misunderstanding these scales can lead to incorrect oven settings, misinterpreted weather reports, or even medical errors. This guide breaks down the science, logic, and practical application behind converting Fahrenheit to Celsius correctly, ensuring you never second-guess a number again.
The Science Behind Temperature Scales
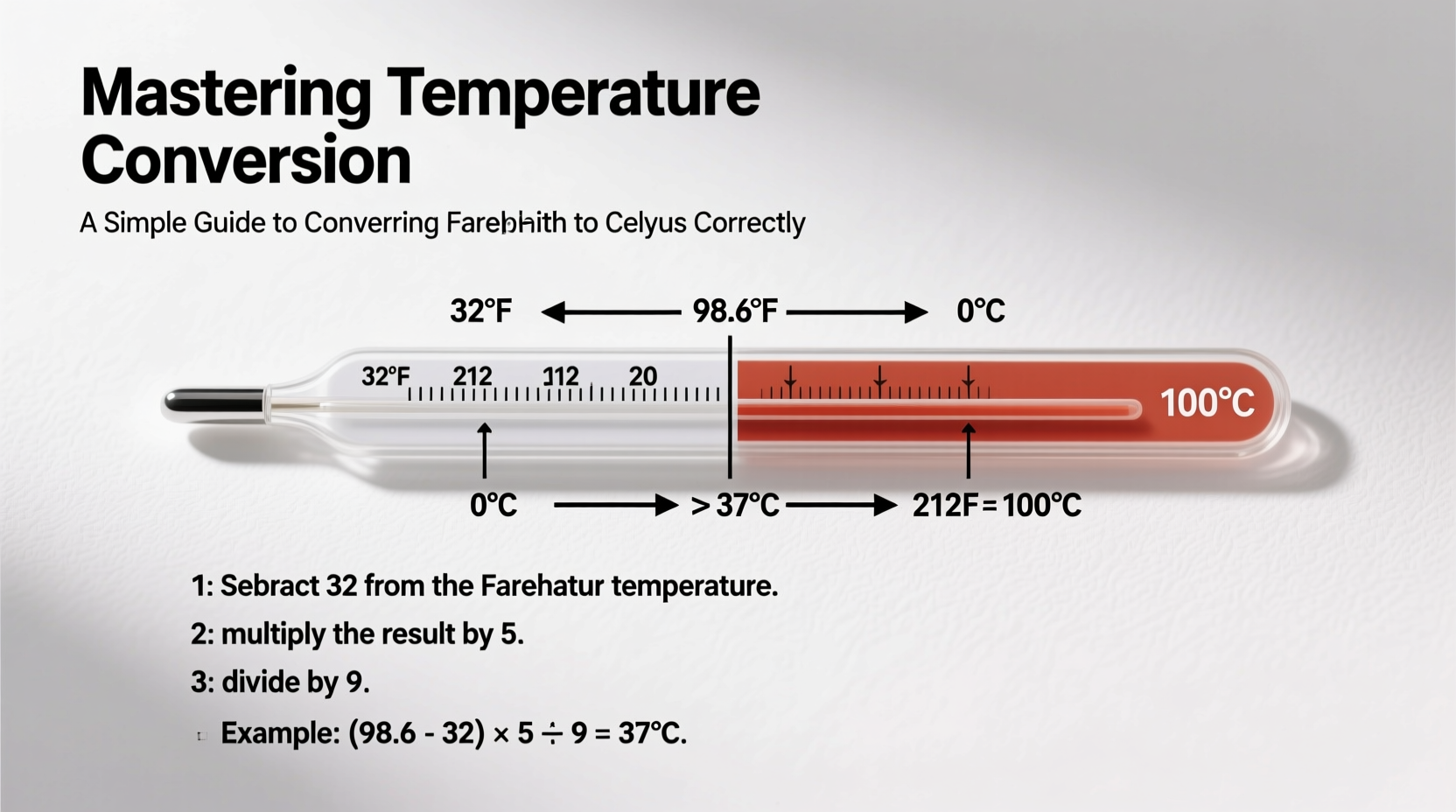
Fahrenheit and Celsius are two of the most widely used temperature scales, each developed with different reference points and purposes. The Fahrenheit scale, introduced by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F under standard atmospheric pressure. It was historically used in English-speaking countries and remains the primary scale in the United States today.
In contrast, the Celsius scale—originally called centigrade—was proposed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742. It defines 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as its boiling point, making it a decimal-based system aligned with the metric system. Most of the world uses Celsius, including in scientific research, medicine, and everyday communication.
Because the scales use different zero points and degree increments, direct comparison isn’t intuitive. A difference of 10 degrees means something entirely different on each scale. Understanding this foundational difference is essential before attempting any conversion.
The Conversion Formula Explained
The formula to convert Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C) is:
°C = (°F – 32) × 5/9
This equation adjusts for both the offset (32°F is 0°C) and the ratio of scale increments (each degree Celsius equals 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit). Let’s break it down step by step using an example: converting 68°F to Celsius.
- Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit value: 68 – 32 = 36
- Multiply the result by 5: 36 × 5 = 180
- Divide by 9: 180 ÷ 9 = 20
The result is 20°C—room temperature. This three-step process works for any Fahrenheit value, whether you're calculating body temperature, oven heat, or outdoor conditions.
Common Conversion Scenarios and Real-World Applications
Understanding conversions isn’t just academic—it has tangible impacts across various domains. Consider the following real-life case:
Mini Case Study: Cooking Across Borders
Sophie, a home baker in London, found a tempting American recipe calling for an oven temperature of 350°F. Without hesitation, she set her oven to 350°C, assuming the units were interchangeable. Ten minutes later, smoke filled the kitchen. Her cake had charred beyond recognition. The mistake? She forgot to convert. 350°F is actually about 177°C—a far cry from 350°C, which is hot enough to melt aluminum.
This common error underscores why accurate conversion matters. In cooking, a variance of even 10–15 degrees can affect texture, doneness, and safety. Similarly, travelers often miscalculate weather expectations. A forecast of 77°F might sound warm, but when converted to 25°C, it reveals a pleasantly mild day—helpful context for packing appropriately.
Key Reference Points and Conversion Table
To build intuition, memorizing a few benchmark temperatures can eliminate the need for calculations in everyday situations. Below is a reference table of commonly encountered temperatures:
| Fahrenheit (°F) | Celsius (°C) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -40°F | -40°C | Extremely cold; the point where both scales intersect |
| 32°F | 0°C | Freezing point of water |
| 68°F | 20°C | Standard room temperature |
| 98.6°F | 37°C | Average human body temperature |
| 212°F | 100°C | Boiling point of water at sea level |
| 350°F | 177°C | Common baking temperature |
Having these values internalized allows for faster decision-making without relying on apps or calculators.
“Precise temperature conversion is critical in fields like meteorology and medicine. A single digit error can alter diagnoses or forecasts.” — Dr. Lena Patel, Climate Research Scientist
Step-by-Step Guide to Accurate Conversion
Follow this five-step process to ensure consistent accuracy when converting Fahrenheit to Celsius:
- Identify the temperature in Fahrenheit: Confirm the value you’re starting with, ensuring it’s in °F and not mistakenly assumed to be Celsius.
- Apply the formula: (°F – 32) × 5/9: Perform the subtraction first, then multiplication, followed by division.
- Round appropriately: For general use, round to the nearest whole number. For scientific applications, keep one decimal place.
- Double-check with a known reference: Compare your result to a familiar benchmark (e.g., 68°F should be near 20°C).
- Verify with technology if needed: Use a trusted calculator or app to confirm results when precision is crucial.
This method reduces the risk of arithmetic errors and builds confidence over time.
Checklist: Avoiding Common Conversion Mistakes
- ✅ Always subtract 32 before multiplying—order of operations matters.
- ✅ Don’t confuse the formula with the reverse (Celsius to Fahrenheit: °F = °C × 9/5 + 32).
- ✅ Be cautious with negative numbers; -10°F is much colder than -10°C.
- ✅ Remember that “hot” and “cold” are relative—80°F feels warm, but 80°C is scalding.
- ✅ Label your units clearly to prevent confusion in notes or shared data.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is 32°F equal to 0°C?
This alignment is based on the freezing point of water under standard atmospheric pressure. Fahrenheit defined 32°F as the temperature at which water freezes, while Celsius set 0°C as the same point. The 32-degree offset accounts for this difference in baseline.
Is there a temperature where Fahrenheit and Celsius are the same?
Yes. At -40 degrees, both scales read the same value. That is, -40°F = -40°C. This occurs due to the linear relationship between the scales and their differing slopes and intercepts.
Can I use my smartphone for quick conversions?
Absolutely. Most smartphones have built-in unit converters in their calculator apps. Simply switch to “convert” mode, select temperature, enter the value, and choose the target scale. However, understanding the manual method ensures reliability when technology isn’t available.
Conclusion: Take Control of Temperature Understanding
Mastering temperature conversion is more than a math exercise—it’s a practical skill that enhances clarity in communication, safety in cooking, and accuracy in health and science. Whether you're traveling abroad, interpreting a medical thermometer, or following an international recipe, knowing how to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius correctly empowers you to make informed decisions. Start by memorizing key benchmarks, practice the formula regularly, and apply the checklist to avoid pitfalls.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?