For homeowners struggling with dead zones, buffering streams, or dropped video calls, achieving consistent Wi-Fi across a large house is more than a convenience—it’s a necessity. As smart devices multiply and remote work becomes routine, weak signals in distant rooms are no longer tolerable. Two common solutions dominate the market: traditional Wi-Fi extenders and modern mesh Wi-Fi systems. While both aim to expand coverage, they differ fundamentally in design, performance, and user experience. Understanding these differences is critical when choosing a solution that truly delivers seamless connectivity.
How Wi-Fi Extenders Work—and Where They Fall Short
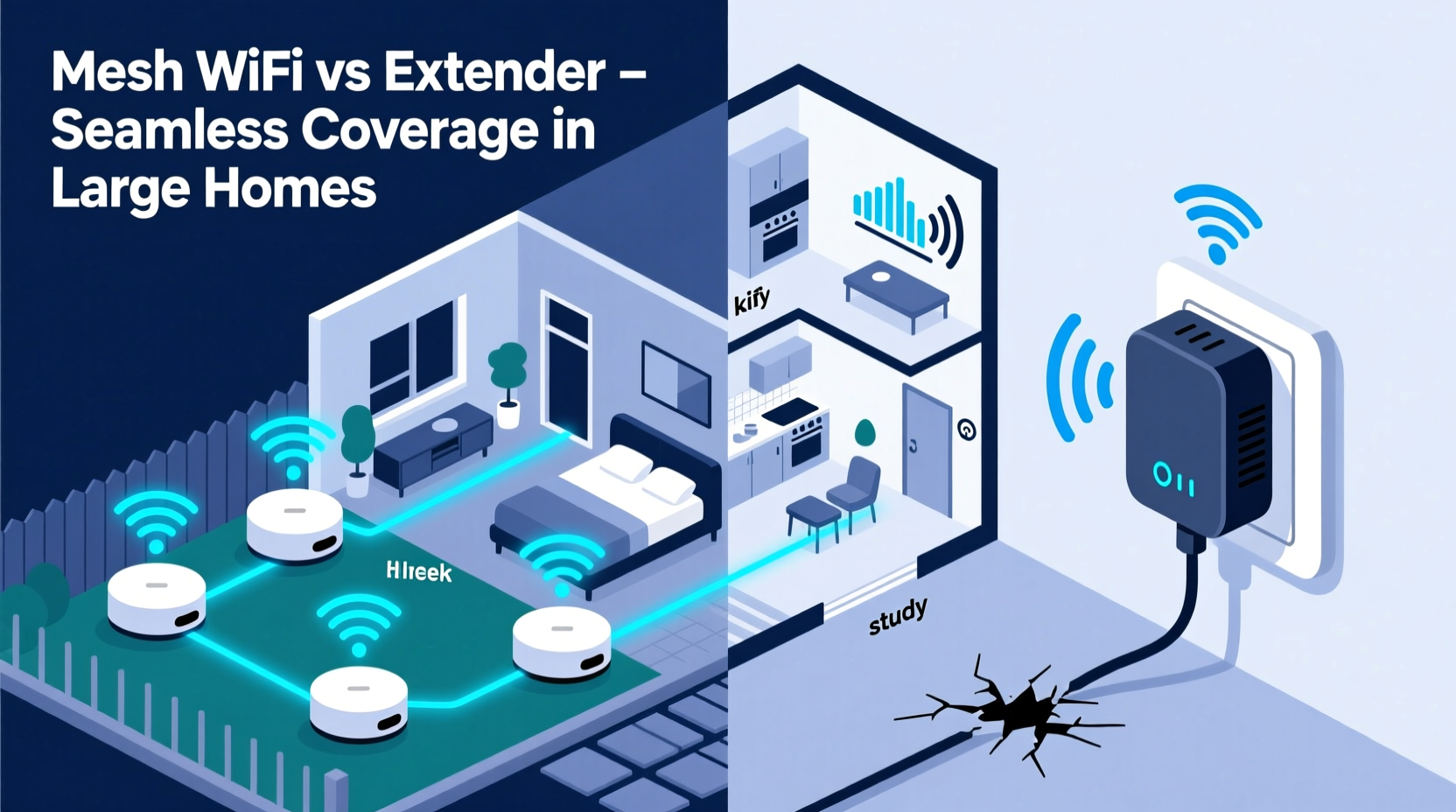
A Wi-Fi extender, also known as a range extender or repeater, functions by receiving your existing router’s signal and rebroadcasting it further into areas with poor reception. It's like placing a megaphone halfway through your yard to amplify someone speaking from the front porch. While this extends reach, it comes with inherent limitations.
Because most extenders operate on the same frequency band to receive and transmit data (unless dual-band), they effectively cut bandwidth in half. If your original connection offers 100 Mbps, devices connected through the extender may only see 40–50 Mbps due to signal processing overhead and interference. Additionally, extenders create a separate network name (SSID), forcing users to manually switch between the primary network and the extended one as they move through the house—anything but seamless.
Interference is another major issue. Since extenders rely on the same radio spectrum as your main router, congestion increases, especially in densely populated neighborhoods. The result? Slower speeds, higher latency, and unreliable connections for gaming or video conferencing.
The Mesh Wi-Fi Advantage: Seamless Roaming and Smarter Networks
Mesh Wi-Fi systems represent a significant evolution in home networking. Instead of relying on a single router and add-on repeaters, mesh networks use multiple interconnected nodes that work together as a unified system. These nodes communicate intelligently, forming a dynamic web of coverage throughout your home.
One of the standout features of mesh Wi-Fi is seamless roaming. Unlike extenders that require manual switching between networks, mesh systems broadcast a single SSID. As you walk from room to room, your device automatically connects to the strongest node without interruption—similar to how cell phones switch towers. This makes mesh ideal for voice calls, live streaming, and mobile gaming.
Modern mesh systems also support tri-band technology. In addition to the standard 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands used for device connectivity, they include a dedicated 5 GHz backhaul channel exclusively for communication between nodes. This eliminates the bandwidth-sharing penalty seen in traditional extenders, preserving speed and stability.
Advanced features such as automatic firmware updates, intuitive mobile apps, parental controls, and built-in security protocols further enhance the user experience. Brands like Google Nest Wifi, Eero, Netgear Orbi, and TP-Link Deco have made mesh systems accessible and easy to manage—even for non-technical users.
“Mesh networks are designed for today’s connected homes. They provide intelligent load balancing, self-healing capabilities, and consistent performance that extenders simply can’t match.” — David Liu, Senior Network Engineer at Broadband Insights Group
Comparing Performance: Real-World Scenarios
To illustrate the practical differences, consider a two-story, 3,000-square-foot home with thick interior walls and a basement office. The main router is located in the living room on the ground floor.
- With a Wi-Fi extender: A single extender placed upstairs improves signal to the bedrooms but creates a new network named “LivingRoom_Ext.” Devices don’t automatically switch, so family members must toggle networks manually. The basement remains a dead zone. Streaming buffers during peak usage hours, and online gaming suffers from lag spikes.
- With a three-node mesh system: One node acts as the router, a second is placed mid-floor, and a third in the basement. All devices connect to one network name. Signal strength remains high in every room. Video calls stay stable, and 4K content streams without buffering—even when multiple users are active.
In tests conducted by independent reviewers, mesh systems consistently outperform extenders in throughput consistency, latency reduction, and device-handling capacity. For example, a Netgear Orbi RBK752 system maintained over 85% of its baseline speed at 50 feet through two walls, while a popular TP-Link RE650 extender dropped to 45% under identical conditions.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Wi-Fi Extender | Mesh Wi-Fi System |
|---|---|---|
| Network Name (SSID) | Separate network often required | Single, unified network |
| Seamless Roaming | No – manual switching needed | Yes – automatic handoff between nodes |
| Backhaul Connection | Shared with client devices (slower) | Dedicated band (faster, less congestion) |
| Setup & Management | Basic interface, limited app support | User-friendly apps, remote access, automation |
| Scalability | Limited; adding more causes interference | Highly scalable with additional nodes |
| Price (Entry-Level) | $30–$70 | $200–$300 (for multi-pack) |
When an Extender Might Still Make Sense
Despite their limitations, Wi-Fi extenders aren’t obsolete. They can be a cost-effective stopgap for small spaces or temporary fixes. For example:
- A studio apartment with spotty coverage behind a bathroom wall.
- A guest bedroom used infrequently where full mesh deployment isn’t justified.
- Budget-conscious households needing basic internet access in one hard-to-reach area.
However, even in these cases, newer plug-in mesh nodes (like Amazon Eero Beacon or Google Nest Wifi Point) often offer better value, blending ease of installation with superior performance. These compact units plug directly into wall outlets and integrate seamlessly into larger mesh ecosystems.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Right Solution
Follow this decision-making process to determine whether mesh Wi-Fi or an extender suits your needs:
- Assess Your Home Layout: Measure square footage, note the number of floors, and identify construction materials. Concrete, brick, and metal framing significantly block Wi-Fi signals.
- Map Your Usage Needs: List all connected devices—smart TVs, laptops, security cameras, thermostats, etc.—and their typical locations. High-density usage demands robust infrastructure.
- Test Current Coverage: Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (e.g., Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android or AirPort Utility for iOS) to check signal strength in various rooms. Note areas below -70 dBm, which indicate poor connectivity.
- Evaluate Budget vs. Long-Term Value: While extenders are cheaper upfront, frequent reboots, inconsistent performance, and eventual replacement reduce long-term ROI. Mesh systems cost more initially but deliver reliability and future-proofing.
- Decide on Expandability: If you plan to add outdoor cameras, a home office in the garage, or smart lighting in a detached shed, choose a system that supports expansion. Mesh scales effortlessly; extenders do not.
- Install and Optimize: Place mesh nodes approximately 20–30 feet apart with minimal obstructions. Avoid placing them near microwaves, cordless phones, or large metal objects that cause interference.
Mini Case Study: Solving Connectivity in a Historic Home
The Thompson family owns a 1920s colonial-style home spanning 3,200 square feet across three levels, including a finished attic. Thick plaster walls and lath construction severely disrupted their ISP-provided router’s signal. Initially, they installed a high-gain extender in the hallway upstairs. While it helped slightly, devices frequently disconnected, and their Ring doorbell lost feed daily.
Frustrated, they invested in a three-pack Eero Pro 6 mesh system. They placed the primary unit near the modem on the first floor, a second in the stairwell, and the third in the attic. Within minutes of setup via the Eero app, all devices connected to a single network named “ThompsonHome.”
Results were immediate: streaming resumed without buffering, Zoom meetings stayed stable, and smart lights responded instantly. The system’s automatic updates and WPA3 encryption provided peace of mind. After six months, uptime exceeded 99.8%, and the family reported no further issues—proving that for complex layouts, mesh wasn’t just better, it was essential.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a mesh system with my existing router?
Yes, most mesh systems can operate in “bridge mode” or “AP mode,” allowing you to disable your old router’s routing functions and use the mesh as the primary network. Check compatibility with your internet service provider before purchasing.
Do Wi-Fi extenders slow down the internet for everyone?
They can. Because extenders repeat the signal using the same radio band, they consume available bandwidth. This affects not only devices connected to the extender but can also degrade performance on the main network due to increased airtime contention.
Is mesh Wi-Fi worth the extra cost?
For homes over 2,000 square feet, multi-level buildings, or those with many connected devices, yes. The improved speed consistency, reliability, and ease of management justify the investment. Over time, fewer troubleshooting sessions and greater productivity offset the initial price difference.
Final Recommendations and Action Plan
For seamless coverage in large homes, mesh Wi-Fi is the superior choice. Its ability to deliver uninterrupted roaming, maintain high speeds, and scale with evolving needs makes it the modern standard. Extenders may seem appealing due to lower cost, but they compromise performance and usability—especially in environments where reliability matters.
If you're still relying on a single router or struggling with outdated extenders, now is the time to upgrade. Start by evaluating your home’s layout and connectivity pain points. Then, select a reputable mesh system that fits your budget and technical requirements. Look for models with tri-band support, strong customer reviews, and ongoing software support.
Once installed, monitor performance and adjust node placement if needed. Most systems offer detailed analytics through companion apps, helping you optimize coverage over time.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?