The persistent beep of a seat belt chime can be more than just an annoyance—it can disrupt focus, increase driver stress, and become especially grating on long trips. While the chime serves a critical safety function by reminding drivers and passengers to buckle up, many people wonder if there’s a way to silence it without putting themselves or others at risk. The good news is that several safe, legal, and practical approaches exist to reduce or eliminate the chime—without disabling essential safety systems.
Before exploring any solution, it's crucial to emphasize: never disable your vehicle’s airbags, sensors, or restraint system. Safety should always come first. This guide focuses on responsible, manufacturer-aligned techniques to manage the chime while maintaining full protection in the event of a collision.
Understanding Why the Chime Exists
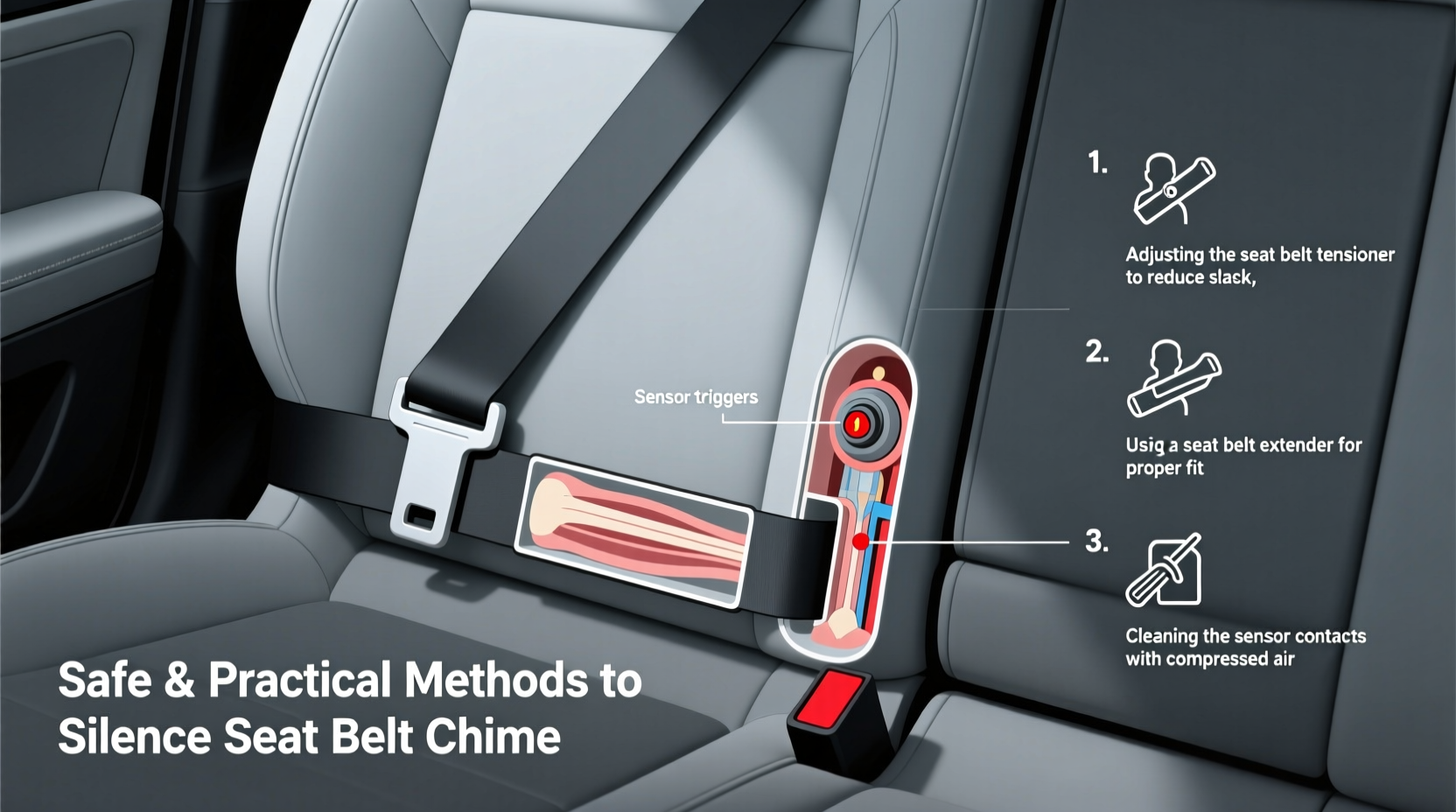
Seat belt chimes are part of a broader passive safety system mandated in most modern vehicles. They activate when the ignition is turned on and the driver or passenger has not fastened their seat belt. The sound typically lasts between 4 to 8 seconds but may repeat intermittently depending on speed and seating occupancy.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), seat belts reduce the risk of fatal injury by 45% for front-seat occupants in passenger cars. The chime is designed to reinforce this life-saving habit, particularly among younger or distracted drivers.
“Safety reminders like seat belt chimes have contributed to increased compliance and fewer fatalities over the past two decades.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Automotive Safety Researcher at the Transportation Institute
While well-intentioned, some users report sensitivity issues with the chime, including hearing impairments, anxiety triggers, or malfunctioning sensors that trigger false alarms. Addressing these concerns responsibly ensures comfort without sacrificing protection.
Safe Methods to Reduce or Silence the Chime
There are multiple ways to address an overactive or unnecessary chime. Below are five reliable, non-destructive strategies that preserve vehicle integrity and safety features.
1. Use a Seat Belt Extender or Weight Simulator Clip (Where Legal)
In certain vehicles—particularly older models or commercial fleets—OEM-approved seat belt clips or extenders can simulate a buckled state. These devices attach to the seat belt latch and mimic the weight and connection of a fastened belt.
Note: Some jurisdictions restrict the use of such devices when the seat is occupied. Always check local regulations before installation.
2. Reset or Recalibrate the Vehicle’s SRS Module
If the chime persists despite proper buckling, the issue may lie in a faulty sensor or misconfigured Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A qualified technician can perform a diagnostic scan using an OBD-II tool and recalibrate the system.
This process often resolves phantom chimes caused by moisture buildup, worn connectors, or software glitches. It does not disable safety functions but restores normal operation.
3. Adjust Driver Profile Settings (in Modern Vehicles)
Many newer cars allow customization through infotainment systems. High-end brands like Toyota, Honda, and Ford offer “chime preferences” under driver settings. For example:
- Toyota Safety Sense: Allows temporary suppression after consistent buckling behavior.
- Honda Sensing: Offers adjustable alert volume or duration.
- Ford Co-Pilot360: Enables mute options during test drives or fleet configurations.
These settings adapt to user habits without removing safety protocols.
4. Install a Programmable Delay Relay (Advanced, Professional Installation Required)
A delay relay can be wired into the chime circuit to limit the duration of the alert—say, from 30 seconds down to 6. This method keeps the reminder active but reduces auditory fatigue.
This modification must be done by a certified automotive electrician to avoid short circuits or interference with airbag deployment signals.
5. Utilize Factory-Installed Mute Features During Maintenance Mode
Some service manuals include a temporary mute function used during repairs. Mechanics activate it via specific key-turn sequences or diagnostic tools. While not intended for daily use, understanding this feature highlights that silencing mechanisms already exist within vehicle architecture—safely and reversibly.
What Not to Do: Common Unsafe Practices
Despite the frustration, certain actions compromise safety and legality. The table below outlines risky behaviors and their consequences.
| Method | Risk Level | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Unplugging the chime module | High | May disable airbag warning lights; illegal in many states |
| Taping the buckle switch | Medium-High | Sensor damage; false readings during crashes |
| Using third-party firmware hacks | Extreme | Void warranty; potential malware in vehicle network |
| Cutting wires near seat base | Extreme | Fire hazard; disables occupancy detection |
Modifications that tamper with electrical pathways or sensor logic endanger both occupants and bystanders. Even if the chime stops, the cost isn’t worth the risk.
Real-World Example: Managing Chimes in Fleet Vehicles
A regional delivery company operating a fleet of 75 vans faced repeated complaints about persistent seat belt alerts. Drivers reported distraction during tight delivery windows, especially when making brief stops.
Instead of disabling systems, the fleet manager partnered with a certified auto tech to implement a dual solution:
- Installed OEM-approved weight sensors calibrated for frequent entry/exit cycles.
- Programmed a 5-second chime window with automatic cutoff upon engine restart if the belt was previously engaged.
The result? A 92% reduction in chime-related complaints and no drop in seat belt usage, verified through telematics data. The fix enhanced comfort while preserving accountability.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Address a Persistent Chime Responsibly
Follow this timeline to resolve chime issues safely and effectively:
- Week 1: Diagnose the Cause
Observe when the chime activates. Is it only for the driver? Does it occur even when belted? Note patterns. - Day 2–3: Consult Your Owner’s Manual
Search for “seat belt warning,” “chime settings,” or “driver assistance preferences.” Look for built-in customization options. - Day 4: Test the Latch Mechanism
Clean debris from the buckle receiver. Spray electronic contact cleaner into the slot and cycle the belt several times. - Day 5: Visit a Certified Technician
Request an SRS diagnostic scan. Ask specifically about chime calibration—not deactivation. - Ongoing: Monitor Behavior
If using a simulator clip or delayed chime, ensure all passengers still buckle up. Never let convenience override caution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I legally disable my seat belt chime?
No federal law prohibits disabling the chime directly, but many states consider it a violation of motor vehicle safety equipment statutes if done in a way that impairs the restraint system. Additionally, doing so may affect insurance claims after an accident if non-use of seat belts is involved.
Why does my chime go off even when I’m wearing the seat belt?
This usually indicates a dirty or damaged buckle sensor, loose wiring, or corrosion in the seat track mechanism. Cleaning the buckle or having a technician inspect the circuit often resolves the issue.
Are seat belt silencers sold online safe to use?
Most are not. Third-party clips or magnets marketed as “silencers” can interfere with crash detection systems. Only use accessories approved by your vehicle manufacturer and installed according to guidelines.
Final Thoughts: Prioritize Safety Without Sacrificing Comfort
The seat belt chime exists for one reason: to save lives. But that doesn’t mean you have to endure constant noise to stay protected. By leveraging factory settings, professional diagnostics, and smart modifications, you can achieve a quieter cabin while keeping every safety layer intact.
Technology evolves to serve human needs—not the other way around. If the chime feels excessive, take action—but do so thoughtfully, legally, and with expert guidance.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?