Choosing the right thermostat for your home isn’t just about comfort—it’s about efficiency, convenience, and long-term savings. For years, programmable thermostats were considered the gold standard for homeowners looking to reduce energy bills without sacrificing control. But with the rise of smart technology, smart thermostats have entered the market promising self-learning capabilities, remote access, and deeper integration with home automation systems. The question remains: is the added intelligence—and higher price tag—of a smart thermostat truly worth it compared to a reliable programmable model?
The answer depends on your lifestyle, technical comfort, and heating and cooling patterns. While both types can save energy, they do so in different ways and with varying levels of user involvement. Understanding their core differences, advantages, and limitations will help determine whether investing in a learning thermostat delivers meaningful returns or simply adds unnecessary complexity.
How Programmable Thermostats Work
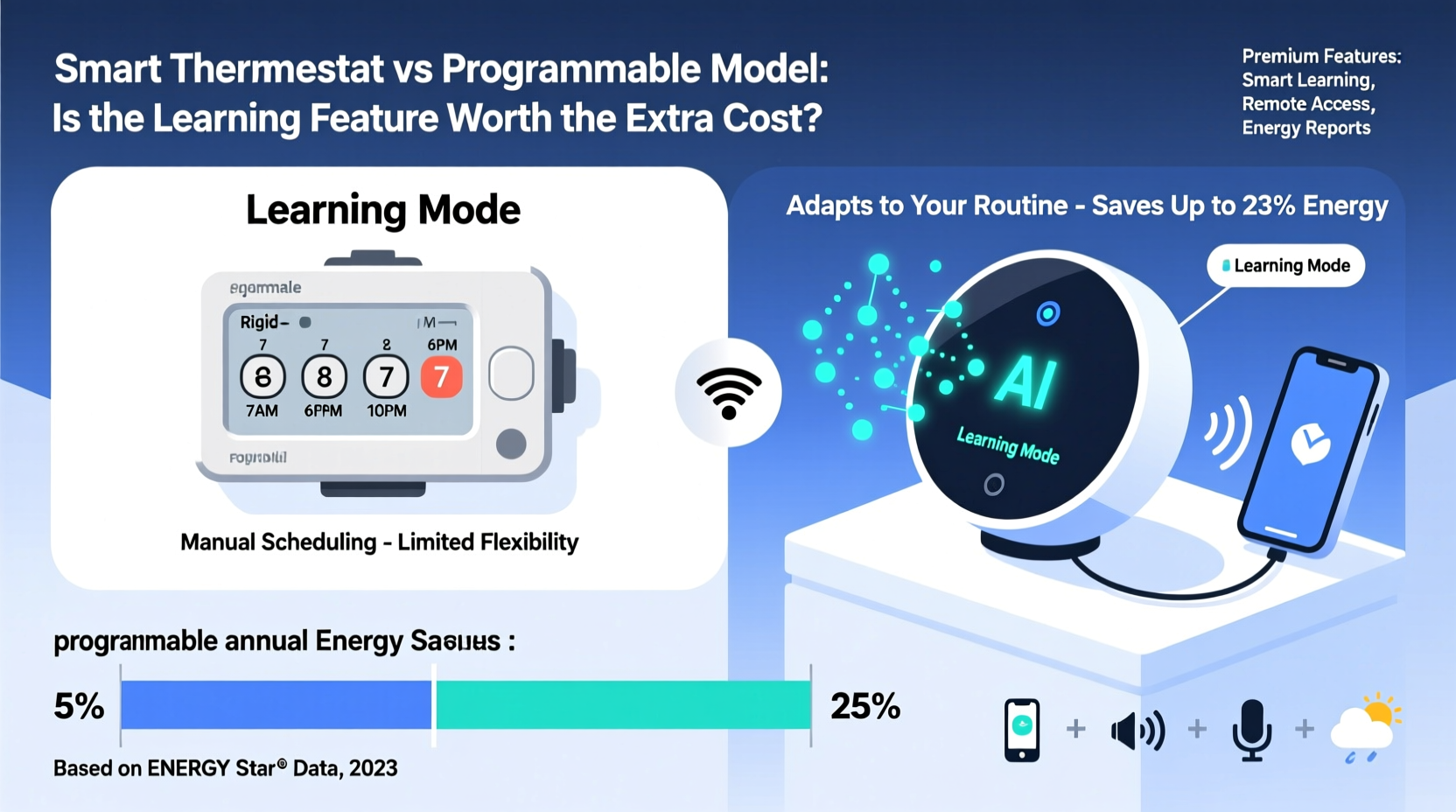
Programmable thermostats allow users to set temperature schedules based on time of day and day of the week. For example, you might program the system to lower the heat at night or when no one is home during work hours, then return to a comfortable setting before you wake up or arrive back from work.
These devices typically offer four scheduling periods per day: wake, leave, return, and sleep. Most models support weekday/weekend programming, giving moderate flexibility for different routines. When used consistently, programmable thermostats can reduce HVAC energy consumption by 5% to 15%, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
However, their effectiveness hinges entirely on correct setup and ongoing maintenance. Many homeowners either never program them properly or override settings too frequently, which diminishes potential savings. A study by the National Resources Defense Council found that nearly half of programmable thermostat owners never programmed theirs at all—rendering them functionally equivalent to basic manual thermostats.
What Makes Smart Thermostats Different?
Smart thermostats go beyond pre-set schedules by incorporating sensors, Wi-Fi connectivity, mobile apps, and machine learning algorithms. Devices like the Nest Learning Thermostat, Ecobee, and Honeywell Home T9 learn your household’s temperature preferences over time and automatically adjust settings accordingly.
Key features include:
- Learning capability: After several days of manual adjustments, the thermostat begins predicting your preferred temperatures and creates a custom schedule.
- Remote access: Control your home’s climate from anywhere via smartphone app, even if you’re on vacation.
- Geofencing: Uses phone location to detect when you’re leaving or approaching home, adjusting temperatures automatically.
- Energy reports: Monthly summaries show usage patterns and suggest improvements.
- Voice assistant integration: Works with Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri for hands-free control.
- Air quality and humidity monitoring: Some models track indoor air conditions and recommend ventilation.
Unlike programmable units, smart thermostats adapt dynamically. If your morning routine shifts due to a late meeting, the system notices the change and adjusts future heating or cooling cycles. This responsiveness reduces wasted energy from rigid schedules that no longer match real-life behavior.
“Smart thermostats don’t just react to inputs—they anticipate needs. That predictive layer is where real efficiency gains happen.” — Dr. Linda Reeves, Energy Efficiency Researcher at MIT Sustainable Systems Lab
Cost Comparison: Upfront vs Long-Term Value
One of the biggest barriers to adopting smart thermostats is cost. A basic programmable thermostat ranges from $30 to $70, while most smart models start around $120 and can exceed $250 for premium versions with room sensors or advanced AI.
Yet price alone doesn’t tell the full story. To evaluate value, consider total ownership cost—including installation, usability, and energy savings.
| Feature | Programmable Thermostat | Smart Thermostat |
|---|---|---|
| Price Range | $30 – $70 | $120 – $250+ |
| Installation | DIY-friendly (often) | May require C-wire or professional help |
| User Engagement Required | High (manual programming) | Low (after initial setup) |
| Remote Access | No | Yes (via app) |
| Learning Capability | No | Yes (adaptive scheduling) |
| Energy Savings Potential | 5–10% (if used correctly) | 10–23% (based on EPA ENERGY STAR data) |
| Lifespan | 7–10 years | 8–12 years |
The Environmental Protection Agency estimates that ENERGY STAR-certified smart thermostats save an average of $50 to $130 per year on energy bills. At $150 upfront, this means payback occurs within 1.5 to 3 years. After that, every dollar saved is pure gain. Additionally, some utility companies offer rebates of $50 or more for installing qualifying smart thermostats, effectively cutting the net cost in half.
Real-World Example: Two Households, Two Choices
Consider two similar households in suburban Chicago, each with a 2,000-square-foot home and gas furnace plus central air conditioning.
Household A installs a $50 programmable thermostat. They set a schedule lowering the temperature by 8°F at night and during work hours. However, after three months, inconsistent overrides and forgotten adjustments lead to only modest savings—about 7% annually, or $90 on a $1,300 yearly HVAC bill.
Household B invests $170 in a smart thermostat. Within a week, it learns their morning and evening routines. Geofencing ensures the house warms up only when family members are en route home. During an unseasonably warm February week, the system detects open windows and pauses heating automatically. Over the first year, they save 18%, or $234. With a $75 utility rebate, their net cost was $95—meaning they recouped their investment in under six months.
This scenario illustrates how behavioral differences impact outcomes. The smart thermostat compensated for human inconsistency; the programmable model did not.
When a Programmable Thermostat Still Makes Sense
Despite the advantages of smart models, programmable thermostats remain a sensible choice in certain situations:
- Stable, predictable routines: If your household follows the same schedule every day (e.g., weekdays 9-to-5, weekends at home), a well-programmed unit performs nearly as efficiently as a smart one.
- Budget constraints: Renters or those planning short-term occupancy may prefer low-cost solutions without long-term ROI expectations.
- Technical simplicity: Older adults or tech-averse users may find smartphone apps and Wi-Fi pairing overwhelming.
- Compatibility issues: Homes lacking a C-wire (common in older HVAC systems) may require additional installation work for smart thermostats.
If you're highly disciplined about maintaining your schedule and rarely deviate from it, a programmable thermostat can deliver solid results without complexity.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Right Option
Follow this decision framework to select the best thermostat for your needs:
- Assess your daily routine. Is it consistent or constantly changing? Frequent travelers, remote workers, or families with irregular schedules benefit more from adaptive learning.
- Evaluate your HVAC system. Check if your current setup includes a C-wire. If not, research whether your chosen smart thermostat supports power-stealing technology or requires professional wiring upgrades.
- Estimate annual HVAC costs. Higher energy bills mean greater absolute savings from efficiency improvements. A smart thermostat offers more financial upside in extreme climates with heavy heating or cooling demands.
- Determine your tech comfort level. Are you comfortable downloading apps, connecting devices to Wi-Fi, and troubleshooting minor glitches? If not, opt for simpler controls.
- Check for rebates. Visit ENERGY STAR Rebate Finder to see available incentives in your area. These can dramatically improve the value proposition of smart models.
- Decide on desired features. Do you want voice control, occupancy sensing, or multi-room zoning? Only smart thermostats with add-on sensors provide these capabilities.
- Calculate break-even point. Divide net cost (after rebates) by estimated annual savings. If it exceeds five years, reconsider unless non-financial benefits (like convenience) are highly valued.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I install a smart thermostat myself?
Most modern smart thermostats are designed for DIY installation and come with step-by-step guides and compatibility checkers. However, if your system lacks a common wire (C-wire), you may need an electrician to install one or use an adapter kit. Always turn off power to your HVAC system before beginning.
Do smart thermostats work with all HVAC systems?
No. While many brands support a wide range of systems—including forced air, heat pumps, radiant, and dual-fuel—not all models are universally compatible. Use online tools like Nest’s Compatibility Checker or Ecobee’s System Matcher to verify before purchasing.
Are smart thermostats secure?
Reputable brands use encryption and regular firmware updates to protect user data. To minimize risk, use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and keep your home Wi-Fi network secure. Avoid connecting to public networks.
Conclusion: Is the Learning Feature Worth the Extra Cost?
The learning feature in smart thermostats isn’t just a gimmick—it’s a practical tool that addresses the biggest weakness of programmable models: human inconsistency. By observing behavior and adapting autonomously, smart thermostats maintain comfort while minimizing waste, even when life doesn’t follow a script.
For homeowners with variable schedules, multiple occupants, or a desire for seamless home integration, the added cost is often justified by faster payback, greater savings, and enhanced convenience. Utility rebates further tip the balance in favor of smart models.
That said, if your life runs like clockwork, you’re on a tight budget, or you prefer minimal tech interaction, a programmable thermostat remains a viable, cost-effective option—provided you actually use it as intended.
In the end, the best thermostat is the one you’ll use correctly and consistently. But for most modern households seeking both comfort and control, the intelligence built into smart thermostats delivers tangible benefits that go well beyond the initial price difference.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?