Wi-Fi connectivity is essential in today’s digital world. Whether you're working from home, streaming your favorite show, or attending a virtual meeting, losing access to your network can be more than just inconvenient—it can disrupt your entire day. When your device shows “unable to join Wi-Fi,” the cause could range from simple signal interference to deeper hardware or configuration problems. The good news is that most issues are fixable with systematic troubleshooting. This guide walks you through practical, step-by-step solutions that address both common and complex reasons behind failed Wi-Fi connections.
1. Verify Basic Connectivity and Signal Strength
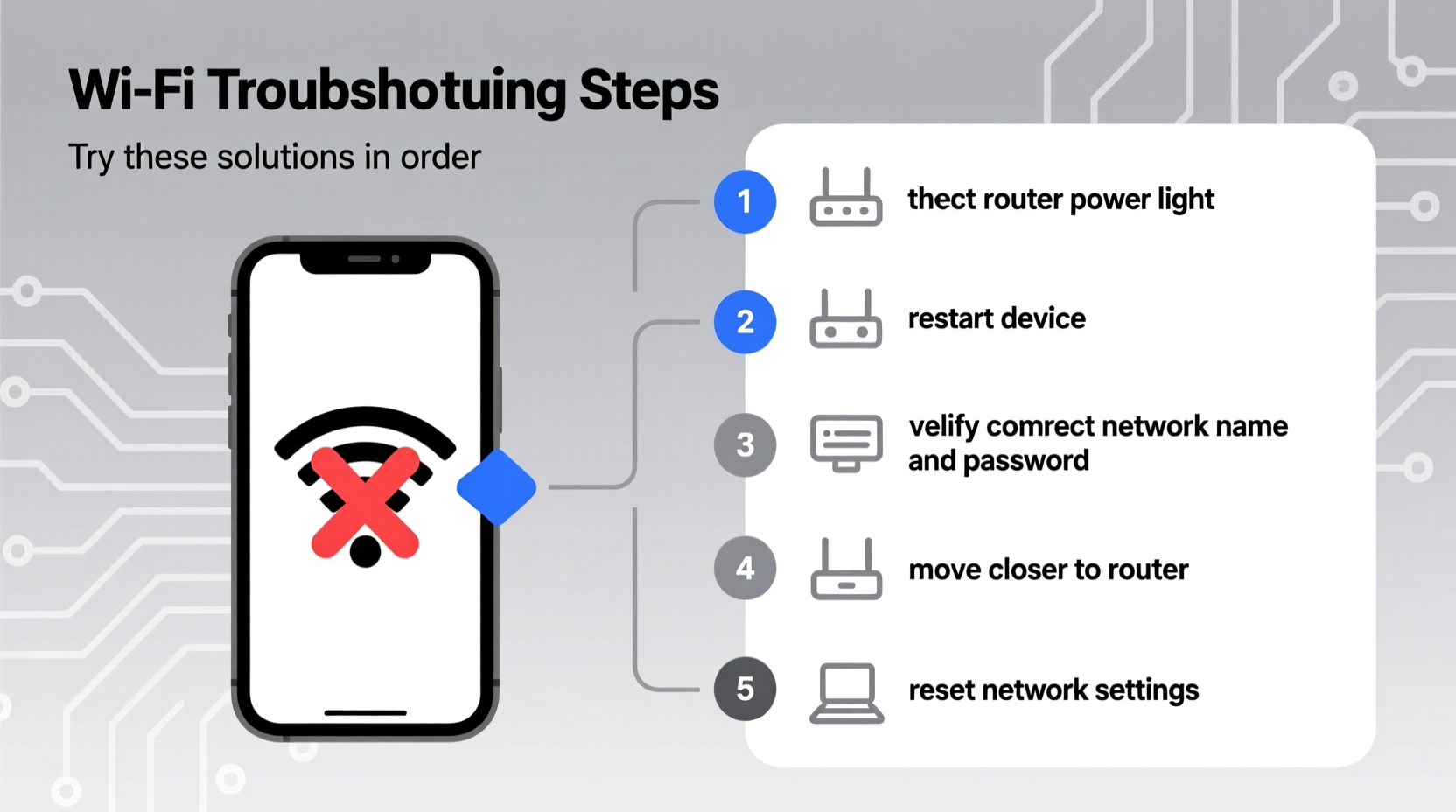
Before diving into advanced fixes, confirm the fundamentals. A weak signal or incorrect network selection can mimic serious technical failures.
- Ensure you're within range of the router. Thick walls, metal objects, and distance can degrade signal strength.
- Check if other devices can connect to the same network. If they can’t, the issue likely lies with the router or internet service.
- Double-check that you’re attempting to join the correct network name (SSID) and entering the right password.
If only one device fails to connect while others work fine, the problem is isolated to that specific device—likely software-related. If no devices connect, focus on the router and internet connection first.
2. Restart Your Devices: Router and Client
One of the most effective yet overlooked solutions is restarting both your router and the device experiencing issues. Power cycling clears temporary memory errors and resets network configurations.
- Turn off your router and modem. Unplug them from power for at least 30 seconds.
- Plug the modem back in and wait until all lights stabilize (usually 1–2 minutes).
- Reconnect the router and wait another minute for it to fully boot.
- Restart the device that couldn't join the network—phone, laptop, tablet, etc.
- Attempt to reconnect to Wi-Fi.
This process resolves over 50% of reported “unable to join” cases according to data from major ISP support logs. It clears IP conflicts, resets DHCP assignments, and re-establishes stable communication between devices.
3. Check for IP Address Conflicts and Renew Network Settings
When multiple devices request the same IP address, or when a device fails to receive one, connectivity breaks down. This often happens after firmware updates or prolonged uptime.
On Windows:
- Open Command Prompt as administrator.
- Type
ipconfig /releaseand press Enter. - Then type
ipconfig /renewand press Enter. - Finally, run
netsh winsock resetto clear corrupted socket entries. - Restart your computer.
On macOS:
- Go to System Settings > Network > Wi-Fi.
- Select your network, click Details, then TCP/IP.
- Click \"Renew DHCP Lease.\"
On Mobile Devices (iOS/Android):
Toggle Airplane mode on for 10 seconds, then off. This forces the device to re-scan and re-authenticate with available networks.
| Device Type | Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Windows PC | Run ipconfig commands | Fresh IP assignment |
| MacBook | Renew DHCP lease | Resolves IP conflict |
| Smartphone | Enable/disable Airplane mode | Forces network refresh |
| Tablet | Forget network & reconnect | Clears saved credentials |
4. Forget Network and Reconnect
Saved network profiles can become corrupted, especially after password changes or firmware updates. Removing and re-adding the network clears outdated settings.
- Go to Wi-Fi settings on your device.
- Locate your network in the list of saved networks.
- Select “Forget This Network” or equivalent option.
- Re-scan for networks, select yours, and enter the password again.
This method is particularly effective when the error message reads “Unable to join, try again later” or “Authentication failed.”
5. Investigate Router-Level Issues
If multiple devices struggle to join, the issue may stem from router settings or limitations.
- MAC Filtering: Some routers block devices not on an approved list. Check your router’s admin panel under Security or Access Control.
- Band Congestion: Older devices may not support 5 GHz bands. Ensure your router broadcasts a compatible 2.4 GHz network.
- Client Limit: Budget routers cap the number of connected devices. Exceeding this limit prevents new joins.
- Firmware Updates: Outdated firmware can cause compatibility issues. Log into your router (usually via 192.168.1.1) and check for updates.
“Over 30% of Wi-Fi join failures in homes are due to outdated router firmware or misconfigured security protocols.” — David Lin, Senior Network Engineer at NetSecure Labs
Mini Case Study: Office Network Lockout
A small marketing firm reported that three employees suddenly couldn’t connect their laptops to the office Wi-Fi. Other devices worked normally. IT staff discovered the router had automatically updated its firmware overnight, which reset security settings to WPA3-only mode. Two older laptops only supported WPA2. By reverting the encryption to WPA2/WPA3 hybrid mode, all devices regained access within minutes. This highlights how firmware updates can silently break backward compatibility.
Troubleshooting Checklist
Use this concise checklist to methodically resolve “unable to join Wi-Fi” errors:
- ✅ Confirm Wi-Fi is enabled on the device
- ✅ Verify correct password entry
- ✅ Restart the device and router
- ✅ Move closer to the router to test signal strength
- ✅ Forget the network and reconnect
- ✅ Renew IP address (via command line or settings)
- ✅ Disable and re-enable Wi-Fi adapter
- ✅ Check router for MAC filtering or client limits
- ✅ Update device OS and router firmware
- ✅ Test with another known-working device
Advanced Fixes for Persistent Problems
If basic steps fail, consider these deeper interventions:
Reset Network Settings
On smartphones and computers, resetting network settings wipes all saved Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth pairings, and VPN configurations. While drastic, it eliminates deep-seated software corruption.
Change DNS Manually
Corrupted DNS settings can prevent successful handshakes. Set your device to use public DNS servers like Google (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
Update Network Drivers
Outdated or faulty drivers are common culprits on Windows machines. Visit your laptop manufacturer’s website or use Device Manager to update the wireless adapter driver.
FAQ
Why does my phone say “unable to join” even with the right password?
This usually indicates a mismatch in security protocol (e.g., WPA3 vs WPA2), IP conflict, or corrupted network profile. Try forgetting the network, restarting the router, and reconnecting.
Can a router block a specific device permanently?
Yes—if MAC filtering is enabled and your device isn’t on the allowed list, it will be blocked. You can find your device’s MAC address in its network settings and add it manually via the router’s admin interface.
Why can I see the network but not join it?
Seeing the SSID means the signal is present, but inability to join suggests authentication failure, IP assignment issues, or interference. Start with forgetting the network and renewing your IP.
Conclusion
Dealing with “unable to join Wi-Fi” doesn’t require technical expertise—just a logical approach. Most issues stem from temporary glitches, outdated settings, or simple misconfigurations that can be resolved in under 15 minutes. By following the steps outlined here—from restarting devices to checking router settings—you regain control over your connectivity. Don’t accept spotty Wi-Fi as normal. Apply these solutions proactively and maintain a reliable, high-performing network environment.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?