Bluetooth speakers offer convenience and portability, but nothing disrupts the experience more than sudden audio dropouts. Whether you're hosting a backyard party, working from home, or relaxing with music, random disconnections can be frustrating. The root causes are often simple—interference, outdated firmware, distance issues, or device limitations—but diagnosing them requires a methodical approach. Understanding the technology behind Bluetooth and common environmental factors can help you maintain a stable, uninterrupted audio stream.
How Bluetooth Works: A Brief Overview
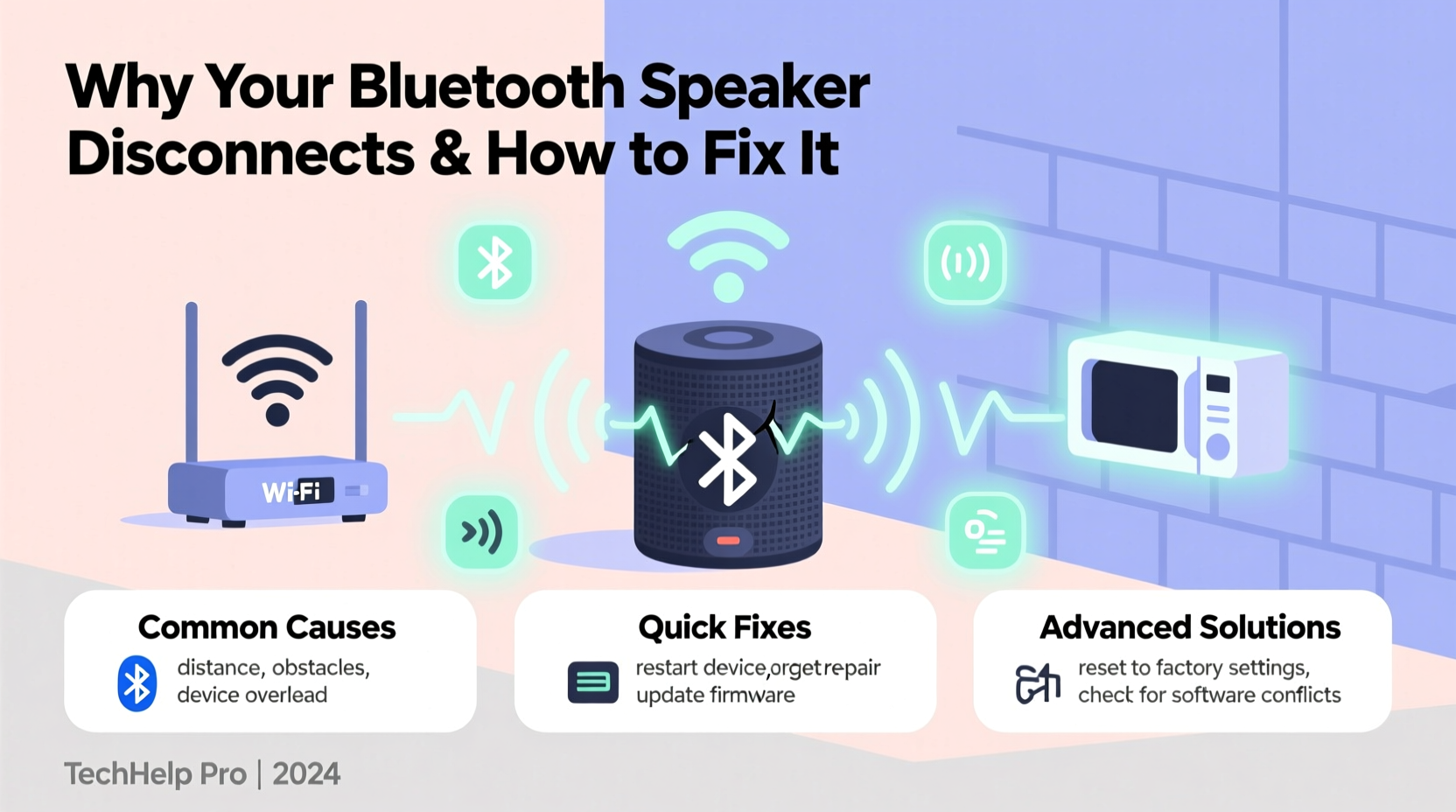
Bluetooth operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, the same as Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, cordless phones, and many smart home devices. It uses short-range wireless communication to transmit data between devices, typically within a range of 30 feet (10 meters) under ideal conditions. However, signal strength degrades quickly in the presence of obstacles like walls, furniture, or even human bodies. Modern Bluetooth versions (4.0 and above) are designed to be more power-efficient and stable, but compatibility and interference remain persistent challenges.
Audio transmission via Bluetooth is not instantaneous. There’s a small delay known as latency, during which data packets travel from the source device (like your phone) to the speaker. If packets are lost due to interference or weak signals, the audio may stutter, pause, or cut out entirely. Unlike wired connections, wireless links rely heavily on line-of-sight and clean frequency channels to function optimally.
“Bluetooth stability depends more on environment than hardware quality alone. Even high-end speakers suffer when surrounded by RF noise.” — Dr. Alan Reyes, Wireless Communication Engineer
Common Causes of Bluetooth Speaker Dropouts
Random disconnections aren’t usually due to a single factor. Instead, they stem from a combination of technical, environmental, and usage-related issues. Identifying the most likely culprit starts with evaluating your setup and habits.
1. Signal Interference from Other Devices
The 2.4 GHz band is crowded. Wi-Fi networks, especially older ones using 2.4 GHz exclusively, can interfere with Bluetooth signals. Microwaves, baby monitors, and wireless gaming controllers also operate in this range and may cause temporary disruptions when active.
2. Physical Obstacles and Distance
Walls, furniture, metal objects, and even large bodies of water (like aquariums) can block or reflect Bluetooth signals. Moving too far from your speaker—or placing it behind a cabinet—can degrade the signal beyond recovery.
3. Low Battery or Power-Saving Modes
When a speaker’s battery is low, some models reduce transmission power to conserve energy, leading to weaker connections. Similarly, power-saving modes may throttle performance or disconnect after periods of inactivity.
4. Outdated Firmware or Software
Manufacturers release firmware updates to improve connectivity, fix bugs, and enhance compatibility. An outdated speaker or source device may struggle to maintain stable connections with modern codecs or pairing protocols.
5. Device Pairing Limits and Memory Overload
Some Bluetooth speakers remember multiple paired devices but can only maintain one active connection. Switching between devices without proper disconnection can confuse the pairing logic, causing unexpected dropouts.
6. Audio Codec Mismatches
Codecs like SBC, AAC, aptX, and LDAC determine how audio data is compressed and transmitted. If your phone and speaker don’t support the same high-quality codec, the system defaults to a lower-bandwidth option, increasing the chance of packet loss under stress.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix Bluetooth Connection Drops
Follow this systematic troubleshooting process to identify and resolve the cause of your speaker’s intermittent behavior.
- Power cycle both devices. Turn off your speaker and source (phone, tablet, laptop), wait 10 seconds, then turn them back on. This clears temporary glitches in the Bluetooth stack.
- Remove and re-pair the speaker. Go to your device’s Bluetooth settings, “Forget” the speaker, then pair it again from scratch. This eliminates corrupted pairing data.
- Reduce physical distance and remove obstacles. Place the speaker within 10–15 feet of your device with minimal barriers between them.
- Check for firmware updates. Visit the manufacturer’s website or app (e.g., Bose Connect, JBL Portable, Sony Music Center) to see if an update is available.
- Disable other wireless devices temporarily. Turn off nearby Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, or Bluetooth peripherals to test if interference is the issue.
- Switch your Wi-Fi to 5 GHz. If your router supports dual bands, connect your phone to the 5 GHz network to free up space on the 2.4 GHz band.
- Test with another source device. Try connecting the speaker to a different phone or tablet. If the problem persists, the issue lies with the speaker. If it works fine, the original device may have Bluetooth driver issues.
- Reset the speaker to factory settings. Most models have a reset button or key combination (e.g., holding power + volume down for 10 seconds). Consult your manual.
Do’s and Don’ts: Best Practices for Stable Bluetooth Audio
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Keep your speaker charged above 30% | Run the speaker until it shuts down from low battery |
| Place the speaker in open areas away from metal objects | Store it inside cabinets or behind TVs |
| Update firmware regularly | Ignore software update notifications |
| Use devices that support aptX or AAC for better audio stability | Expect flawless performance from budget devices with basic SBC codec only |
| Limit the number of active Bluetooth devices nearby | Surround your setup with multiple wireless gadgets |
Real-World Example: Solving Dropouts at Home
Sarah, a remote worker in Chicago, experienced frequent audio cuts while using her portable Bluetooth speaker during virtual meetings. She initially assumed the speaker was defective. After testing it with her phone and confirming stable playback, she realized the issue only occurred when connected to her laptop.
She followed the troubleshooting steps: restarted both devices, removed the pairing, and reconnected. The problem persisted. Then, she noticed her Wi-Fi speed dropped whenever the audio cut out. Investigating further, she discovered her router and laptop were both using the 2.4 GHz band. By switching her laptop to the 5 GHz network and updating her laptop’s Bluetooth drivers, the dropouts stopped completely. The root cause was RF congestion—not faulty hardware.
This case illustrates how seemingly isolated audio issues can stem from broader network dynamics. Diagnosing such problems requires looking beyond the speaker itself.
Troubleshooting Checklist
- ✅ Reboot speaker and source device
- ✅ Forget and re-pair the Bluetooth connection
- ✅ Check speaker battery level (keep above 30%)
- ✅ Ensure no physical obstructions between devices
- ✅ Update speaker firmware via manufacturer app
- ✅ Disable nearby 2.4 GHz devices (Wi-Fi, microwave)
- ✅ Test with a second source device
- ✅ Reset speaker to factory settings
- ✅ Move closer to the speaker (within 10 feet)
- ✅ Confirm your device supports efficient audio codecs
When Hardware Might Be the Issue
Sometimes, despite all efforts, the problem lies in the hardware itself. Older Bluetooth speakers using version 2.1 or 3.0 lack the adaptive frequency hopping and error correction found in newer models. These legacy devices are far more susceptible to interference and range limitations.
Additionally, internal antenna design plays a crucial role. Compact speakers often sacrifice antenna quality for aesthetics, resulting in weaker signal reception. If you’ve tried every software fix and still experience dropouts across multiple environments and devices, the speaker may simply be reaching its technical limits.
In such cases, upgrading to a model with Bluetooth 5.0 or higher can make a dramatic difference. These versions offer quadruple the range, double the speed, and improved coexistence with other wireless technologies. Look for features like multipoint pairing and support for aptX Adaptive or LDAC for high-fidelity, stable streaming.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my Bluetooth speaker cut out when I move around?
Movement can break the line-of-sight between your device and speaker, especially if you walk into another room or behind large objects. Bluetooth signals weaken rapidly through walls and furniture. Staying within 15 feet and minimizing obstructions helps maintain a stable link.
Can Wi-Fi really affect my Bluetooth speaker?
Yes. Both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth use the 2.4 GHz band. When multiple devices compete for bandwidth, interference occurs. This is especially common in dense urban apartments or offices. Switching your Wi-Fi to 5 GHz or using Ethernet can significantly reduce conflicts.
Does playing music at high volume cause disconnections?
Not directly. However, high volume increases data throughput, which demands more from the Bluetooth connection. If the signal is already weak or congested, this added load can lead to buffer underruns and audio dropouts. Lowering volume slightly may help in marginal signal conditions.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Listening Experience
Random Bluetooth speaker disconnections are rarely unavoidable. With a clear understanding of wireless dynamics and a structured approach to troubleshooting, most issues can be resolved without replacing equipment. Start with the basics—restarting devices, re-pairing, and reducing interference—then progress to firmware updates and environmental adjustments. In many cases, small changes yield immediate improvements.
If you've followed the checklist and still face problems, consider whether your speaker has reached its technological limit. Newer Bluetooth standards offer superior reliability, and investing in updated hardware may be the most effective long-term solution. Don’t accept poor performance as normal—your listening experience deserves better.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?