Random shutdowns are among the most frustrating issues laptop users face. Unlike a system crash or blue screen, a sudden power-off gives no warning and often interrupts critical work. While software glitches can contribute, persistent random shutdowns usually point to underlying hardware failure or thermal stress. Understanding the root causes—especially which hardware components are likely at fault—can save time, money, and data. This guide explores the most common culprits, diagnostic methods, and actionable steps to restore stability.
Overheating: The Silent Killer of Laptop Performance
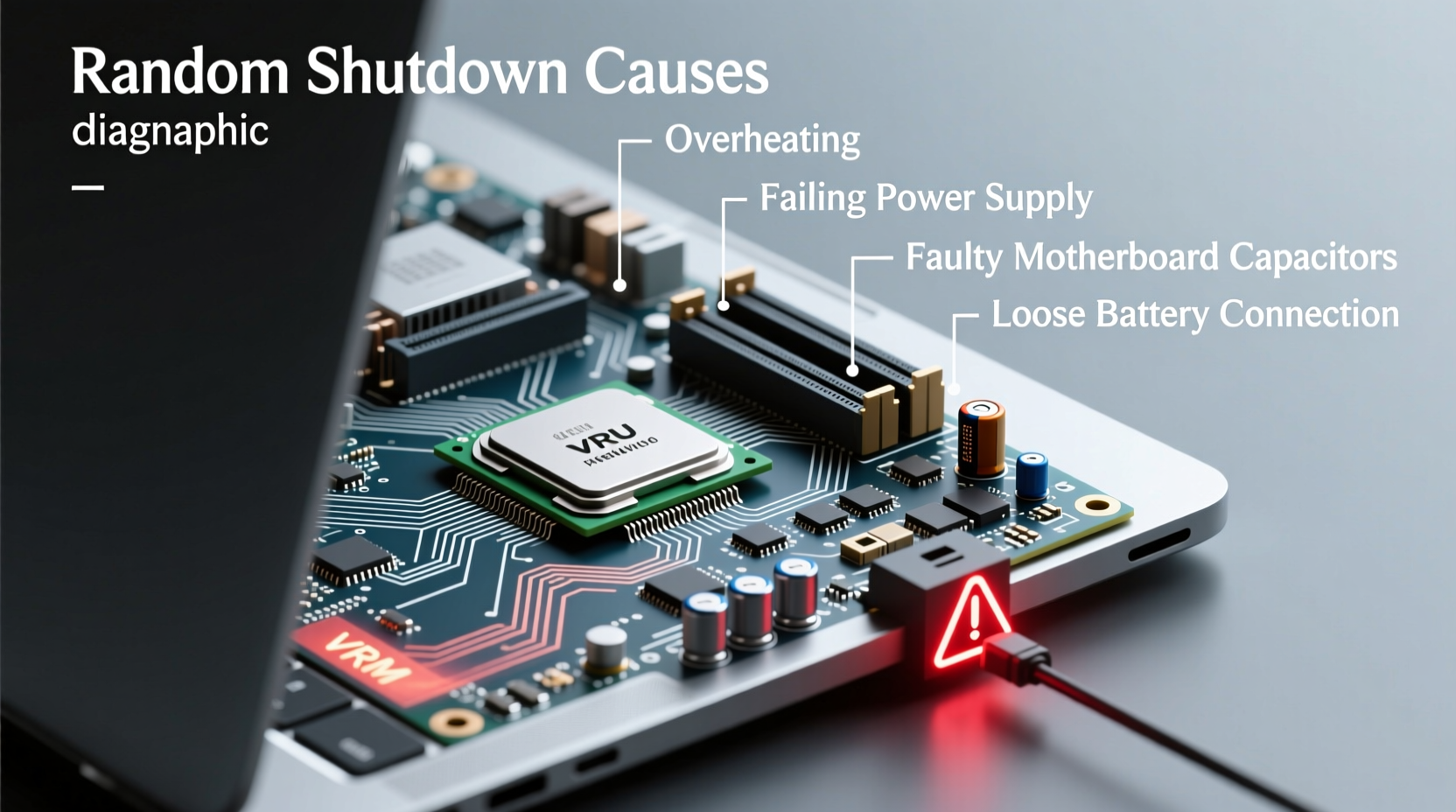
Laptops generate significant heat during operation, especially under load. When cooling systems fail to dissipate this heat efficiently, internal temperatures rise beyond safe thresholds. Most modern laptops have built-in thermal protection that forces an immediate shutdown to prevent permanent damage to sensitive components like the CPU and GPU.
Dust accumulation in fans and heatsinks is one of the leading causes of overheating. Over time, dust blocks airflow, reducing cooling efficiency. Additionally, degraded thermal paste between the processor and heatsink reduces heat transfer, causing the CPU to overheat even during light tasks.
High ambient temperatures, such as using a laptop on a bed or cushion, also restrict airflow. These soft surfaces block intake vents, trapping heat inside the chassis. Always use your laptop on a hard, flat surface or a dedicated cooling pad to maintain proper ventilation.
Signs Your Laptop Is Overheating
- Fan runs constantly at high speed
- Bottom or keyboard area feels excessively hot
- Shutdowns occur during video playback, gaming, or multitasking
- Performance throttling (sluggish response under load)
“Thermal management is the cornerstone of laptop longevity. A machine that frequently hits thermal limits will degrade faster—even if it doesn’t show immediate symptoms.” — Dr. Alan Zhou, Hardware Systems Engineer at TechReliability Labs
Failing Power Supply and Battery Issues
The power delivery system—including the AC adapter, charging circuit, and battery—is another frequent source of unexpected shutdowns. If any part of this chain fails, the laptop may lose power without warning, particularly when switching between battery and wall power.
A damaged or underpowered AC adapter cannot deliver consistent voltage. Cheap third-party chargers often lack the necessary amperage or voltage regulation, leading to instability. Similarly, a swollen or aged battery may not hold charge properly, causing the system to shut down when the internal power buffer drops below operational levels—even if the battery indicator shows remaining charge.
How to Test Power Components
- Inspect the charger for frayed cables, bent pins, or loose connections.
- Try a known-good OEM charger to rule out adapter failure.
- Check battery health via operating system tools (e.g., Windows’ power report or macOS System Information).
- Remove the battery (if possible) and run the laptop solely on AC power to test stability.
| Component | Symptom | Potential Fix |
|---|---|---|
| AC Adapter | Laptop powers off when unplugged or intermittently while plugged in | Replace with manufacturer-specified charger |
| Battery | Shuts down at 20%+ charge; swelling visible | Replace battery immediately |
| Charging Port | Loose connection, intermittent charging | Repair or replace motherboard connector |
RAM and Storage Failures Leading to System Collapse
While less common than thermal or power issues, failing RAM or storage drives can cause abrupt shutdowns. Faulty memory modules can corrupt data being processed, leading to uncorrectable errors that trigger a system halt. Similarly, a dying SSD or HDD may fail to read critical boot files or system pages, resulting in a sudden loss of operation.
Memory errors often go undetected until they cause crashes. Symptoms include random freezes, corrupted files, and shutdowns during memory-intensive applications. Solid-state drives with worn NAND cells or failed controllers can exhibit similar behavior—especially if the drive enters a read-only or locked state unexpectedly.
Diagnostic Steps for RAM and Storage
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic or MemTest86 to check for RAM errors.
- Use built-in tools like CHKDSK (Windows) or First Aid in Disk Utility (macOS) to scan storage integrity.
- Monitor SSD health using S.M.A.R.T. data via tools like CrystalDiskInfo.
- If possible, test with one RAM stick at a time to isolate faulty modules.
“We’ve seen cases where a single bad memory module caused daily shutdowns. After replacement, the system ran flawlessly for years.” — Lisa Tran, Senior Technician at PCMedics Repair Network
Graphics and Motherboard Failures: Advanced Hardware Risks
The motherboard is the central hub connecting all components. When it begins to fail—due to capacitor degradation, trace damage, or solder joint cracks—system stability suffers dramatically. One of the earliest signs is erratic shutdowns, often occurring without pattern or warning.
Integrated or discrete GPUs are also prone to failure, especially under sustained graphical load. Overheating, poor driver integration, or manufacturing defects can cause the GPU to draw excessive power or generate errors that force the system to shut down. In some cases, BIOS-level protections detect GPU anomalies and initiate emergency power-downs.
Real-World Case: Gaming Laptop Failing Under Load
Mark, a freelance video editor, reported his high-performance laptop shutting down during 4K rendering. Initial checks ruled out software issues. Thermal imaging revealed the GPU reaching 105°C within minutes. Upon disassembly, technicians found clogged heat pipes and dried thermal pads. After cleaning the cooling system and replacing the GPU interface pads, the unit stabilized and has operated normally for over a year. This case highlights how combined hardware wear—cooling + component aging—can manifest as sudden shutdowns.
Warning Signs of Motherboard or GPU Failure
- Shutdowns occur only during graphics-heavy tasks (gaming, editing)
- No display output despite power-on indicators lighting up
- Burning smell near the hinge or keyboard area
- Visible bulging capacitors on the motherboard (requires disassembly)
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Random Shutdowns
Follow this structured approach to identify and resolve the root cause of unexpected shutdowns:
- Observe the Pattern: Note when shutdowns occur—during startup, under load, after a few minutes, or randomly. This helps narrow the cause.
- Check Event Logs: On Windows, open Event Viewer and look for critical errors (Event ID 41: Kernel-Power) around the time of shutdowns. On macOS, review system logs in Console.app.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use HWMonitor, Core Temp, or Macs Fan Control to track CPU/GPU temps in real time.
- Test with Minimal Configuration: Disconnect peripherals, remove external drives, and boot with only essential hardware.
- Boot into Safe Mode: If the laptop remains stable in Safe Mode, the issue may be software-related. If it still shuts down, focus shifts to hardware.
- Run Hardware Diagnostics: Use manufacturer tools (e.g., Dell SupportAssist, HP PC Hardware Diagnostics) or third-party utilities to test RAM, storage, and power systems.
- Physically Inspect Internals: If comfortable, open the laptop to check for dust, swollen batteries, or damaged components.
- Seek Professional Repair: For motherboard, GPU, or complex thermal repairs, consult a certified technician.
Troubleshooting Checklist
- ✅ Clean air vents and fans with compressed air
- ✅ Replace degraded thermal paste or pads
- ✅ Test with a known-good power adapter
- ✅ Check battery health and replace if degraded
- ✅ Run memory and disk diagnostics
- ✅ Monitor temperatures under load
- ✅ Update BIOS and drivers to latest versions
- ✅ Inspect for physical damage or burning smells
- ✅ Backup data immediately if instability persists
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a virus cause my laptop to shut down randomly?
While malware can cause system instability, true random shutdowns are rarely due to viruses. More commonly, malware leads to slowdowns, pop-ups, or unauthorized network activity. However, a malicious program could overload the CPU, indirectly causing overheating and shutdowns. Always run a full antivirus scan if software issues are suspected, but prioritize hardware checks first.
Why does my laptop shut down even when plugged in?
This typically indicates a problem beyond the battery—such as a failing AC adapter, malfunctioning charging circuit, or severe overheating. Even when connected to power, if the motherboard detects unstable voltage or excessive heat, it will initiate a shutdown to protect internal components. Test with a different charger and monitor internal temperatures to isolate the cause.
Is it safe to continue using a laptop that shuts down randomly?
No. Continued use risks permanent hardware damage, data corruption, and complete system failure. Each uncontrolled shutdown stresses storage drives and can corrupt the operating system. Back up your data immediately and begin diagnostics. If the issue persists, stop regular use until repaired.
Conclusion: Take Action Before It’s Too Late
Random laptop shutdowns are not normal—and they should never be ignored. Whether triggered by overheating, power delivery flaws, or failing internal components, these events signal that your device is under stress. Left unchecked, minor hardware issues can escalate into catastrophic failures. By systematically diagnosing temperature, power, memory, and motherboard health, you can identify the culprit and take corrective action before data loss or irreversible damage occurs.
Start with simple maintenance: clean the vents, verify your charger, and monitor system temperatures. If problems persist, leverage diagnostic tools or consult a professional. Most importantly, back up your data regularly—because no troubleshooting step matters if your files are gone. Your laptop is a critical tool; treat its warnings seriously, and it will serve you reliably for years to come.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?