Smart speakers have transformed how we interact with our homes—turning on lights, checking the weather, or playing music with just a few spoken words. But anyone who’s said “Play jazz music” only to hear a podcast about Japanese history knows the frustration when these devices mishear commands. Despite advances in artificial intelligence, voice recognition isn’t perfect. Background noise, accent variations, and hardware limitations all play a role in why your smart speaker sometimes gets it wrong. Understanding these constraints not only sets realistic expectations but also empowers you to use your device more effectively.
The Science Behind Voice Recognition
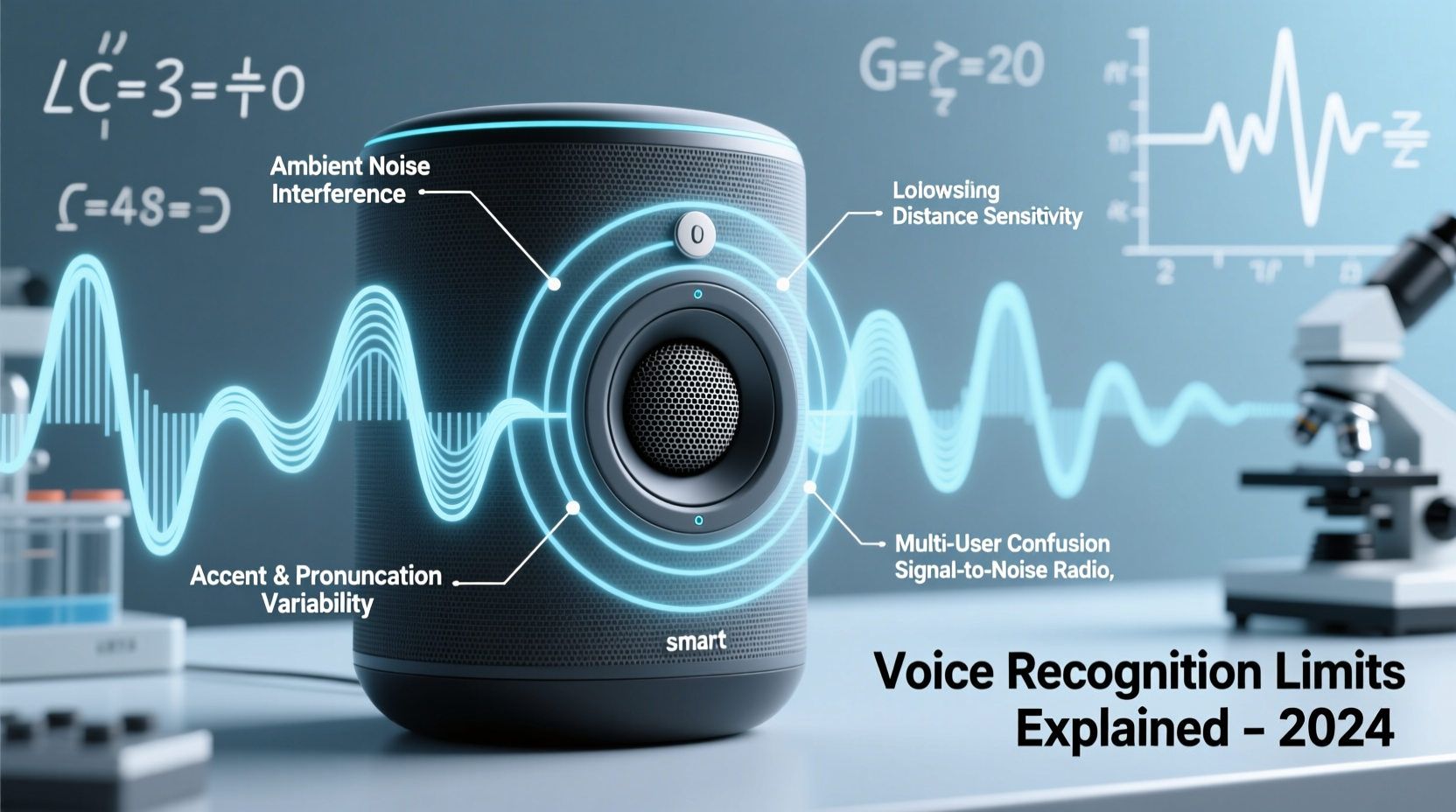
Voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri rely on automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. These systems convert spoken language into text by analyzing audio signals, identifying phonemes (the smallest units of sound), and matching them to known words using statistical models and deep learning algorithms.
The process involves several stages: wake-word detection, audio preprocessing, acoustic modeling, language modeling, and intent interpretation. Each stage introduces potential points of failure. For example, if the wake word isn't clearly detected due to ambient noise, the system never starts listening. Even after activation, poor microphone quality or overlapping sounds can distort input, leading to incorrect transcriptions.
Modern ASR systems are trained on vast datasets that include diverse accents, dialects, and speaking styles. However, no dataset is comprehensive enough to cover every variation in human speech. Regional inflections, fast talking, or unusual pronunciations may fall outside the model’s expected patterns, increasing error rates.
“Speech recognition works best when conditions are controlled—clear speech, quiet environment, standard vocabulary. Real life rarely meets those criteria.” — Dr. Lena Patel, NLP Researcher at MIT Media Lab
Common Reasons Smart Speakers Mishear Commands
No single factor explains all misunderstandings, but several recurring issues contribute significantly to misinterpretations.
Background Noise Interference
Household appliances, TVs, pets, and conversations create competing sound frequencies. Even low-level hums from refrigerators or fans can mask parts of your command. Smart speakers use beamforming microphones to focus on the direction of the speaker, but they can’t eliminate all interference, especially in large or echo-prone rooms.
Accent and Dialect Challenges
While major platforms support multiple languages and regional variants, performance varies. A British user asking for “tomato soup” might be understood instantly, while someone with a strong Scottish brogue saying “turn off the bedroom light” could trigger “play Taylor Swift live.” Training data often overrepresents certain demographics, leaving non-native speakers or those with less common accents at a disadvantage.
Command Ambiguity
Vague or poorly structured requests increase confusion. Saying “call him” assumes the assistant knows who “him” is. Similarly, “increase volume” without specifying which device leads to guesswork. The more context provided, the better the chances of accurate execution.
Hardware Limitations
Not all smart speakers are created equal. Budget models may have fewer microphones or lower-quality components, reducing their ability to capture clear audio. Distance from the device also matters—speaking from another room strains even high-end units.
Software and Language Model Gaps
Voice assistants interpret commands based on probabilistic language models. If a phrase is rare or structurally unusual, the system may substitute a more common alternative. For instance, “set timer for ten minutes” is straightforward, but “start countdown for 10 mins” might fail because the phrasing differs from typical training examples.
Do’s and Don’ts: Optimizing Voice Command Accuracy
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Use simple, direct language (\"Turn on the kitchen lights\") | Use slang or ambiguous terms (\"Make it brighter in here\") |
| Stand within 6–8 feet of the speaker | Shout or whisper—both distort natural speech patterns |
| Train your device with your voice (via voice profiles) | Assume it remembers preferences without setup |
| Update firmware regularly for improved recognition | Ignore software updates—they often include accuracy fixes |
| Minimize background noise before issuing commands | Give commands during loud TV scenes or appliance operation |
Step-by-Step Guide to Improving Voice Recognition Performance
Frustration with misheard commands doesn’t mean your device is faulty—it may just need optimization. Follow this sequence to enhance reliability:
- Run a voice calibration test. Use your assistant’s built-in voice training feature (e.g., Alexa’s \"Improve Alexa’s understanding\" or Google’s \"Voice Match\"). Speak sample phrases clearly so the system learns your tone, pitch, and pacing.
- Position the speaker correctly. Place it on a flat surface away from walls, corners, or fabric-heavy furniture that can absorb sound. Avoid placing it near sources of vibration or airflow like vents.
- Reduce ambient noise. Turn off unnecessary electronics, close windows near traffic, and pause music or videos before giving critical commands.
- Check microphone access settings. Ensure no physical mute switch is engaged and that privacy settings aren’t blocking audio input.
- Teach the assistant names and preferences. Register household members’ voices, define room names, and link smart devices properly so references like “turn off John’s lamp” are actionable.
- Use consistent phrasing. Stick to commands the system has successfully recognized before. Create routines with standardized triggers like “Good morning” instead of varying expressions daily.
- Monitor for firmware updates. Enable automatic updates or manually check monthly. New versions often refine speech models and fix bugs affecting accuracy.
Real-World Example: Maria’s Kitchen Frustration
Maria, a bilingual teacher in Miami, frequently used her Google Nest Mini to control lights and timers while cooking. She noticed it often misheard “preheat oven to 350” as “play fever tune 350,” especially when her blender was running. After testing different approaches, she discovered three key solutions: first, she moved the speaker from under a cabinet (where sound bounced unpredictably) to an open counter. Second, she activated Spanish-English bilingual mode in settings, allowing smoother transitions between languages. Third, she began pausing the blender before speaking. Within a week, command success rose from 60% to over 90%. Her experience highlights how small environmental and behavioral adjustments can dramatically improve performance.
Expert Tips to Work Around Voice Recognition Limits
Even with optimal conditions, some limitations remain inherent to current technology. Here’s how experts recommend navigating them:
- Leverage visual feedback. Pair your speaker with a smart display. Seeing transcribed commands lets you catch errors before execution.
- Create unique device names. Instead of generic labels like “lamp,” use “blue desk lamp” to reduce ambiguity among similar devices.
- Use routine-based triggers. Set up multi-step actions under simple commands like “I’m home” or “bedtime,” minimizing repeated individual instructions.
- Rephrase rather than repeat. If a command fails, try rewording it instead of repeating verbatim—“Set alarm for 7 AM” vs. “Wake me up at seven.”
Frequently Asked Questions
Can children’s voices confuse smart speakers?
Yes. Children’s higher-pitched voices and developing articulation patterns differ significantly from adult speech models. Most systems perform better with users aged 13 and older. Some platforms allow voice profiles for kids, improving accuracy through targeted training.
Why does my speaker understand my partner but not me?
This usually stems from differences in accent, speaking speed, or vocal frequency. It may also indicate that one person has completed voice enrollment while the other hasn’t. Enabling personalized responses and training the system with both voices typically resolves the imbalance.
Will future updates fix voice recognition issues permanently?
Ongoing improvements are likely, but perfection is unlikely due to the infinite variability of human speech and environments. Future systems may integrate contextual awareness—like recognizing ongoing activities or emotional tone—to reduce errors, but fundamental challenges will persist.
Conclusion: Embracing the Imperfections
Voice recognition technology has come remarkably far, yet it remains a tool shaped by physics, linguistics, and machine learning—not magic. Your smart speaker mishearing commands isn’t a flaw; it’s a reflection of the complex task it performs in real time. By understanding its limits—background noise sensitivity, linguistic biases, hardware constraints—you gain control over how to use it effectively. Small changes in placement, phrasing, and maintenance yield outsized improvements in reliability.
Rather than expecting flawless performance, treat your smart speaker as a responsive but imperfect collaborator. Train it, speak clearly, and design your interactions around its strengths. As AI continues evolving, today’s frustrations will gradually fade—but for now, the most powerful upgrade isn’t in the cloud. It’s in how you use your voice.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?