Streaming has transformed how we consume entertainment, but nothing disrupts the experience faster than a spinning buffering icon. Whether you're watching a movie, catching up on a series, or live-streaming sports, constant interruptions can be frustrating. Buffering doesn't always mean your internet is slow—it could stem from device limitations, network congestion, or even outdated firmware. Understanding the root cause is the first step toward fixing it. This guide breaks down why your TV buffers during streaming and provides practical, easy-to-implement solutions that anyone can apply.
Understanding How Streaming Works
Streaming relies on a continuous flow of data from the internet to your TV. When you press play, your device requests video data in small chunks. These chunks are temporarily stored (buffered) before being played. If the incoming data rate drops below what’s needed for playback—typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps)—the buffer empties, and the video pauses to refill.
Most high-definition (HD) streams require at least 5 Mbps, while 4K Ultra HD content demands 15–25 Mbps. However, bandwidth isn’t the only factor. Latency (delay in data transmission), packet loss, and Wi-Fi interference also affect performance. Even if your plan promises high speeds, real-world conditions often fall short, especially during peak usage hours.
“Buffering is rarely about raw speed alone. It’s about consistency and stability of the connection.” — James Lin, Network Performance Analyst at Broadband Insights Group
Common Causes of TV Buffering
Before attempting fixes, it helps to identify the source of the problem. Here are the most frequent culprits:
- Insufficient internet speed: Your plan may not support the resolution you’re trying to stream.
- Wi-Fi signal interference: Walls, appliances, and neighboring networks can weaken your signal.
- Network congestion: Multiple devices using the same connection simultaneously can strain bandwidth.
- Outdated hardware: Older routers or streaming devices may struggle with modern streaming demands.
- Server-side issues: Sometimes, the problem lies with the streaming service, not your setup.
- Background downloads: Automatic updates or cloud backups can consume bandwidth without your knowledge.
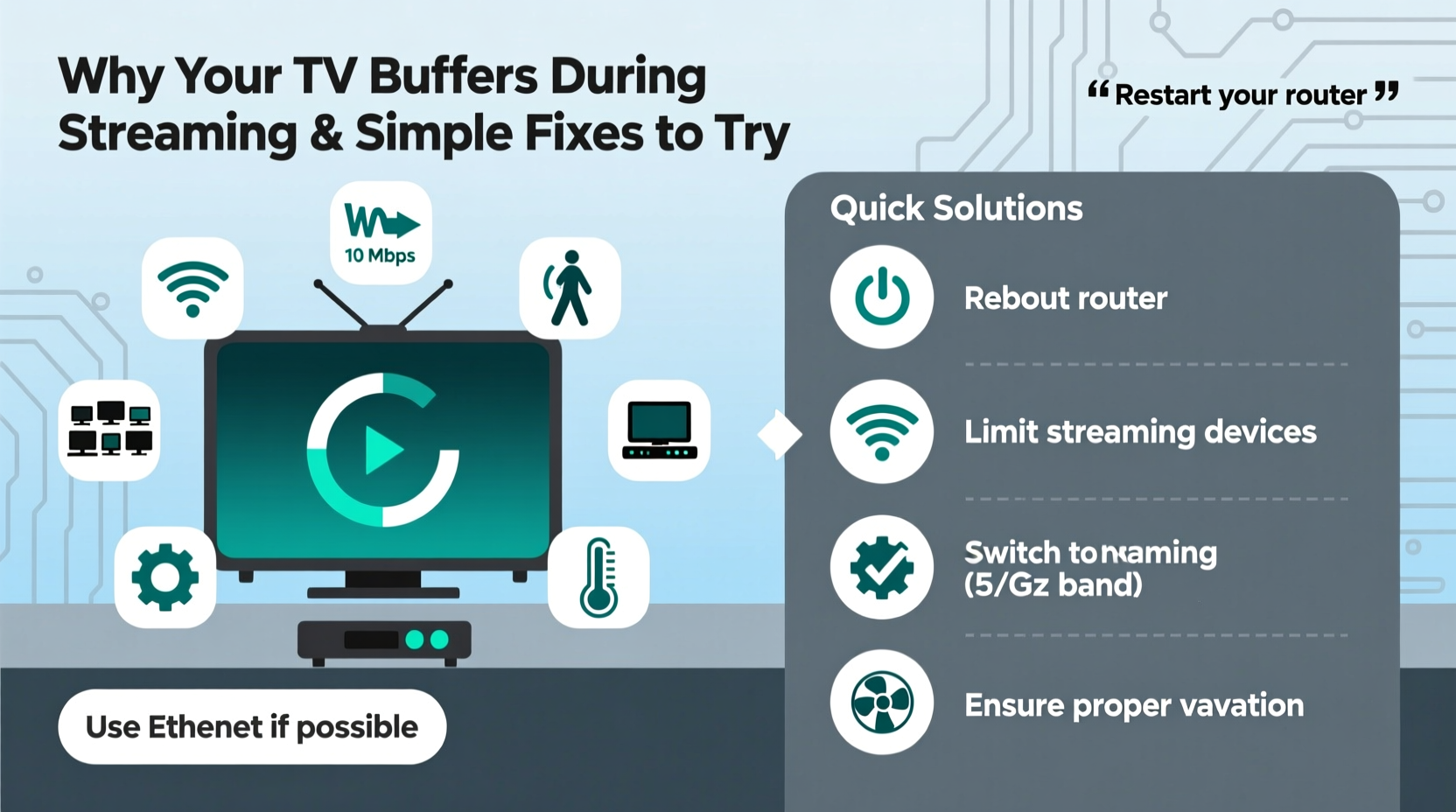
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix Buffering Issues
Solving buffering problems doesn’t require technical expertise. Follow this logical sequence to diagnose and resolve the issue efficiently.
- Test your internet speed using a tool like Speedtest.net or Fast.com. Perform the test on the same device experiencing buffering.
- Check the required bandwidth for your streaming service and quality setting (e.g., Netflix recommends 15 Mbps for 4K).
- Restart your router and streaming device. A simple reboot clears temporary glitches and resets connections.
- Move closer to your router or eliminate physical obstructions between your TV and the Wi-Fi source.
- Switch to a wired Ethernet connection if possible. Wired connections are more stable and faster than Wi-Fi.
- Reduce the number of active devices on your network. Pause downloads, stop other streams, or disconnect unused gadgets.
- Update firmware on your router, smart TV, or streaming stick. Manufacturers release updates to improve performance and fix bugs.
- Change your DNS settings to Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) for potentially faster domain resolution.
- Lower the video quality in your streaming app settings to reduce bandwidth demand.
- Contact your ISP if speeds are consistently below what you’re paying for.
When to Consider Upgrading Equipment
If you’ve followed the steps above and still face issues, your hardware may be the bottleneck. Routers older than three years often lack support for modern Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax). Similarly, early-generation streaming devices such as the Roku 1 or Fire Stick (first gen) have limited processing power and memory, making them prone to lag.
| Device Type | Recommended Minimum Standard | Action if Below Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Router | Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or newer | Upgrade to Wi-Fi 6 for better range and speed |
| Streaming Device | Roku 3+, Fire Stick 4K, or equivalent | Replace older models with current-gen devices |
| TV Ethernet Port | 100 Mbps or higher | Use a media bridge if no port exists |
| Internet Plan | 25+ Mbps for multiple users/4K | Upgrade plan if consistently below requirement |
Optimizing Your Home Network for Streaming
Your home network is the backbone of your streaming experience. Even with fast internet, poor network design can lead to inconsistent performance.
Start by positioning your router centrally, away from thick walls and electronic interference (like microwaves or cordless phones). Avoid placing it inside cabinets or behind large objects. If your TV is far from the router, consider using a Wi-Fi extender, mesh system, or powerline adapter to extend coverage.
Multipoint mesh systems like Google Nest Wifi or Eero provide seamless roaming and stronger signals across large homes. Unlike traditional extenders, which often create a separate network, mesh systems operate under one SSID, automatically connecting devices to the strongest node.
You can also prioritize streaming traffic using Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router. QoS allows you to assign higher priority to specific devices or applications, ensuring your TV gets the bandwidth it needs during peak usage times.
Real Example: Sarah’s Weekend Movie Night Fix
Sarah loved hosting family movie nights, but every weekend, her smart TV would buffer halfway through films. She had a 100 Mbps internet plan, so she assumed the connection was fine. After testing her speed on the TV, however, she discovered it was only receiving 12 Mbps over Wi-Fi.
Her router was in the basement, two floors away from the living room. She tried repositioning it but saw minimal improvement. Instead, she purchased a mesh Wi-Fi system and placed a satellite node near the TV. The next test showed 85 Mbps—more than enough for 4K streaming. Since then, her movie nights run smoothly without a single pause.
Do’s and Don’ts of Preventing Buffering
Avoid common mistakes that undermine your streaming quality. The following table outlines key behaviors to adopt—or avoid.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use Ethernet when possible | Place your router in a closet or basement corner |
| Limit simultaneous high-bandwidth activities | Ignore firmware updates for your devices |
| Set streaming quality manually during peak hours | Assume your ISP is always at fault |
| Reboot your network weekly | Stream 4K with less than 15 Mbps stable speed |
| Monitor connected devices via your router app | Use outdated streaming apps or devices |
Frequently Asked Questions
Does closing other apps on my smart TV help reduce buffering?
Yes. While smart TVs are designed to manage background processes, having multiple apps open—especially those accessing the internet—can consume memory and CPU resources. This indirectly affects streaming performance. Closing unused apps frees up system resources and may improve playback stability.
Can my neighbor’s Wi-Fi slow down my streaming?
Potentially, yes. In densely populated areas like apartments, many Wi-Fi networks operating on the same channel can cause interference. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (on a smartphone) to check for congested channels, then log into your router settings and switch to a less crowded one (e.g., channels 1, 6, or 11 on 2.4 GHz; non-overlapping channels on 5 GHz).
Is it better to use the built-in smart system or an external streaming device?
External devices like Roku, Apple TV, or Amazon Fire Stick often outperform built-in smart platforms. They receive more frequent updates, offer better interfaces, and typically have stronger Wi-Fi receivers. If your TV’s native apps are sluggish or frequently buffer, adding a dedicated streaming box can significantly improve performance.
Expert-Recommended Maintenance Checklist
Prevention is the best remedy. Use this checklist monthly to keep your streaming setup running smoothly:
- ✅ Reboot your router and modem
- ✅ Test internet speed on your TV or streaming device
- ✅ Check for firmware updates (router, TV, streaming stick)
- ✅ Review connected devices and remove unknown ones
- ✅ Clean dust from vents on your router and TV
- ✅ Adjust streaming quality based on current network load
- ✅ Verify Ethernet cables are securely connected (if used)
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Streaming Experience
Buffering doesn’t have to be a regular part of your viewing routine. With a clear understanding of how streaming works and access to straightforward troubleshooting methods, you can eliminate interruptions and enjoy seamless playback. Most fixes require no special tools—just a few minutes of your time and a willingness to test different approaches. Whether it’s upgrading your router, switching to Ethernet, or simply restarting your devices, each step brings you closer to frustration-free streaming.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?