If your internet crawls every evening just as you’re about to stream a movie or join a video call, you're not imagining it. Millions of households experience the same frustrating drop in WiFi performance after sunset. The good news: this isn’t random bad luck. It’s a predictable pattern with identifiable causes—and more importantly, solutions. Understanding why your WiFi slows down at night empowers you to take control of your home network and restore reliable speeds when you need them most.
What Causes Nighttime WiFi Slowdowns?
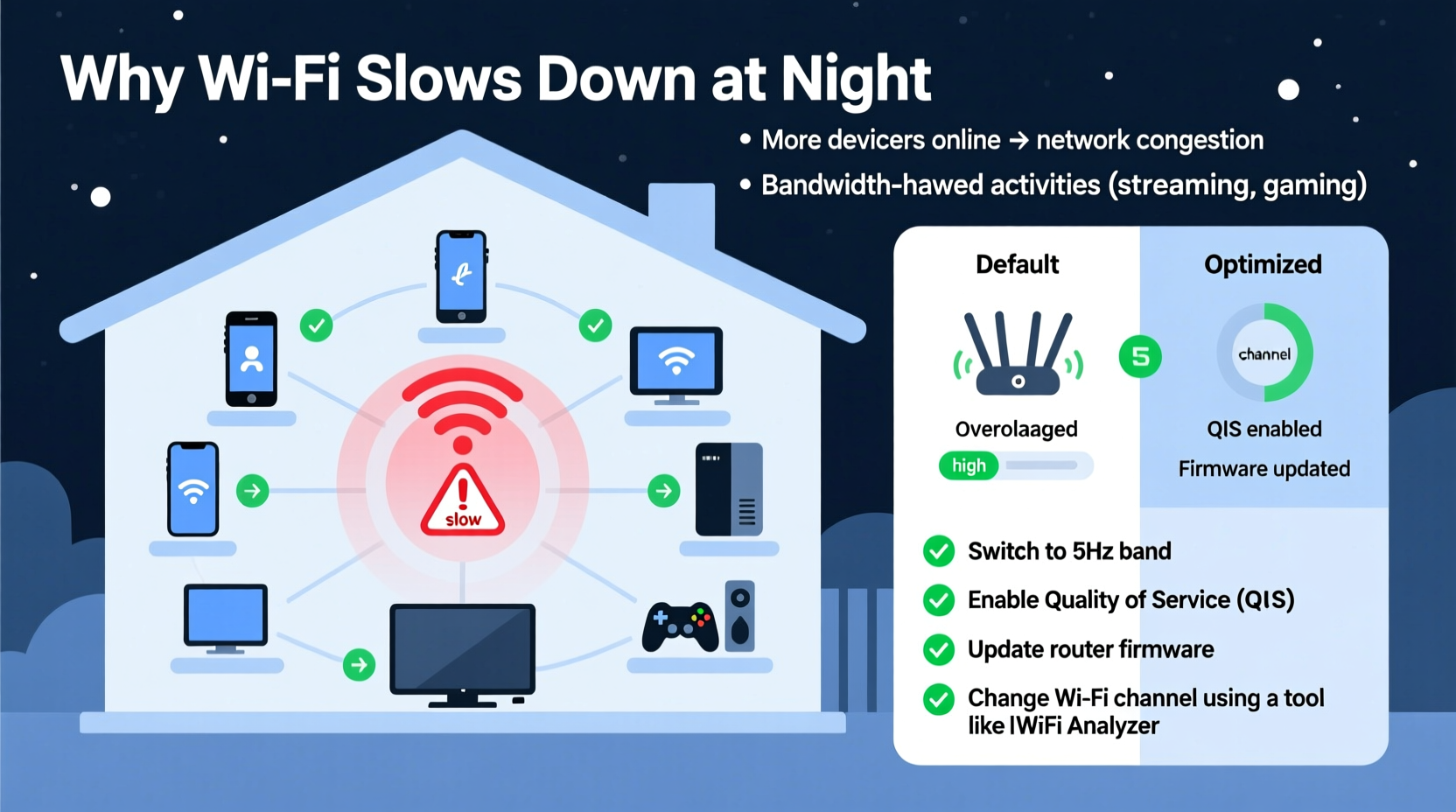
The root cause of evening slowdowns usually boils down to one word: congestion. During the day, many people are out of the house—commuting, working, or at school. Internet usage is spread across different networks and times. But by 6 PM, homes fill up. Families return, devices power on, and dozens of nearby routers begin competing for airspace. This surge in demand affects both your internal network and the broader infrastructure your ISP relies on.
WiFi operates over radio frequencies—mainly 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. These are shared resources, much like lanes on a highway. When too many vehicles (devices) try to use the same road at once, traffic slows. In urban and suburban areas, especially apartment complexes, dozens of neighboring networks can overlap on the same channels, creating interference that degrades signal quality and throughput.
Additionally, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) may be experiencing network-level congestion. ISPs often oversell bandwidth under the assumption that not everyone uses their full allocation simultaneously. But during peak hours—typically between 7 PM and 11 PM—this assumption breaks down. As thousands of users in your area stream HD video, play online games, or download large files, the local node serving your neighborhood becomes overloaded. Even if your router is flawless, you’re still limited by the pipe feeding it.
Common Sources of Home Network Congestion
Inside your own home, several factors compound the problem:
- Multiple active devices: Smart TVs, phones, tablets, gaming consoles, and smart home gadgets all draw bandwidth simultaneously.
- Background updates: Devices often schedule automatic updates overnight, consuming data without your awareness.
- Poor router placement: A router tucked behind furniture or near appliances like microwaves or cordless phones suffers from signal degradation.
- Aged or underpowered hardware: Older routers may struggle with modern demands, especially if they don't support newer standards like Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax).
Each of these issues worsens during peak hours, turning manageable delays into unwatchable buffering circles.
Router Tweaks to Improve Evening Performance
You can't control your neighbors’ routers or your ISP’s infrastructure, but you *can* optimize your own setup. Simple adjustments to your router settings can significantly reduce interference and improve responsiveness—even during busy evenings.
Change Your WiFi Channel
The 2.4 GHz band has only three non-overlapping channels: 1, 6, and 11. If your neighbors are also using channel 6 (the default on many routers), switching to channel 1 or 11 could reduce crosstalk. For the 5 GHz band, there are more options (up to 25 non-overlapping channels), so selecting a less crowded one improves performance.
To find the least congested channel:
- Download a WiFi analyzer app (like NetSpot, WiFi Analyzer for Android, or iStumbler for macOS).
- Scan nearby networks and note which channels are most saturated.
- Log into your router’s admin panel (usually via
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1). - Navigate to Wireless Settings and manually select a less-used channel.
Enable Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS allows you to prioritize certain devices or applications over others. For example, you can give streaming or video calls higher priority than background downloads or smart bulbs. Most modern routers include QoS in their firmware.
Steps to set up QoS:
- Access your router’s interface.
- Look for “QoS,” “Bandwidth Control,” or “Traffic Prioritization.”
- Assign priority levels based on device MAC address or application type (e.g., VoIP, gaming, video).
- Save settings and reboot if necessary.
Switch to the 5 GHz Band
If your devices support it, connect them to the 5 GHz network instead of 2.4 GHz. While 5 GHz has shorter range, it offers faster speeds and far less interference because fewer devices operate on it. Modern dual-band routers broadcast two separate networks—rename them clearly (e.g., “HomeWiFi_2G” and “HomeWiFi_5G”) so users know which to choose.
Update Firmware Regularly
Router manufacturers release firmware updates to fix bugs, patch security holes, and improve performance. An outdated router may lack optimizations needed for current traffic loads. Check your router brand’s website or admin panel for available updates—and install them quarterly.
Reboot Automatically
Routers can develop memory leaks or connection glitches over time. Scheduling a daily reboot (e.g., at 3 AM) clears temporary issues and refreshes connections. Many routers allow you to set this under \"Administration\" or \"Maintenance\" settings.
“Most home users never change their router settings after installation. A few minutes of configuration can double effective performance during peak hours.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Network Engineer at Broadband Insights Group
Do’s and Don’ts: Optimizing Your Home Network
| Action | Do | Don’t |
|---|---|---|
| Router Placement | Place centrally, elevated, away from walls and metal objects | Hide in a closet or basement |
| Channel Selection | Use a WiFi analyzer to pick the least crowded channel | Stick with default auto-setting blindly |
| Device Management | Disconnect unused devices; use guest networks wisely | Let ten devices stream 4K video simultaneously |
| Security | Use WPA3 encryption and strong passwords | Share your password freely with neighbors |
| Hardware | Upgrade to Wi-Fi 6 if supporting multiple high-demand devices | Use a 10-year-old router for a smart home |
Real-Life Example: The Johnson Family Fix
The Johnsons lived in a mid-rise apartment building in Chicago. Every evening, their Netflix streams would stutter, Zoom calls froze, and their son couldn’t game without lag. They assumed they needed a new plan—until they ran a WiFi scan using an Android app. The results showed 27 nearby networks, with 19 crammed onto channel 6 of the 2.4 GHz band. Their router was set to “auto,” which kept hopping into the most congested lane.
They logged into their router, switched to channel 1, enabled QoS to prioritize laptops and gaming consoles, and moved the router from under the TV stand to a shelf in the hallway. They also connected all capable devices to the 5 GHz network. After applying these changes, average speeds increased from 12 Mbps to 48 Mbps during peak hours. No service upgrade required—just smarter configuration.
Step-by-Step Guide to Nighttime WiFi Optimization
Follow this sequence to systematically improve your evening connectivity:
- Assess Current Performance: Run a speed test at night (use fast.com or speedtest.net). Note download/upload rates and latency.
- Analyze Surrounding Networks: Use a WiFi scanner app to identify channel congestion on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Adjust Router Channels: Log into your router and switch to a less crowded channel. Save and reboot.
- Enable QoS: Prioritize critical devices like work laptops or streaming boxes.
- Optimize Device Connections: Manually connect high-performance devices to 5 GHz. Disconnect idle ones.
- Schedule Reboots: Set your router to restart daily at off-peak hours.
- Monitor Results: Retest speeds over three consecutive nights. Adjust as needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can my ISP throttle my connection at night?
Some ISPs implement traffic shaping or throttling during peak hours, especially if you exceed a data cap. However, outright throttling solely based on time is less common in regions with net neutrality protections. If you suspect throttling, run tests with and without a VPN—if speeds improve with a VPN, your ISP may be inspecting and limiting specific types of traffic.
Should I upgrade my internet plan to fix nighttime slowdowns?
Not necessarily. Doubling your bandwidth won’t help if the issue is local interference or poor router settings. First, apply the tweaks outlined above. If problems persist even after optimization, then consider upgrading—especially if your household regularly uses more than four high-bandwidth devices.
Does distance from the router matter more at night?
No—but perceived signal strength can degrade due to increased interference. Two routers on the same channel within close proximity will interfere more when both are heavily used. A weak signal combined with congestion leads to frequent retransmissions, which slows everything down. That’s why central placement and proper channel selection are crucial.
When to Consider Hardware Upgrades
If you’ve optimized settings and still face slowdowns, it might be time for new hardware. Consider these upgrades:
- Wi-Fi 6 Router: Offers better handling of multiple devices, improved efficiency, and stronger security.
- Mesh WiFi System: Ideal for larger homes or multi-floor layouts. Extends coverage evenly and reduces dead zones.
- Wired Connections: For stationary devices like desktop PCs or smart TVs, use Ethernet cables. Wired connections are immune to radio interference and provide maximum stability.
Even the best router can’t overcome a severely undersized internet plan. If your household streams 4K content on three devices while someone works remotely and another plays online games, you likely need at least 200–300 Mbps. Assess total demand before blaming the router.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Connection
Nighttime WiFi slowdowns are a widespread but solvable issue. They stem from a mix of network congestion, suboptimal router settings, and increased household demand. By understanding the real causes—and making targeted adjustments—you can reclaim fast, stable internet when you need it most. You don’t need a technical degree or expensive gear. Just a few strategic changes to your router’s configuration can make a dramatic difference.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?