If your internet speeds are fine on most devices but painfully slow on just one—your phone, laptop, or tablet—it’s easy to assume the entire network is at fault. But when other gadgets stream, browse, and download without issue, the problem likely lies with that specific device or its connection to your network. This common yet frustrating scenario can stem from outdated hardware, software glitches, interference, or misconfigured settings. The good news: in most cases, it’s fixable without calling your ISP or buying new gear.
Understanding why one device lags while others perform well requires a methodical approach. Unlike whole-network slowdowns caused by bandwidth caps or router failures, isolated performance drops point to localized causes. By systematically eliminating potential culprits, you can restore full speed and avoid unnecessary frustration.
Common Causes of Single-Device Internet Slowness
Before diving into solutions, it helps to understand what might be behind the lag. A single slow device doesn’t necessarily reflect poor service—it could be due to internal limitations or environmental factors unique to that machine.
- Outdated Wi-Fi adapter: Older laptops or phones may support only legacy Wi-Fi standards (like 802.11n), limiting their maximum speed compared to newer devices using Wi-Fi 5 or Wi-Fi 6.
- Background apps consuming bandwidth: Software updates, cloud backups, or streaming services running in the background can hog your connection unnoticed.
- Distance and physical obstructions: If the device is far from the router or blocked by walls, appliances, or metal objects, signal strength weakens significantly.
- DNS or IP configuration issues: Incorrect network settings can delay data routing, causing sluggish browsing even with strong signal bars.
- Firmware or OS bugs: Outdated operating systems or firmware may introduce connectivity bugs that affect only certain devices.
- Router-level throttling or QoS settings: Some routers prioritize traffic based on device type or usage, unintentionally slowing down less-critical gadgets.
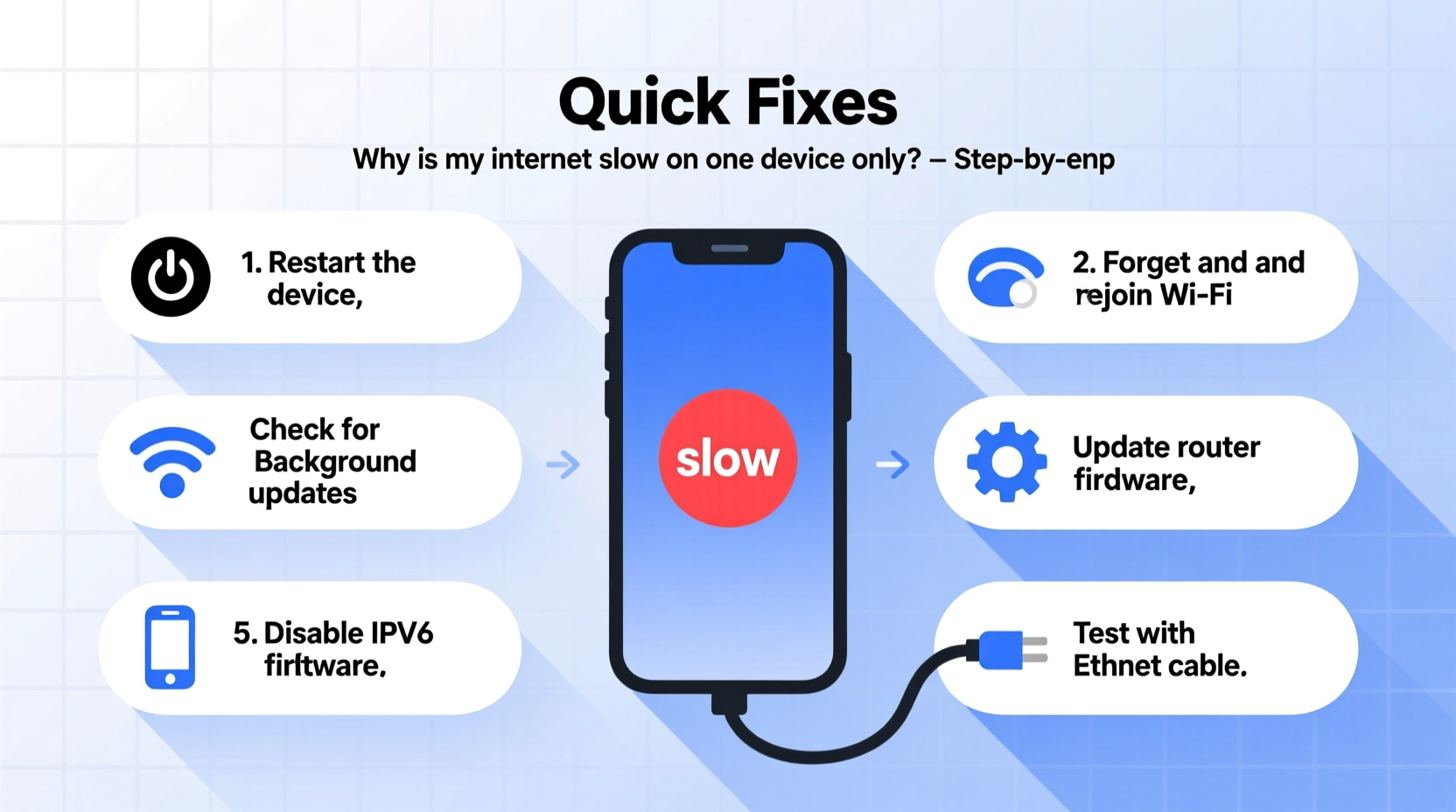
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Follow this structured sequence to identify and resolve the root cause efficiently. Start simple and escalate as needed.
- Reboot the device and router. A soft reset clears temporary glitches. Turn off the slow device and unplug your router for 30 seconds before powering back on.
- Check real-time speed on multiple devices. Use a speed test app (like Speedtest by Ookla) simultaneously across all devices to confirm the issue is isolated.
- Move closer to the router. Eliminate distance and obstacles as variables. If speed improves near the router, signal range or interference is likely the culprit.
- Forget and rejoin the Wi-Fi network. On the affected device, go to Wi-Fi settings, select your network, choose “Forget,” then reconnect by entering the password again. This refreshes the handshake process.
- Disable Bluetooth and other wireless functions temporarily. Interference from nearby 2.4 GHz devices (especially older Bluetooth peripherals) can degrade Wi-Fi performance.
- Check for active downloads or syncs. Review background processes—cloud storage apps like Dropbox or OneDrive, automatic OS updates, or streaming apps may be silently using bandwidth.
- Switch between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. If your router broadcasts both, try connecting the slow device to the other band. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds over short distances; 2.4 GHz travels farther but is more congested.
- Update device drivers or system software. Install pending OS updates. For Windows laptops, update the Wi-Fi adapter driver via Device Manager. On Macs, ensure macOS is current.
- Change DNS servers. Default ISP DNS can be slow. Switch to Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) in network settings.
- Factory reset network settings. As a last resort, reset network configurations on the device. Note: You’ll need to re-enter Wi-Fi passwords.
Do’s and Don’ts: Quick Reference Table
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Restart your router weekly to prevent memory leaks | Ignore firmware updates for your router or device |
| Use the 5 GHz band for high-bandwidth activities near the router | Place your router behind a TV or microwave (sources of interference) |
| Limit background apps syncing over Wi-Fi | Assume slow speed always means poor ISP service |
| Test speed with multiple tools (Speedtest, Fast.com, Google’s speed test) | Run speed tests while other large downloads are active |
| Keep devices updated with latest security patches | Leave old devices connected if they’re not in use—they still consume resources |
Real-World Example: The Case of the Lagging Laptop
Sarah noticed her Netflix streams constantly buffering on her 2017 MacBook Pro, despite her new iPhone showing full bars and smooth playback. Her roommate’s gaming console also had no issues. Frustrated, she almost upgraded her internet plan—until she decided to troubleshoot.
She started by testing speed on the MacBook near the router: results were still below 10 Mbps, while her phone showed over 80 Mbps. After forgetting the Wi-Fi network and reconnecting, no change occurred. Then she checked Activity Monitor and discovered her backup software was uploading years of photos to iCloud, consuming nearly all upload bandwidth and indirectly affecting download responsiveness.
After pausing the backup and switching her DNS to Cloudflare, her browsing and streaming returned to normal. The issue wasn’t the hardware or internet plan—it was background activity and suboptimal settings. Sarah scheduled future backups for late-night hours and set up DNS profiles for faster resolution.
“Many single-device slowdowns aren’t about raw speed—they’re about how bandwidth is being used behind the scenes. Monitoring background processes is often the fastest path to improvement.” — Marcus Lin, Network Systems Engineer at NetFlow Dynamics
Tips for Device-Specific Optimization
Different devices have different vulnerabilities. Tailor your approach based on what’s acting up.
Smartphones & Tablets
- Disable automatic app updates over Wi-Fi in settings unless necessary.
- Turn off Wi-Fi Assist (iOS) or Adaptive Wi-Fi (Android), which can interfere with stable connections.
- Ensure location services aren’t forcing constant network scanning, which drains battery and disrupts signal stability.
Laptops (Windows/Mac)
- On Windows, disable “Metered Connection” if enabled—it throttles background data.
- Check Power Management settings: some laptops reduce Wi-Fi adapter performance to save energy.
- Use Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac) to spot bandwidth-hungry processes.
Gaming Consoles & Smart TVs
- Enable Quality of Service (QoS) on your router to prioritize gaming or streaming traffic.
- Manually assign a static IP to the device to prevent DHCP delays during connection.
- Update firmware—older consoles may lack optimizations for modern routers.
Preventive Checklist for Long-Term Stability
To avoid recurring slowdowns, adopt these habits regularly:
- ✅ Reboot your router every 7–10 days to clear cache and prevent overheating.
- ✅ Update all device operating systems and router firmware monthly.
- ✅ Audit connected devices weekly—remove unknown or unused ones.
- ✅ Set up separate guest networks for IoT devices to reduce main network load.
- ✅ Position your router centrally, elevated, and away from electronics that emit interference.
- ✅ Use dual-band steering if available, allowing devices to automatically connect to the optimal frequency.
- ✅ Monitor bandwidth usage through your router’s admin panel or ISP portal.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my phone slow on Wi-Fi but fast on data?
This typically indicates a Wi-Fi-specific issue. Your cellular connection bypasses local network problems. Try forgetting the Wi-Fi network, restarting the phone, and checking for software updates. Also, verify that Wi-Fi Throttling or Low Data Mode isn’t enabled.
Can a virus or malware cause slow internet on one device?
Yes. Malware can run hidden processes that consume bandwidth, such as botnet activity or unauthorized file sharing. Run a full antivirus scan and check firewall logs for unusual outbound connections. Unexplained data spikes when the device is idle are a red flag.
Does my device’s age affect Wi-Fi speed?
Absolutely. Devices older than 4–5 years often support only Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), maxing out at 150–600 Mbps under ideal conditions—far below modern Wi-Fi 5/6 capabilities. Even with a gigabit connection, the bottleneck is the device’s hardware, not your service.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Connection
Slow internet on one device doesn’t have to derail your productivity or entertainment. With targeted troubleshooting, you can isolate the issue and apply precise fixes—often in under 15 minutes. Most problems aren’t rooted in faulty equipment or inadequate service, but in overlooked settings, interference, or background demands.
The key is staying proactive. Regular maintenance, smart configuration, and awareness of how your devices interact with your network can prevent slowdowns before they start. Don’t accept sluggish performance as inevitable. Diagnose, act, and reclaim the speed you’re paying for.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?