Itching in the genital area is a common but often uncomfortable experience that many people hesitate to discuss. While occasional irritation can happen to anyone, persistent or severe itching may signal an underlying condition requiring attention. Understanding the root causes and knowing how to respond appropriately can make a significant difference in both comfort and long-term health.
The skin in the genital region is sensitive and prone to irritation from various sources—ranging from hygiene habits to infections and skin disorders. Rather than ignoring discomfort or self-diagnosing incorrectly, it’s important to assess symptoms carefully and take informed steps toward relief.
Common Causes of Genital Itching
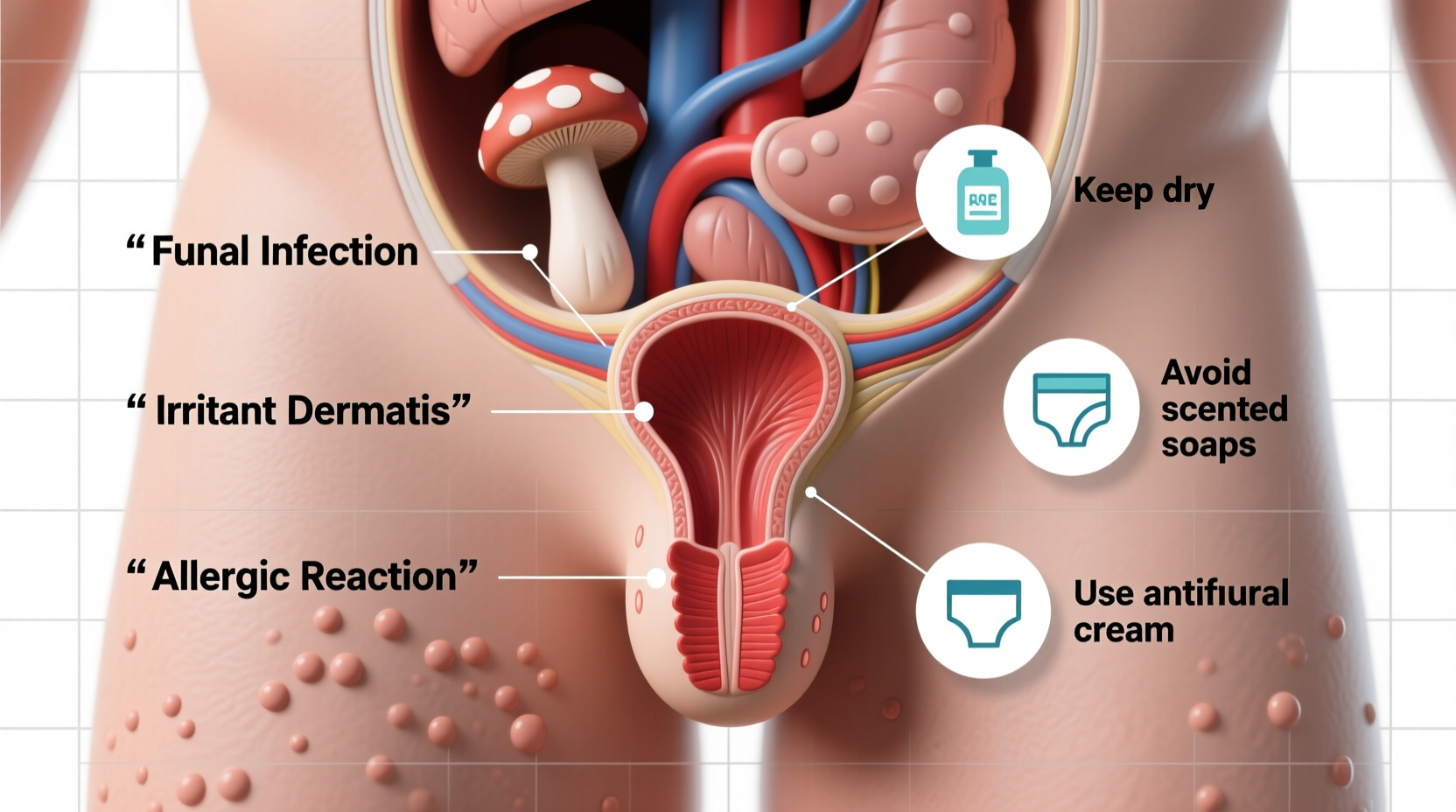
Genital itching doesn’t always indicate a serious problem, but identifying the cause is essential for proper treatment. Below are some of the most frequent contributors:
- Fungal Infections (Yeast Infections): Candida overgrowth is a leading cause, especially in women. Symptoms include intense itching, thick white discharge, redness, and swelling.
- Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): An imbalance of vaginal bacteria can lead to itching, along with a fishy odor and grayish discharge.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Herpes, trichomoniasis, and pubic lice (“crabs”) frequently cause genital itching. Herpes may also present with painful blisters.
- Skin Conditions: Eczema, psoriasis, or lichen sclerosus can affect the genital area, causing chronic itching and changes in skin texture.
- Irritants and Allergens: Soaps, detergents, scented toilet paper, laundry products, or synthetic underwear may trigger allergic reactions or contact dermatitis.
- Poor Hygiene or Excessive Cleaning: Both under-cleaning and over-washing (especially with harsh soaps) can disrupt natural pH balance and cause irritation.
- Hormonal Changes: Menopause or postpartum hormonal shifts can lead to vaginal dryness and thinning of tissues, resulting in itching.
- Sweat and Moisture Buildup: Wearing tight, non-breathable clothing during exercise or in hot weather traps moisture, creating an environment conducive to yeast and bacterial growth.
When to See a Doctor
While mild, temporary itching may resolve on its own, certain signs warrant medical evaluation:
- Itching persists beyond a few days despite home care
- Pain, burning, or soreness accompanies the itch
- Unusual discharge, odor, or visible sores appear
- You suspect an STI due to recent unprotected sex
- Itching recurs frequently (may indicate an undiagnosed condition)
“Persistent genital itching should never be ignored. It can be a clue to infections, hormonal imbalances, or skin diseases that are treatable when caught early.” — Dr. Lena Patel, OB-GYN Specialist
Effective Relief Tips and Home Care
For mild cases, several practical measures can soothe irritation and prevent worsening symptoms:
- Wear Breathable Underwear: Choose 100% cotton underwear that allows airflow and reduces moisture retention.
- Avoid Irritating Products: Switch to fragrance-free, hypoallergenic soap and unscented toilet paper. Avoid bubble baths and perfumed wipes.
- Keep the Area Dry: After bathing or swimming, gently pat the area dry. Consider changing out of wet workout clothes promptly.
- Apply Cold Compresses: A clean, cool cloth can reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from itching.
- Use Over-the-Counter Antifungals: If you suspect a yeast infection, antifungal creams like clotrimazole may help—but only use if symptoms clearly match a previous diagnosed episode.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat a Balanced Diet: Reducing sugar intake may help prevent yeast overgrowth, as sugar feeds Candida.
| Cause | Symptoms | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Yeast Infection | Thick discharge, redness, intense itch | Antifungal cream or suppository |
| Bacterial Vaginosis | Fishy odor, gray discharge, mild itch | See doctor for antibiotics |
| Pubic Lice | Severe nighttime itching, visible nits | Medicated shampoos and laundering fabrics |
| Contact Dermatitis | Red rash, burning after product use | Discontinue irritant, use soothing ointment |
| Hormonal Dryness | Dry, thin skin, discomfort during sex | Mild moisturizers or estrogen therapy (doctor-guided) |
Real-Life Example: Sarah’s Experience
Sarah, a 32-year-old teacher, began experiencing mild genital itching after switching to a new brand of scented laundry detergent. Initially, she assumed it was a yeast infection and used an over-the-counter antifungal, but her symptoms worsened. The skin became red and raw, especially at night.
After visiting her gynecologist, she learned she had developed contact dermatitis—an allergic reaction to the fragrance chemicals in the detergent. Her doctor advised switching to a fragrance-free brand and prescribed a short course of low-dose hydrocortisone cream. Within a week, her symptoms resolved completely.
Sarah’s case highlights the danger of self-treating without a proper diagnosis. What seemed like a routine yeast infection turned out to be a simple allergy that required a different approach.
Prevention Checklist
To minimize the risk of future episodes, follow this actionable checklist:
- ✅ Wear loose-fitting, cotton underwear daily
- ✅ Use only unscented, gentle cleansers for intimate areas
- ✅ Change out of wet swimsuits or workout clothes within 30 minutes
- ✅ Avoid douching or using vaginal sprays
- ✅ Practice safe sex and get regular STI screenings if sexually active
- ✅ Wash underwear in fragrance-free detergent
- ✅ Wipe front to back after using the toilet
- ✅ Stay hydrated and maintain balanced blood sugar levels
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause genital itching?
Indirectly, yes. Stress weakens the immune system, making you more susceptible to yeast infections and other conditions that cause itching. Additionally, stress can exacerbate existing skin disorders like eczema.
Is it safe to use hydrocortisone cream on genital itching?
Low-dose hydrocortisone cream (1%) can be used short-term for inflammatory skin conditions like dermatitis, but only under medical guidance. Long-term use can thin the delicate genital skin and worsen certain infections.
Why does itching get worse at night?
Nocturnal itching is common due to increased focus on bodily sensations when distractions fade. Also, body temperature rises slightly at night, which can intensify irritation. In cases of pubic lice or pinworms, nighttime movement of parasites increases itch perception.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Comfort and Health
Genital itching is more than just a nuisance—it’s a signal from your body that something may be off. Whether it’s due to an infection, an allergic reaction, or hormonal shifts, understanding the cause is the first step toward effective relief. Ignoring symptoms or repeatedly self-treating without success can delay proper care and potentially worsen the condition.
By adopting gentle hygiene practices, choosing non-irritating products, and seeking medical advice when needed, you can restore comfort and protect your intimate health. Don’t let embarrassment stand in the way of well-being. Listen to your body, act wisely, and prioritize accurate information over guesswork.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?