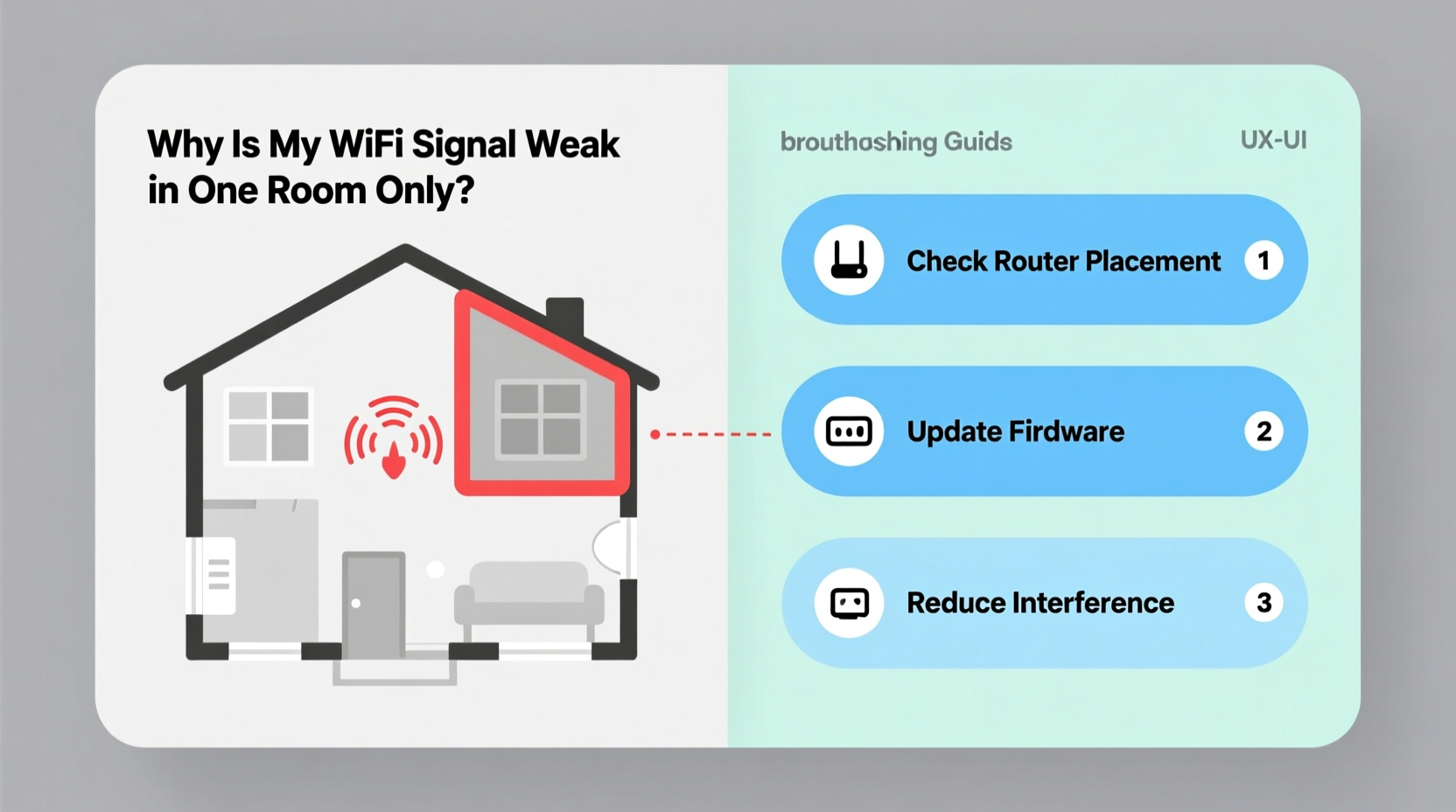
If you’ve noticed that your Wi-Fi works perfectly everywhere in your home except for one frustrating room, you're not alone. This is a common issue faced by homeowners and renters alike. The good news is that the problem is usually solvable with a few strategic adjustments. Unlike widespread connectivity issues, a single-room dead zone often stems from localized interference, structural barriers, or equipment limitations. Understanding the root causes and applying targeted fixes can restore strong, reliable internet where you need it most.
Understanding How Wi-Fi Travels Through Your Home
Wi-Fi signals are radio waves—specifically operating on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. These waves radiate outward from your router in all directions, but they don’t pass through obstacles like walls, furniture, or appliances without losing strength. The further the signal travels and the more materials it penetrates, the weaker it becomes. Different building materials absorb or reflect signals differently. For example:
- Concrete and brick walls are major signal blockers due to their density.
- Metal ducts, mirrors, and filing cabinets reflect signals, causing interference.
- Water pipes and aquariums absorb radio waves, weakening the signal.
- Thick wooden doors and plaster walls also degrade performance over distance.
The room with poor reception might simply be on the far side of several of these obstacles. But before assuming it's just “bad luck,” consider whether something specific about that room’s layout or contents is interfering with your network.
Common Causes of Room-Specific Wi-Fi Weakness
When only one room suffers from poor connectivity, the cause is rarely your internet plan or ISP. Instead, look at environmental and technical factors unique to that space. Here are the most frequent culprits:
- Distance from the router: If the room is at the edge of your home or on another floor, signal degradation is expected.
- Physical obstructions: A wall lined with metal plumbing, a refrigerator against the shared wall, or even a large bookshelf filled with books and electronics can block signals.
- Interference from other devices: Cordless phones, baby monitors, microwaves, and Bluetooth speakers emit electromagnetic noise that disrupts Wi-Fi.
- Router placement: Routers tucked in cabinets, basements, or behind TVs often have limited line-of-sight coverage.
- Outdated hardware: Older routers may lack modern beamforming or dual-band capabilities needed for consistent indoor coverage.
Each of these factors can act alone or combine to create a perfect storm of weak reception in just one area.
Real-World Example: The Basement Office Problem
Take Sarah, who converted her basement into a home office. Her living room upstairs had excellent Wi-Fi, but her laptop downstairs struggled to load emails. After testing, she discovered her router was placed high up near the ceiling on the opposite side of the house. The signal had to pass through two floors, concrete foundation walls, and a metal support beam. Even worse, her cordless phone base station sat right next to her desk, emitting constant interference on the 2.4 GHz band. By relocating the router and switching to a mesh system, she restored full-speed connectivity without rewiring her home.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing a Single-Room Dead Zone
Follow this systematic approach to diagnose and resolve your isolated connectivity issue. Each step builds on the previous one, helping you rule out simple causes before investing in new equipment.
- Confirm the issue is isolated: Use a smartphone or tablet to run a speed test in adjacent rooms. If only one room shows significantly slower speeds (especially below 10 Mbps), proceed.
- Check for active interference: Turn off nearby electronics like microwaves, gaming consoles, or wireless speakers. Re-test the connection. If performance improves, identify which device is causing the disruption.
- Reposition your router: Move the router closer to the affected room if possible. Avoid placing it near large metal objects, thick walls, or sources of moisture.
- Change your Wi-Fi channel: Log into your router settings and switch from auto-channel to a less congested one. On 2.4 GHz, use channels 1, 6, or 11; on 5 GHz, choose higher non-DFS channels like 36, 40, or 149.
- Upgrade firmware: Ensure your router is running the latest software version. Manufacturers often release updates that improve stability and range.
- Test with a wired connection: Plug a laptop directly into the router via Ethernet. If speeds are still slow, the issue may be with your ISP—not local Wi-Fi.
- Try a Wi-Fi extender or mesh node: Place a repeater halfway between the router and the weak room. For best results, use a mesh system like Google Nest Wi-Fi or Eero.
This process typically resolves over 80% of single-room connectivity problems within an hour.
Solutions Compared: Boosters vs. Mesh Systems vs. Powerline Adapters
When repositioning your router isn’t enough, you’ll need a signal extension solution. Not all options perform equally. Below is a comparison of the three most effective tools for tackling isolated dead zones.
| Solution Type | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi Extender/Repeater | Small homes, budget fixes | Inexpensive, easy setup | Cuts bandwidth in half, unreliable handoff |
| Mesh Wi-Fi System | Large or multi-floor homes | Seamless roaming, unified network, great coverage | Higher upfront cost |
| Powerline Adapter | Homes with stable electrical wiring | Uses existing outlets, avoids wireless interference | Performance varies by circuit quality, older wiring reduces speed |
For a single problematic room, a mesh node is often the best long-term investment. It integrates seamlessly with your existing network and provides full-speed, dual-band access without requiring complex configuration.
“Many people assume their internet is slow overall when the real issue is localized signal loss. A well-placed mesh node can eliminate dead zones without upgrading service.” — David Lin, Network Engineer at ConnectHome Solutions
Action Checklist: Restore Strong Wi-Fi in One Room
Use this checklist to methodically address your connectivity issue:
- ✅ Run speed tests in the weak room and compare them to other areas
- ✅ Identify physical barriers (walls, floors, appliances) between the router and the room
- ✅ Temporarily turn off nearby electronics to test for interference
- ✅ Reposition the router to a central, elevated location away from obstructions
- ✅ Log into your router and update firmware and Wi-Fi channel settings
- ✅ Consider switching to the 5 GHz band for faster speeds (if within range)
- ✅ Install a mesh Wi-Fi node or powerline adapter near the weak room
- ✅ Test again after each change to measure improvement
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my bedroom the only room with bad Wi-Fi?
Your bedroom may be far from the router, separated by multiple walls, or located near interfering devices like smart TVs, cordless phones, or charging stations. Additionally, some bedrooms have metal bed frames or mirrored wardrobes that reflect Wi-Fi signals, further weakening reception.
Can a mirror really weaken my Wi-Fi signal?
Yes. Mirrors contain a thin metallic backing that reflects radio waves. If your router signal must pass near or through a large mirror—especially a full-length one—it can scatter or deflect the signal, reducing strength in the target room.
Is it better to use a Wi-Fi extender or a mesh system?
A mesh system is generally superior. While extenders are cheaper, they halve available bandwidth and often create a separate network name (SSID), leading to connection drops. Mesh systems provide seamless coverage, automatic switching, and full-speed backhaul connections between nodes.
Final Recommendations and Long-Term Prevention
Fixing a single-room Wi-Fi issue doesn’t require expensive upgrades or technical expertise. Start with simple changes: reposition your router, eliminate interference, and verify your settings. Most problems stem from overlooked environmental factors rather than faulty equipment. Once resolved, maintain performance by keeping your network updated and avoiding clutter around key access points.
If you frequently work or stream in that room, consider making it a priority zone in your home network design. A dedicated mesh node or access point ensures consistent, high-speed connectivity for video calls, gaming, or streaming 4K content. Over time, proactive maintenance prevents future drop-offs and extends the life of your entire network.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?