If you’ve ever found yourself walking from room to room just to get a stable internet connection, you’re not alone. Many homeowners experience frustratingly slow or nonexistent WiFi in specific areas of their homes—especially basements, back bedrooms, or garages. The problem isn’t always your internet plan; it’s often about how the signal travels through your space. Understanding why this happens and what you can do about it makes all the difference between buffering endlessly and streaming smoothly.
WiFi signals are radio waves, and like any wave, they weaken over distance and struggle with obstacles. Walls, appliances, and even furniture can block or reflect the signal, creating dead zones. But before you assume you need a costly upgrade, consider that simple, low-cost fixes often solve the issue. With a few strategic adjustments and affordable tools, you can restore strong, reliable coverage throughout your home.
Why Your WiFi Slows Down in One Room
The first step to fixing slow WiFi is diagnosing the root cause. While it might seem random, signal degradation usually follows predictable patterns based on physics, layout, and interference.
- Distance from the router: WiFi strength diminishes with distance. The farther a room is from your router, especially if it’s on another floor or at the opposite end of the house, the weaker the signal becomes.
- Physical obstructions: Thick walls (especially concrete or brick), metal framing, mirrors, and large appliances absorb or reflect WiFi signals. A single thick wall can reduce signal strength by up to 50%.
- Interference from electronics: Devices like microwaves, cordless phones, baby monitors, and Bluetooth gadgets operate on the 2.4 GHz band—the same as most routers. When active, they create electromagnetic noise that disrupts your signal.
- Router placement: Routers tucked in cabinets, behind TVs, or near the floor emit signals unevenly. WiFi spreads outward and downward less effectively when obstructed or poorly positioned.
- Network congestion: If multiple devices are streaming, gaming, or downloading simultaneously, bandwidth gets divided. This can make one room feel slower, especially if it already has a weak signal.
“Signal strength drops exponentially with distance and obstacles. Even small changes in router placement can yield significant improvements.” — Dr. Linda Park, Network Engineer & IEEE Member
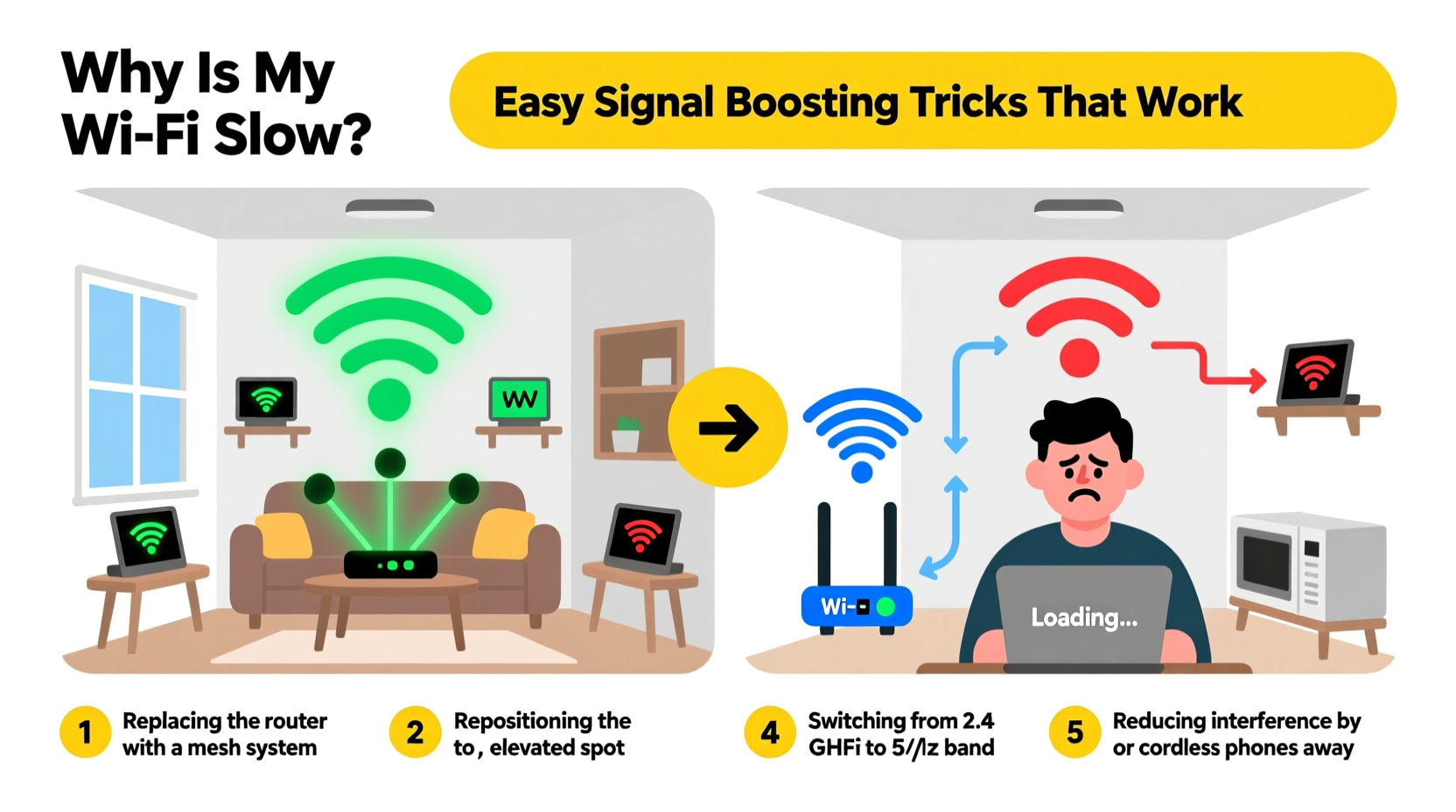
Easy Signal Boosting Tricks That Actually Work
You don’t need to be a network technician to improve your WiFi. Many effective solutions are simple, inexpensive, and require no permanent modifications.
1. Reposition Your Router for Optimal Coverage
The location of your router is the single most impactful factor in signal distribution. Central, elevated placement allows signals to radiate evenly in all directions.
Avoid placing it in basements, closets, or behind entertainment centers. These locations trap signals and increase latency. If possible, position the router’s antennas vertically—this enhances horizontal signal spread across floors.
2. Switch Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Bands
Most modern routers broadcast on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Each has trade-offs:
| Band | Speed | Range | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4 GHz | Slower (up to 150 Mbps) | Longer range, better wall penetration | Distant rooms, IoT devices |
| 5 GHz | Faster (up to 1 Gbps) | Shorter range, blocked easily | Streaming, gaming, nearby devices |
If the slow room is far from the router, connect devices to the 2.4 GHz network for better reach. For high-bandwidth activities in closer proximity, use 5 GHz. Some routers automatically switch bands—check settings to ensure optimal performance.
3. Use a WiFi Extender (With Caution)
WiFi extenders repeat your existing signal to expand coverage. They’re affordable and easy to install, but come with caveats. Poorly placed extenders can halve your speed because they relay data through the same channel.
For best results:
- Place the extender halfway between the router and the problem room.
- Ensure the extender receives a strong signal from the router (at least 75%).
- Use models with dual-band support and Ethernet backhaul if possible.
4. Upgrade to a Mesh WiFi System
For larger homes or complex layouts, mesh systems outperform traditional extenders. Instead of repeating a weakened signal, mesh nodes create a seamless, unified network with intelligent routing.
Nodes communicate with each other and dynamically choose the fastest path for data. You can place them throughout your home—living room, bedroom, basement—and enjoy consistent speeds everywhere.
5. Reduce Interference from Household Electronics
Electromagnetic interference is a silent WiFi killer. Microwaves, refrigerators, and even LED lights can disrupt your signal during operation.
To minimize interference:
- Keep the router at least 5–6 feet away from major appliances.
- Switch to wired peripherals (keyboard, mouse, speakers) when possible.
- Use the 5 GHz band for critical tasks—it’s less crowded than 2.4 GHz.
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose and Fix Slow WiFi
Follow this logical sequence to identify and resolve your connectivity issues:
- Test your current speed: Use a tool like Speedtest.net on a device in the slow room. Note download, upload, and ping values.
- Compare with a close device: Run the same test near the router. If speeds are significantly faster, the issue is likely signal loss.
- Check connected devices: Log into your router dashboard and see how many devices are using bandwidth. Disconnect unused ones.
- Change router channels: In your router settings, switch from auto-channel to a less congested one (e.g., Channel 1, 6, or 11 on 2.4 GHz).
- Reposition the router: Move it to a central, open location. Retest speeds after 10 minutes.
- Add a booster: Install a WiFi extender or mesh node in a strategic location. Re-run the speed test.
- Upgrade firmware: Check your router manufacturer’s website for updates that may improve performance.
This process typically resolves 80% of localized slowdowns without spending a dime.
Mini Case Study: Fixing the Basement Office
Mark, a freelance graphic designer, struggled with lagging video calls in his basement office. His main router was upstairs near the kitchen. Initial tests showed 2 Mbps download speed in the basement versus 120 Mbps upstairs.
He tried moving his laptop closer to the stairs—minimal improvement. After reading about interference, he noticed his router sat beside the microwave. He relocated the router to a shelf in the hallway and switched his basement devices to the 2.4 GHz network.
Next, he purchased a $60 mesh node and placed it on the first-floor landing. Speeds in the basement jumped to 85 Mbps—more than enough for HD conferencing and cloud backups. Total time invested: under two hours. Total cost: less than $70.
Mark’s experience shows that layered solutions—repositioning, band switching, and smart hardware—can transform a dead zone into a productive workspace.
Do’s and Don’ts of WiFi Optimization
| Do | Don't |
|---|---|
| Place the router centrally and elevated | Hide the router in a cabinet or closet |
| Use 2.4 GHz for distant rooms | Force 5 GHz in weak-signal areas |
| Update router firmware regularly | Ignore security or performance updates |
| Use mesh systems for large homes | Rely solely on cheap repeaters |
| Limit active devices during critical tasks | Allow unlimited downloads during Zoom meetings |
FAQ
Can walls really block WiFi?
Yes. Materials like concrete, brick, metal, and plaster lath significantly weaken WiFi signals. Even drywall with insulation reduces strength. Each wall can cut signal power by 25–75%, depending on thickness and composition.
Is a WiFi extender the same as a mesh system?
No. Extenders simply rebroadcast your signal, often reducing speed. Mesh systems use multiple synchronized nodes to create a single, intelligent network with better handoffs and load balancing.
Will restarting my router help with slow speeds?
Temporarily, yes. Restarting clears memory leaks, resets connections, and can resolve software glitches. However, it won’t fix structural issues like poor placement or outdated hardware.
Final Checklist: Quick Wins for Better WiFi
- ✅ Move the router to a central, open, elevated spot
- ✅ Switch problem-room devices to 2.4 GHz
- ✅ Restart the router weekly
- ✅ Update router firmware
- ✅ Test speed before and after changes
- ✅ Limit bandwidth-heavy tasks during important calls
- ✅ Install a mesh node if extenders fail
Take Control of Your Home Network Today
Slow WiFi in one room doesn’t have to be a permanent annoyance. With a clear understanding of signal behavior and a few practical adjustments, you can eliminate dead zones and enjoy consistent performance throughout your home. The solutions aren’t complicated or expensive—they just require attention to detail and a willingness to experiment.
Start with free fixes like repositioning your router and optimizing band usage. If those fall short, invest in a quality mesh system tailored to your home’s size and layout. Every household deserves reliable connectivity, regardless of architecture or device count.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?