In modern electrical systems, efficiency, reliability, and performance are paramount—especially in industrial and commercial environments. While single-phase power is sufficient for most homes and small appliances, larger operations demand a more robust solution. That’s where three-phase power comes in. More than just an upgrade, three-phase power is a fundamental shift in how electricity is delivered and used. It powers factories, data centers, large HVAC systems, and even electric vehicle charging stations. But what exactly makes it so effective? And why should businesses and engineers prioritize it over traditional single-phase setups?
This article breaks down the mechanics of three-phase power, explores its core advantages, and explains why it has become the gold standard for high-capacity electrical infrastructure.
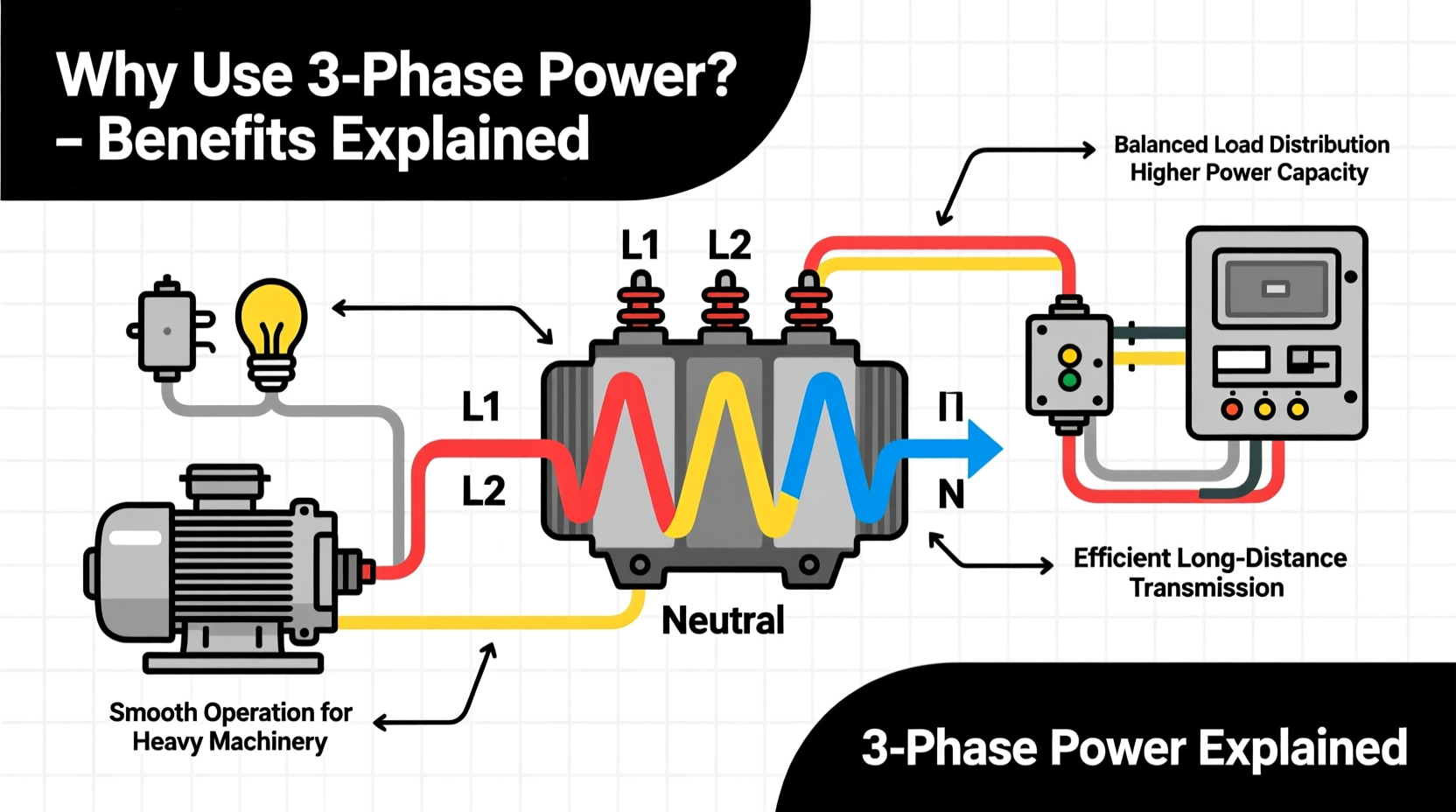
Understanding the Basics: What Is Three-Phase Power?
Electricity can be delivered in different configurations, with single-phase and three-phase being the two most common. Single-phase power uses one alternating current (AC) waveform, typically delivering 120V or 230V depending on the region. It’s well-suited for lighting, outlets, and household appliances.
Three-phase power, by contrast, uses three alternating currents that are offset by 120 degrees from each other. This means the voltage peaks occur in sequence across the three conductors, creating a smoother and more consistent delivery of energy. The result is a system that delivers constant power without the dips inherent in single-phase systems.
The three wires (often labeled L1, L2, and L3) carry these waveforms, and they can be connected in either a \"wye\" (Y) or \"delta\" (Δ) configuration. Wye connections include a neutral wire and are common in mixed-use systems, while delta configurations are often used in industrial motors where balanced loads dominate.
Key Benefits of Three-Phase Power
The advantages of three-phase power extend far beyond raw capacity. Its design offers tangible improvements in efficiency, cost, and equipment longevity.
- Higher Power Density: Three-phase systems deliver more power using less conductor material compared to single-phase. This means you get more work out of the same amount of copper or aluminum.
- Greater Efficiency: Motors and compressors running on three-phase power operate more smoothly and generate less heat, reducing energy waste and extending equipment life.
- Improved Load Balancing: With three phases, electrical loads can be distributed evenly, minimizing strain on any one line and reducing the risk of overloads.
- Smaller Equipment Footprint: Because three-phase motors don’t require start capacitors or complex starting mechanisms, they are physically smaller and simpler than their single-phase counterparts.
- Cost-Effective at Scale: While initial installation may require specialized equipment, the long-term savings in energy consumption and maintenance make three-phase power more economical for high-demand applications.
“Three-phase power isn’t just about delivering more electricity—it’s about delivering it smarter. The continuous power flow reduces mechanical stress on motors, which translates directly into lower maintenance costs.” — Dr. Alan Reeves, Electrical Systems Engineer
Applications Where Three-Phase Power Excels
Three-phase power is not always necessary, but it becomes indispensable in certain settings. Below are some real-world examples where its benefits are most pronounced.
Industrial Manufacturing
Factories rely on heavy machinery such as CNC machines, conveyor belts, and robotic arms—all of which require steady, high-torque motor operation. Three-phase power ensures smooth startup and consistent performance under load, reducing wear and downtime.
Commercial Buildings
Large office complexes, shopping malls, and hospitals use extensive HVAC systems, elevators, and backup generators. These systems benefit from the balanced load distribution and higher efficiency of three-phase circuits.
Data Centers
With thousands of servers running 24/7, data centers demand reliable, scalable power. Three-phase distribution allows operators to supply high-density racks efficiently while maintaining thermal and electrical stability.
Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
Fast-charging EV stations draw significant power. Three-phase connections enable faster charging times and reduce grid strain during peak usage.
Agricultural Operations
Farms using irrigation pumps, grain dryers, and refrigeration units often adopt three-phase power to handle seasonal spikes in energy demand.
Three-Phase vs. Single-Phase: A Practical Comparison
| Feature | Single-Phase Power | Three-Phase Power |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Stability | Peaks and dips with each cycle | Nearly constant due to overlapping phases |
| Power Delivery | Lower total power capacity | Up to √3 (1.73x) more power with same current |
| Motor Efficiency | Less efficient; needs starting aids | Self-starting, smoother operation |
| Conductor Material | Requires thicker wires for high loads | Uses less material for same power output |
| Typical Use Cases | Homes, small offices, lighting | Factories, data centers, large HVAC |
Mini Case Study: Upgrading a Small Factory
A mid-sized plastics manufacturing plant in Ohio operated on single-phase power for years. As production demands grew, the company added more injection molding machines. However, frequent voltage drops caused motors to stall, and energy bills climbed unexpectedly.
An electrical audit revealed that the single-phase system was overloaded and inefficiently distributing power. The plant upgraded to a three-phase supply, rewired critical machinery, and rebalanced the load across phases.
Results within six months included a 22% reduction in energy consumption, fewer equipment failures, and a 30% increase in production uptime. The initial investment paid for itself in under two years—proving that the right power infrastructure can transform operational performance.
How to Transition to Three-Phase Power: A Step-by-Step Guide
Moving from single-phase to three-phase power requires planning and coordination. Follow this sequence to ensure a smooth transition:
- Assess Your Power Needs: Audit all major equipment and calculate total load requirements. Identify which devices would benefit most from three-phase input.
- Consult a Licensed Electrician: Verify whether your local utility can supply three-phase power. Some rural areas may require upgrades to the grid connection.
- Design the System Layout: Plan panel placement, circuit routing, and grounding. Decide between wye or delta configurations based on load types.
- Upgrade Distribution Panels: Install a three-phase main panel and subpanels as needed. Ensure proper labeling and safety disconnects.
- Reconnect Critical Equipment: Begin with high-load machinery. Test phase balance and monitor voltage stability.
- Train Staff: Educate maintenance teams on the differences in servicing three-phase systems, including lockout/tagout procedures.
- Monitor Performance: Use power meters to track efficiency gains and identify imbalances early.
FAQ
Can I run three-phase equipment on single-phase power?
Not directly. However, phase converters or variable frequency drives (VFDs) can simulate three-phase output from a single-phase source. These solutions work but are less efficient and may shorten motor life if undersized.
Is three-phase power dangerous?
Like any high-voltage system, three-phase power requires proper handling. It carries higher voltages and fault currents, so only qualified personnel should install or service it. When properly maintained, it is as safe as any industrial electrical system.
Do homes ever use three-phase power?
Most residential homes use single-phase power. However, large homes with extensive HVAC systems, workshops, or private data/server rooms may opt for three-phase service, especially in regions where it’s readily available.
Conclusion: Power Smarter, Not Harder
Three-phase power isn’t just for factories and skyscrapers—it represents a smarter way to manage energy in any setting where performance and reliability matter. From smoother motor operation to reduced energy costs and better scalability, the benefits are clear and measurable.
Whether you're managing a growing business, designing a new facility, or simply trying to understand your building’s electrical backbone, recognizing the value of three-phase power is a step toward greater efficiency. Don’t let outdated infrastructure limit your potential. Evaluate your needs, consult with experts, and consider how upgrading your power system could unlock new levels of productivity.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?