
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(483 products available)




























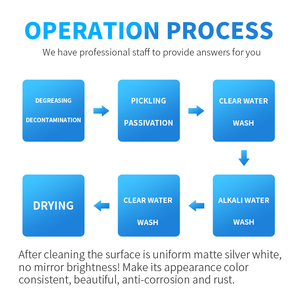






Passivation paste is produced in variegated types. They include:
Stainless Steel Passivation Paste
Usually, stainless steel passivation paste is tailored to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel surfaces. Typically, it is especially used in settings that warrant heightened resistance to oxidation and corrosion such as the medical, aerospace, and chemical processing industries. In addition, this paste, often consisting of citric acid or nitric acid, is designed to be applied selectively to areas that require passivation. More importantly, it promotes the formation of a protective chromium layer on the steel, thus, prolonging the lifespan of the material in adverse environments.
Aluminum Passivation Paste
Generally, aluminum passivation paste is developed to enhance the corrosion resistance of aluminum and its alloys. Mostly, it is utilized in such high-stakes environments as construction or marine applications. In addition, this paste, consisting of chromates or other passivating agents, aids in creating a protective film on the aluminum surface. Ideally, this film retards oxidation and keeps the metal from degrading. Also, the paste enables targeted application, thus, making it practical for treating specific areas of aluminum components exposed to the elements.
Copper Passivation Paste
Conventionally, copper passivation paste is designed to mitigate the corrosion that often affects copper and its alloys. Normally, it is applicable in such industries as electrical and electronics where copper is ubiquitously used. Ideally, this paste usually contains thiourea or other copper-specific inhibitors. Therefore, when applied, it helps in maintaining the integrity of the metal by preventing tarnish and corrosion. Also, the paste allows for improved longevity and electroconductivity by passivating the copper surface.
Iron and Carbon Steel Passivation Paste
This passivation paste for iron and carbon steel comes with a formulation that incorporates nitric acid and other passivating agents. Ideally, it is refined for use in environments where these metals are likely to corrode due to exposure to moisture or acidic substances. More importantly, the paste expedites the formation of a passive oxide layer on the metal surface. Thus, countering corrosion and safeguarding the material from degradation. Also, it is fit for use in such industries as construction and manufacturing where carbon steel is a staple structural component.
Passivation paste carries variegated features. They include:
Composition and Active Ingredients
Usually, passivation paste comes with a chemical composition that is tailored to promote the passivation process in metals. Normally, the key components included in the paste are organic acids such as citric acid or nitric acid. Conventionally, these acids play an indispensable role in removing surface contaminants like iron particles and rust. Also, they promote the formation of a passive oxide layer that reinvigorates corrosion resistance. Often, this layer is crucial for protecting metal surfaces in adverse environments. In addition, some passivation pastes incorporate corrosion inhibitors.
Selective Application
Normally, one of the distinguishing features of passivation pastes is their ability to enable selective application. Conventionally, they are applied to specific areas that require passivation. Such as welded joints, heat-affected zones (HAZ), or intricate components. Thus, this targeted approach usually affords enhanced protection for critical areas that are prone to corrosion. Nonetheless, it allows businesses to optimize resource utilization by limiting the use of chemicals to indispensable zones.
Gel-like Consistency
Conventionally, passivation paste is manufactured with a gel-like consistency. This formulation enables it to adhere effectively to vertical or overhead surfaces without dripping or running off. Also, this property ensures that the active ingredients stay in contact with the metal long enough to carry out the passivation reaction. Therefore, this promotes an even and effective treatment across irregularly shaped surfaces.
Easy Application and Removal
Commonly, passivation pastes are easy to apply using a paintbrush, applicator, or by hand. In addition, they allow for precise control during application. Normally, many products come with the feature of easy removal. Ideally, the processed metal is usually rinsed with water. This, in turn, halts the passivation reaction and leaves the surface clean and passivated. Moreover, this ease of use contributes to their integration into maintenance routines and on production lines.
Versatility among Metal Types
Typically, passivation pastes are fit for use on a variety of metals. Mostly, they include stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and carbon steel. Thus, their adaptability makes them invaluable for industries that work with multiple metal substrates. Besides, they come with a unified solution to mitigate corrosion, further enhancing their utility across divergent manufacturing contexts.
Passivation paste has variegated uses. They include:
Corrosion Resistance in Marine Applications
Passivation paste plays an indispensable role in safeguarding metal components in marine environments from the adverse effects of saltwater exposure. Normally, when applied to stainless steel, aluminum, and other susceptible metals, the paste assists in forming a protective oxide layer. Usually, this layer mitigates corrosion, which is critical for such industries as shipbuilding, offshore oil rigs, and marine equipment manufacturing. Besides, it prolongs the lifespan of critical components, making for reduced maintenance costs and enhanced operational reliability.
Enhanced Durability in the Construction Industry
The construction industry abundantly employs passivated metals for structural and architectural applications. Customarily, passivation paste reinforces corrosion resistance on steel and aluminum used in buildings, bridges, and other structures. Also, it comes with the ability to retard rust formation when exposed to moisture and atmospheric elements. In addition, this aid ensures that the integrity and safety of structures are maintained over the long term. Thus, this ultimately results in increased durability and reduced need for frequent repairs or replacements.
Protection of Plumbing Systems
Passivation paste is applicable to plumbing systems, where it mitigates corrosion in pipes and fittings made of stainless steel or copper. Ideally, the paste delineates the metal's ability to resist chemical exposure, such as water with varying pH levels or chemical contaminants. Moreover, this protection is indispensable for drinking water systems, chemical processing plants, and waste treatment facilities. Besides, it guarantees that plumbing infrastructure maintains purity and operates effectively without the risk of metal leaching into the water.
Preventing Electrochemical Corrosion in Electronics
Passivation paste's role in protecting metals extends to electronics, where it helps to prevent electrochemical corrosion. Normally, electronic components frequently incorporate copper or copper alloys. Nonetheless, passivating these metals with specialized pastes safeguards them from environmental exposure. Ideally, this preservation is pivotal for maintaining the electrical conductivity and overall functionality of components. They include connectors, circuit boards, and wiring. In addition, without passivation, these components would be vulnerable to oxidation. This would adversely impact the performance.
Maintenance of Increased Aesthetic Appeal
Besides functional protection, passivation pastes help maintain the aesthetic value of metal surfaces. Usually, upon exposure to elements, metals like stainless steel tarnish or develop unsightly stains. Even though this tarnishing is integral in applications where appearance matters. Such as architectural design or high-end marine gear, passivation treatments counter this tarnishing. Therefore, the metals retain their original luster. This comes in handy in meeting both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Here are some factors business owners should consider when purchasing passivating compounds.
Type of Metal
Manufacturers should start by settle for passivation pastes that are ideal for the specific metals undergoing passivation. For instance, stainless steel passivation pastes ought to composed of nitric acid or citric acid. Ideally, aluminum passivation pastes should also be constructed from nitric acid or chromic acid. Thus, pastes made of such acids will be effective when used on metals they are suitable for.
Contaminated surface conditions
Unfortunately, it is not possible to eliminate all impurities on the metal surface. Therefore, business owners should settle for passivation pastes that are suitable for their metal's contaminated surface conditions. If the surface is heavily contaminated with ferrous particles, manufacturers should get passivation pastes with higher ferrous ion recall to counter the contaminants.
Environmental suitability
Manufacturers should ensure the selected passivation paste is suitable for the environment in which the metals will operate. For instance, pastes with corrosion inhibitors should be constructed with a neutral pH and non-restricted use to ensure they don’t adversely affect the environment. More importantly, manufacturers should buy passivating compounds that adhere to their country’s environmental regulations and standards.
Type of application
To increase efficiency, business owners should settle for passivating compounds with the most suitable application method. It is worth noting that application methods will vary depending on the type of passivating paste. For instance, some can be sprayed, while in other cases, the only suitable application method is brushing. Moreover, there are pastes that can only be applied in places with controlled temperatures and humidity and those that are ideal for outdoor use. Therefore, business owners should ensure the applicability of the passivating paste they choose.
Post-treatment requirements
Business owners should consider the details of the post-treatment of the passivation paste. To make the cleaning process easier, manufacturers should purchase pastes that are easy to remove. Alternatively, for pastes that require washing, owners can settle for pastes with more robust adherence to improve passivation.
The key benefit of using stainless steel passivation paste is improved resistance to tarnishing and corrosion. When the passivation treatment is applied, it forms a protective oxide layer. This layer prevents contaminants from interfering with the metals.
Unfortunately, there are side effects that come with improper use of passivation paste. Ideally, when the paste is not rinsed properly, or when it is left on for an extended period without application, it can damage the metal surface. For this reason, always ensure proper application when dealing with passivation paste.
Yes, passivation paste can be eco-friendly. Usually, manufacturers use citric acid -a green alternative to nitric acid. In addition, citric acid is biodegradable and does not pose serious health risks like nitric acid. Moreover, the majority of passivating paste manufacturers are using eco-friendly compounds for passivation adhesives to adhere to the set regulations. Therefore, passivating compounds are safe for the environment.
No, all passivation pastes are not the same. Each type has distinct formulations that are ideal for specific metals. For instance, stainless steel passivation is ideal for nitric acid and citric acid, while aluminum passivation paste is constructed with chromic acid or nitric acid. Therefore, business owners should ensure they have the right paste for their metal substrate.