
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(39966 products available)

























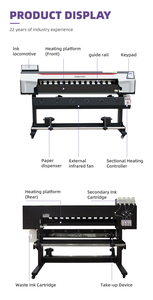
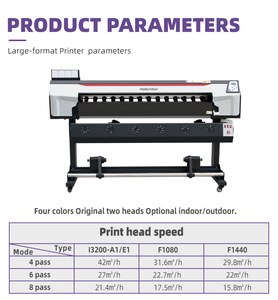









Software factories provide various services to clients. These services range from application development to infrastructure management.
Application Software Factory
An application software factory focuses on creating apps for different systems. These systems can include mobile devices, desktops, or the web. They often use a software development kit (SDK) to help build applications quickly. This tool ensures that apps work well on various platforms. Mobile app software factories, in particular, build apps for phones and tablets using tools like Swift for iOS or Android Studio for Android. They follow specific rules called guidelines to ensure apps meet platform requirements. They may also use cross-platform tools like Flutter or React Native. This choice allows them to develop apps for multiple platforms at once.
System Software Factory
The focus of system software factories is on creating important software that helps other programs run smoothly. For example, they might build operating systems, device drivers, or system utilities. These software forms a foundation for application software. People working in system software factories are usually skilled in low-level programming languages like C or assembly. They use these languages to interact closely with computer hardware. Their work ensures that all devices function properly and can support application software.
Web Software Factory
Web software factories are all about online software. They use tools and frameworks to build websites and web apps efficiently. Software factories in this category utilize programming frameworks such as Angular, React, or Django. These are to speed up the development process. They also follow best practices for creating scalable and secure web applications. This is particularly important in today’s connected world. With the growing urgency of cybersecurity, web software factories ensure that their products are safe from potential threats.
Game Software Factory
As noted earlier, game software factories focus on creating video games. This is done for consoles, PCs, and mobile devices. These software factories employ game designers, artists, and programmers who work together to produce engaging content. Moreover, game software factories help develop both the code and visuals of a game. They also use specialized tools known as game engines. These engines include Unity and Unreal Engine. They serve to simplify the development process and enable high-quality graphics and physics.
Embedded Software Factory
Embedded software factories create code for special devices. These are not regular computers but tools that run specific programs to perform tasks. For example, they might work on software for medical devices or cars. The code you see in these machines is different from regular computers. It’s made using languages like C or C++ to work on small, limited systems. The factories often use templates to make the coding quicker. They also have to test the code very carefully. This is done because even small bugs can cause serious issues in devices like heart monitors or car brakes.
Platform Software Factory
A platform software factory builds systems that let users create or share other programs. Think of it as a toolkit for developers. These factories make software like cloud storage spaces or tools for coding. They use languages like Java or Python, which are popular for these big systems. To speed things up, they usually customize existing platforms instead of starting from scratch. This type of software factory also often checks their code works well with different devices and stays secure against attacks.
Automation and Standardization
Software factories automate much of the development work. This reduces how much time and effort is needed to create software. They use templates and automated tools to make the process quicker and more consistent. For instance, when making a new application, developers do not have to start from scratch every time. The software factory provides pre-written code and templates for common tasks. This is called application programming interface (API) reusability. Think of it as a car factory using the same pieces to build many cars fast. These standard parts help developers create software quickly without many errors.
Collaboration and Teamwork
Software factories work well as a team. They bring different people together who each have special skills. For example, one person might be good at designing how the software looks. Another person writes the code to make it work. Software factories use tools that let everyone share and track their work easily. If someone makes a change, everyone else can see it right away. This teamwork leads to better software being made faster. Think of a doctor, engineer, and business person all working on health app together. Each helps make the app better.
Continuous Integration and Deployment
Software factories update and release software often. They do not wait weeks or months between releases. Thanks to special tools, new code can go live as soon as it is ready. This process is called continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD). It is like a factory assembly line where each step happens quickly. When developers finish a piece of work, it gets automatically tested. If it passes, the latest version of the software is published right away.
Focus on User-Centered Design
Consumers of any kind force software factories to focus on the people who will use the software. To understand how to serve these end users better, software factories create designs that consider the user's needs and experiences. They do this by researching how users interact with existing software. They then use this information to improve what they are offering. For example, if users struggle to find features, the design may change to be clearer and more user-friendly. By focusing on the user, software factories help create software that is easier and more pleasant to use. This encourages more users to buy and use the software.
Assess Development Capabilities
For a software factory to produce quality work, its clients have to consider its technical capabilities. This will ensure that the factory can handle the business’s desired projects. One way to do this is by looking at their development experience. This means checking what types of software they have made before. Businesses should also look at what programming languages and tools the factory prefers to use. It is wise to pick a factory that has worked on software similar to what the business needs, whether mobile apps, web tools, or custom programs. Additionally, it helps if the factory has experience with popular platforms like iOS, Android, or Windows. Ultimately, a software factory with the right development skills will be in a better position to create software that works well and looks good.
Evaluate Process and Methodology
Just like factories build things in an organized way, software factories have steps for building programs. Clients should look at how the factory manages work and what methods they use for designing and testing. Common approaches are Agile, which makes small updates regularly, or Waterfall, which plans everything upfront. It is helpful if the chosen software factory has a clear and proven process for creating and testing software. This ensures that potential projects are handled in an orderly way, reducing the chances of mistakes or delays.
Examine Quality Assurance Practices
It is vital that software works well and does not have errors. To ensure this, clients have to check how the software factory tests their work. They have to ask if there is a special group that focuses on finding problems before software gets to users. Clients should also find out if the factory has a clear way of fixing any issues that come up.
Review Past Work and Client Feedback
The work a software factory has done before can show how good they are. Clients should look at examples of past projects to see if they have made quality software. They should also read reviews or talk to other companies that have worked with the factory. If previous clients felt happy with the software and support, it means the factory would likely deliver good results.
Consider Communication and Collaboration
It is important for businesses to work well with the software factory. Good communication leads to better results. Clients should consider how the factory keeps in touch and if they are open to feedback. It is vital that there is a clear line of communication where either party is free to reach out through whichever means necessary.
Application Development
As mentioned earlier, a key job for software factories is making software applications. Imagine a business wanting a new mobile app for customers or a web program for staff. They hire a software factory to create these tools. The factory team uses development kits and standard designs to build the app or program quickly and reliably. They follow clear steps and check often to ensure the software meets requirements. This process helps firms get useful new tools without big delays.
Custom Software Solutions
Large companies or those with unique needs may require software not available off the shelf. They need something that is tailored to suit their operational needs. In these situations, a software factory builds custom solutions. For instance, a healthcare provider needs software to manage patient records. The software factory then creates software specifically for that client. This customized approach gives businesses solutions that fit their exact requirements. It helps improve how they operate daily.
Web Platform Creation
Popular practices in this day and age require organizations to establish web presence. They, therefore, need to create reliable and functional websites. In these cases, they hire software factories to help them create such platforms. Just like in the application development scenario above, web software factories are hired to create these online platforms. These factories then use web tools to create the platform quickly. They follow best practices like agile workflows. This ensures the new web platform is secure, scalable, and able to grow with the company.
Game Development
The gaming industry also relies heavily on software factories. These factories have the skilled personnel and resources to create complex games for consoles, PCs, and mobile devices. They use their own game development tools. As noted earlier, these factories use game engines to create the games. These games can be] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Quality and Standardization
Utilizing a software factory leads to enhanced quality and consistency in software products. This is mainly because software factories implement standardized processes and best practices across all projects. For a web application software factory, for instance, it could standardize certain frameworks or libraries for web development. This means every project would use the same tried-and-true tools. It then becomes easy to spot and fix issues across all applications. It also means app development for each new project becomes quicker as lessons learned from past projects are easily shared.
Cost-Effectiveness
A software factory can create applications at a lower cost compared to traditional development. This is mainly because of the ability to automate many parts of the coding and development process. For instance, in a mobile app software factory, creating interfaces or basic functionalities can often be automated. A smart system could have prebuilt "code blocks" ready to go. These would cut down the time developers spend doing repetitive tasks. The end result is developers can focus on writing custom code for clients that really need it.
Scalability
A software factory modelled on the assembly line approach allows resource numbers to be adjusted easily. As such, if demand spikes, more developers can quickly start joining the team. Perhaps a large gaming project is coming. A game software factory could then pull in extra programmers from their pool of developers. These developers would all get up to speed fast on the factory’s standard processes. This flexible approach helps to ensure deadlines get met without overworking the existing staff.
Focus on Core Business Activities
Utilizing a software factory enables organizations to delegate their software development tasks. They can therefore focus on their core competencies and business activities. For example, if a startup wants to build a new photo sharing mobile app, they don't have to hire a full-time team for this. They can turn to a mobile app software factory. The factory has developers and designers ready to handle the app project. This leaves the startup team free to concentrate on marketing strategy and customer support instead.
To pick a software factory, it is important to understand their skills first. One should check out projects they completed before to see if they match what is required. It is also vital to make sure the factory’s work steps fit the team’s style. The product quality must also be evaluated. Finally, one should look at how well the factory communicates and what feedback previous clients have given.
Software factories know that things sometimes change while building software. They use flexible methods like Agile that allow for adjustments. If requirements or designs shift, the factory can adapt quickly. Regular check-ins with the client ensure alignment throughout development.
Many software factories provide ongoing support after the initial release. This can include fixing issues, updating software for new systems, or adding features. It is important to clarify post-launch support terms before starting the project. This ensures long-term needs are covered.
Pricing structures can vary by software factory. Some charge by the hour for the time spent on the project. Others offer a fixed rate based on the scope of work. Additional costs may arise for managing the project or for support after delivery. It is advisable to review the pricing model in depth to understand the total potential cost.