
All categories
Featured selections
Trade Assurance
Buyer Central
Help Center
Get the app
Become a supplier

(39 products available)

















































Wireless ethernet radio modems have marked a crucial development in long-distance and reliable data communication.
Not only do these modems offer flexibility in installation and scalability of network systems, but they are also designed to enable operation in various challenging environments. These attributes make them ideal for sectors like construction, agriculture, and energy, where traditional wiring systems are highly impractical.
Point-to-Point Modems
As their name indicates, ,point-to-point modems establish a direct communication line between two fixed locations. These systems maintain a tight data exchange rate, making them suitable for transmitting large volumes of data across considerable distances—often up to several miles without any degradation in speed. The telecommunications sector heavily employs this type of modem to connect central hubs with remote transmission sites.
Point-to-Multipoint Modems
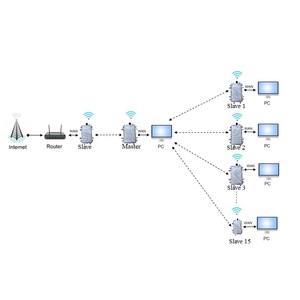
A point-to-multipoint system expands the communication capacity from one point to multiple secondary nodes. Such modulation is analogous to a tree structure, with a single root node communicating with various leaves. These modems find broad applications when a central data depot needs to communicate with several remote sensors or operational sites over short distances. Construction and mining industries frequently use them to interconnect machinery and field equipment.
Multipoint Modem
This modem type allows several remote units to communicate within the same range. They make network topologies easier by interconnecting various devices, such as ethernet over telephone modems, creating a comprehensive communication system.
Industrial Ethernet Modems
These are ruggedized modems. They operate under Industrial Ethernet standards, supporting IP-based communication systems. Created for extreme conditions, industrial modems support temperature variations, moisture, dust, and vibrations. Thus, they have become a reliable solution for industries like oil and gas, utilities, and manufacturing.
Long Range Modems
Designed for extensive communication spans, long-range radio modems can communicate over 10 miles. They achieve this distance by combining high power with narrowband modulation. These modems are commonly employed in remote and rural settings where traditional communication infrastructure is lacking. Examples may include monitoring pipelines, tracking vehicles, or connecting remote field offices.
Remote Monitoring
Wireless ethernet radio modems are indispensable in remote monitoring applications. They create dependable communication lines for monitoring systems located in different regions seamlessly. Industries like oil and gas, mining, and utilities widely use these modems to transmit real-time data, covering pressure, temperature, and equipment status. This enables proactive decision-making and minimizes the requirement to be physically present at monitoring sites.
SCADA Systems
They play a crucial role in developing and operating SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Systems. By connecting different field devices to centralized control centers, these modems facilitate the steady flow of operational data. In sectors such as water treatment and power distribution, wireless ethernet radio modems enable the automation and remote control of operational tasks, thus enhancing efficiency and reliability.
Grid and Infrastructure Management
In the electrical and telecom grids, these modems are used to connect various infrastructure components, including telephone ethernet modems, tower sites, substations, and other critical locations. They aid in real-time data transmission, assisting in managing, fault detection, maintenance scheduling, and optimizing resource use. It, therefore, enhances the performance and dependability of management systems.
These Cordless phone modems have revolutionized how industries carry out their communication tasks. industries like construction rely heavily on these modems to maintain communication between work sites, enhance operational efficiency, and reduce the time spent on data transmission. With their rugged design and long-range capabilities, wireless ethernet radio modems have become an integral part of managing wide-ranging industrial activities.
Networking and Connectivity
They are commonly used in the industrial domain, especially with expanding demands for networking and connectivity. WLAN radio modems establish stable connections between devices and systems, promoting data sharing and communication across multiple operational and design areas. They are paramount in integrating the IoT (Internet of Things) into industrial ecosystems, enabling the deployment of smart devices and applications that monitor and enhance industrial activities in real time.
Frequency Bands
Radio modems are specified by the frequency bands they operate on. Common bands include 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and sub-6 GHz ranges. Each band has advantages concerning range, bandwidth, and susceptibility to interference. The choice of frequency band depends heavily on the particular application and environmental conditions.
Transmission Power
The transmission power directly influences the range of these modems. Higher transmission power can cover longer distances, but it may consume more power. Most wireless ethernet radio modems are designed to operate indifferently. They can adjust their transmission power to suit their operating conditions.
Data Rate
It refers to the rate of data that can be transmitted by these radio modems. Most of the wireless ethernet radio modems have data rates ranging from a few kilobits per second (Kbps) to several megabits per second (Mbps). It, therefore, depends on the model. The required data rate for an application depends on the data needs of the user, such as video streaming or simple text.
Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint Communication
Radio modems can perform the function of point-to-point and point-to-multipoint communication. They are versatile communication devices that support both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. This versatility allows them to be used in various applications. While point-to-point is suitable for direct communication between two locations, point-to-multipoint effortlessly connects a central hub to several remote nodes.
Ethernet Interface
Modems connect to existing network infrastructures using standard Ethernet ports. It allows easy integration into current industrial networking systems.
Robust and Weatherproof Design
The wireless ethernet radio modems are designed to operate seamlessly under extreme industrial conditions. Be it high or low temperatures, moisture, or dust; these radio modems have weatherproof designs that protect them from thermal, water, and dust damage.
Built-in Security Features
Security is paramount when it comes to industrial communication. Most of these radio modems come with encryption protocols and secure access controls to ensure the transmitted data is kept confidential.
Range
The range is one of the most important considerations to take into account. These modems are quite important because they help create connections over vast distances while also providing reliable data transmission. Therefore, when selecting a modem, it is important to determine the maximum distance between the transmitter and the receiver. Doing this will help select a modem that meets the desired communication range.
Data Rate
It is important to consider the required data rate for the application in mind. Wireless ethernet radio modems come in handy when transmitting basic control signals. They transmit from a few kilobits per second to several megabits per second. Higher data rates are often critical for bandwidth-intensive applications like video surveillance. However, if it is for simple telemetry, lower data rates would suffice.
Environmental Conditions
Since most of these radio modems operate outdoors, it is important to consider their ability to withstand various environmental conditions. These conditions include temperature variations, humidity, dust, and even mechanical vibrations. It ensures that the chosen modem is weatherproof and has a robust design with a good operating temperature range to ensure reliability in outdoor operations.
Frequency Band
These bands range from 900 MHz to 5 GHz, including several subcategories. The frequency band selected will have a big impact on the range and ability to penetrate obstacles like buildings and trees. Lower frequencies offer better range and penetration. On the other hand, higher frequencies tend to provide wider bandwidth and data rates. But they also reduce range and penetration capability.
Assess Application Needs
To select the optimal modem, one needs to assess the specific communication requirements and limitations of the intended applications. Such limitations include range, data rate, and environmental conditions. It will help the user narrow down the key specifications needed to support operational efficiency.
Compare Different Models
After determining the needs, it's worthwhile to compare several modem types. Pay particular attention to differences in range, data rates, and frequency bands. This thorough comparison will ensure that one has a comprehensive understanding of the available options. It will make the selection process more straightforward.
Consider Scalability
If the application is likely to evolve over time, one should consider the scalability of the chosen modem. Can it support additional nodes or expand the communication range? Selecting a scalable solution now will save complications in the future.
Review Industry Standards
Selecting a modem compliant with industry standards will ensure easier integration into the current network infrastructure. Moreover, it helps provide interoperability with other communication devices.
A1: These modems communicate long distances wirelessly in industrial settings. They connect remote equipment to central operations for monitoring and control.
A2: The range varies by model and environment, with some reaching several miles. Those using high-frequency bands offer better coverage in challenging terrains.
A3: These radio modems are built to resist extreme temperatures, moisture, and dust, making them suitable for outdoor operations in different climates.
A4: Most of these industrial radio modems are powered through standard electrical outlets. Others offer power-over-ethernet options.
A5: Yes, encryption and secure access protocols protect the data. This ensures that only authorized users can access the transmitted information.