In an age where visual information dominates online communication, the ability to understand what you see in a photo is invaluable. Whether you’ve come across an unfamiliar plant, a mysterious artwork, or a product worn by someone in a viral post, Google Reverse Image Search offers a fast, reliable way to uncover answers. This powerful tool allows you to upload or link an image and find related content, origins, and context—often within seconds. Mastering it can save time, prevent misinformation, and unlock insights that text-based searches simply can’t provide.
Why Reverse Image Search Matters Today
Visual data floods our digital lives. From social media posts to news articles, images often carry critical information—but not always accurate captions. Misinformation spreads when photos are misattributed or taken out of context. Reverse image search acts as a fact-checking mechanism, helping users trace the source of an image, verify authenticity, and gather background details.
Photographers, researchers, journalists, and casual internet users alike benefit from this functionality. It helps detect plagiarism, identify fashion items, locate higher-resolution versions, or even discover if a profile picture on a dating app is fake. The technology behind it analyzes pixels, patterns, colors, and shapes to match against billions of indexed images across the web.
“Reverse image search is one of the most underutilized tools for digital literacy. It empowers users to question and verify before believing.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Digital Forensics Researcher at MIT Media Lab
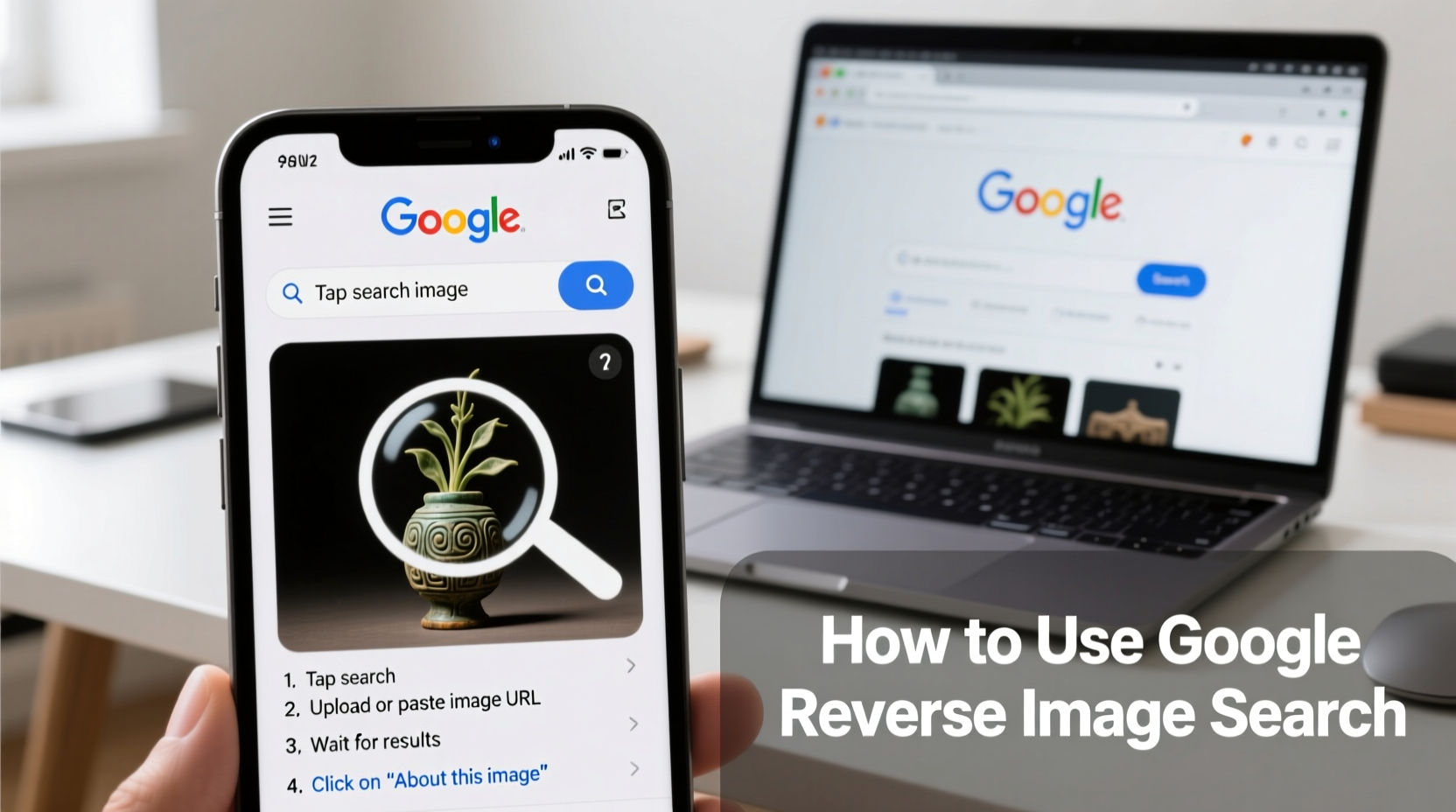
Step-by-Step: How to Use Google Reverse Image Search
Using Google’s reverse image search is simple whether you're on desktop or mobile. Follow these steps for optimal results:
- Open Google Images (images.google.com) in your browser.
- Click the camera icon in the search bar. This opens the reverse image search interface.
- Choose your method:
- Upload an image from your device.
- Paste an image URL if the photo is already online.
- Wait for Google to process and return visually similar results, related pages, and potential sources.
- Analyze the results: Look for original sources, metadata, usage history, and contextual websites.
Mobile Users: Use the Google App
On smartphones, open the Google app or Chrome browser, navigate to Google Images, and tap the camera icon in the search bar. You can then choose a photo from your gallery or take a new one using your camera. Google Lens integration enhances recognition by identifying objects in real time through your phone’s camera feed.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Reverse image search isn’t just for curiosity—it has tangible uses across different scenarios. Consider this real-life example:
Mini Case Study: Identifying a Fake Social Media Profile
Sarah noticed a connection request from someone with a strikingly attractive profile picture on a professional networking site. Something felt off. She saved the image, used Google Reverse Image Search, and discovered the same photo was linked to multiple accounts across travel blogs, modeling portfolios, and even dating sites. A quick check revealed it belonged to a stock model, not a real person. Thanks to reverse search, Sarah avoided a potential scam.
This case illustrates how reverse image search protects against identity fraud and catfishing—a growing concern in online interactions.
Maximizing Accuracy: Tips and Best Practices
To get the most accurate results, follow these proven strategies:
- Use high-quality images: Blurry or low-resolution photos reduce matching precision.
- Crop strategically: Focus on the key element—like a logo, face, or object—rather than including large irrelevant backgrounds.
- Try multiple formats: If the uploaded image fails, convert it to JPG or PNG and retry.
- Check date filters: In results, use “Tools” > “Any time” to filter by recency and track when the image first appeared online.
- Look beyond the first page: Sometimes relevant matches appear in later result sets or within obscure forums and archives.
Common Use Cases and What You Can Identify
Google Reverse Image Search excels in diverse identification tasks. Here’s a breakdown of common applications:
| Use Case | What You Can Discover | Best Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Unknown Plant or Animal | Species name, habitat, care tips | Crop close-up; pair with “plant ID” or “wildlife species” keywords |
| Fashion Item | Brand, price, where to buy | Search cropped image; check shopping tabs in results |
| Artwork or Painting | Artist, title, museum location, auction history | Include frame edges if visible; search across art databases linked in results |
| Screenshot Verification | Original source, date of creation, context | Use “Visually similar images” to trace earliest appearance |
| Product Identification | Model number, reviews, alternatives | Focus on unique design features or labels |
Do’s and Don’ts of Reverse Image Searching
To avoid frustration and improve outcomes, adhere to these guidelines:
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| ✔ Crop to the subject of interest | ✖ Upload heavily edited or filtered images |
| ✔ Verify findings across multiple sources | ✖ Assume the top result is always correct |
| ✔ Use incognito mode to avoid personalized results skewing accuracy | ✖ Share sensitive personal images publicly during upload |
| ✔ Save and organize useful matches for future reference | ✖ Rely solely on automated results without human judgment |
FAQ: Common Questions About Google Reverse Image Search
Can I use reverse image search on private or password-protected images?
No. Google can only analyze images accessible on the public web or those you upload directly. If an image resides behind a login wall (e.g., private social media), it won’t be indexed unless shared elsewhere publicly.
Is it legal to use someone else’s photo for reverse search?
Yes, as long as you’re using it for research, verification, or personal use. However, downloading and redistributing copyrighted images without permission may violate laws. Always respect intellectual property rights.
Why does Google sometimes return no useful results?
This happens when the image is too obscure, highly edited, or not yet indexed. Try enhancing contrast, cropping tightly, or converting to a different file format. Also, consider that very recent or niche images may not appear in search results immediately.
Checklist: Your Reverse Image Search Action Plan
Before finishing your next reverse image search session, ensure you’ve completed these steps:
- ✅ Saved the image to your device (if needed)
- ✅ Cropped or enhanced the image for clarity
- ✅ Uploaded via Google Images or pasted the URL
- ✅ Reviewed both “Pages that include the image” and “Visually similar images”
- ✅ Checked publication dates and domains for credibility
- ✅ Cross-referenced findings with external sources
- ✅ Documented the origin and purpose of the image
Conclusion: Take Control of Visual Information
Google Reverse Image Search transforms how we interact with digital content. It turns passive viewers into active investigators, capable of verifying truth, discovering knowledge, and protecting themselves from deception. Whether you're tracking down a vintage poster, confirming a news photo’s legitimacy, or shopping based on a celebrity look, this tool puts powerful intelligence at your fingertips.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?