Understanding how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is more than just a math exercise—it’s a daily necessity for travelers, cooks, scientists, healthcare workers, and weather watchers. While many rely on digital tools, knowing how to manually convert temperatures builds confidence, improves accuracy, and enhances comprehension of thermal data across contexts. This guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, offers real-world applications, and equips you with tools to master temperature conversion effortlessly.
The Science Behind Temperature Scales
Celsius and Fahrenheit are two of the most widely used temperature scales in the world. Developed in the 18th century, each was designed with different reference points and purposes in mind.
Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, introduced his scale in 1742, setting 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as its boiling point at sea level. This decimal-based system aligns with the metric system, making it intuitive and widely adopted across scientific communities and most countries.
In contrast, Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, created his scale earlier in 1724. He set 32°F as the freezing point of water and 212°F as its boiling point. His original benchmarks included a brine solution’s freezing point (0°F) and human body temperature (~96°F, later adjusted to 98.6°F). Though less intuitive, Fahrenheit remains standard in the United States for everyday use.
The key takeaway: while both scales measure the same physical phenomenon—heat energy—their starting points and increments differ significantly, necessitating precise conversion when switching between them.
The Conversion Formula Explained
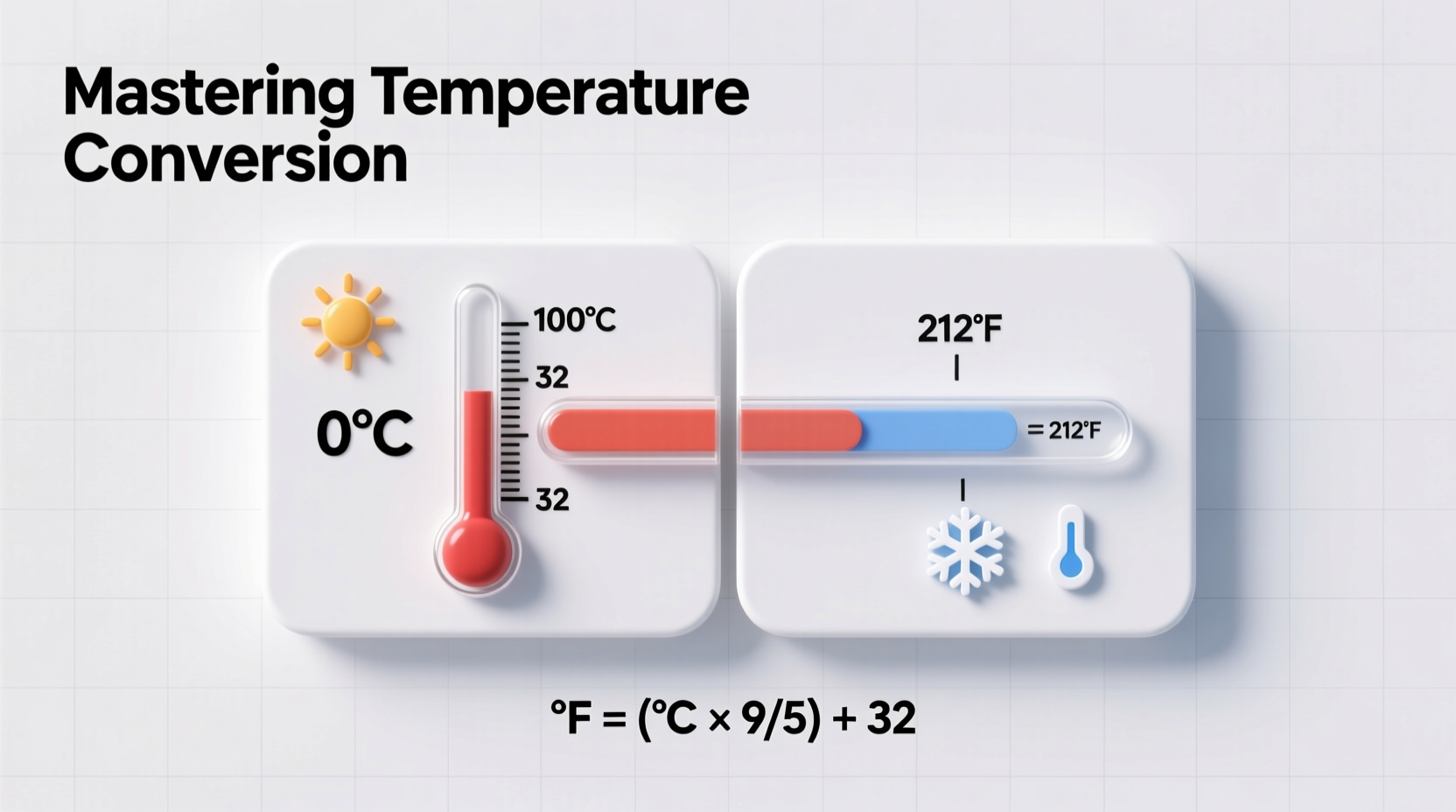
The mathematical relationship between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) is linear and consistent. The formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This equation reflects two adjustments: scaling the Celsius value to match Fahrenheit’s larger degree intervals (by multiplying by 9/5 or 1.8), then shifting the zero point by adding 32 to align with Fahrenheit’s offset baseline.
For example, to convert 20°C to Fahrenheit:
- Multiply 20 by 9/5 → 36
- Add 32 → 36 + 32 = 68
- Result: 20°C = 68°F
Conversely, to go from Fahrenheit to Celsius, reverse the process:
°C = (°F − 32) × 5/9
Take 86°F:
- Subtract 32 → 86 − 32 = 54
- Multiply by 5/9 → 54 × 5/9 = 30
- Result: 86°F = 30°C
Practical Applications Across Daily Life
Temperature conversion isn’t abstract—it shows up in kitchens, clinics, classrooms, and travel plans. Recognizing where and why it matters improves both accuracy and safety.
Cooking and Baking
Many international recipes list oven temperatures in Celsius, while U.S. ovens typically display Fahrenheit. Misreading these can lead to undercooked meals or burnt dishes. For instance, a French recipe calling for 180°C requires an oven setting of 356°F—not 180°F, which would be far too low.
Weather Interpretation
When traveling or checking global forecasts, understanding local temperature units is essential. A 25°C day is a pleasant 77°F, but misreading it as 25°F would suggest extreme cold (-4°C)—a significant misunderstanding.
Health Monitoring
Fever thresholds vary slightly by scale. In Celsius, a fever typically starts at 38°C (100.4°F). Medical professionals often need to convert readings when reviewing records from different countries.
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -40 | -40 | Only point where both scales are equal |
| 0 | 32 | Water freezes |
| 20 | 68 | Room temperature |
| 37 | 98.6 | Average human body temperature |
| 100 | 212 | Water boils at sea level |
Step-by-Step Guide to Accurate Conversions
Follow this five-step process to ensure precision and build fluency over time:
- Identify the temperature and unit: Confirm whether the given value is in °C or °F.
- Select the correct formula: Use °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32 for Celsius to Fahrenheit.
- Perform multiplication first: Handle the fraction or decimal step before addition.
- Add or subtract the offset: Don’t forget the +32 (or -32 in reverse).
- Round appropriately: For everyday use, round to the nearest whole number unless precision is critical.
With practice, intermediate benchmarks help estimate results. For example, every 5°C equals 9°F, so increasing by 5°C means adding 9°F. From 20°C (68°F), 25°C is roughly 77°F—a quick mental shortcut.
“Understanding temperature conversion is fundamental in meteorology. It ensures consistency in global climate reporting.” — Dr. Lena Patel, Climatologist, National Weather Institute
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced users make errors when converting temperatures. Awareness of frequent pitfalls leads to greater accuracy.
- Forgetting to add 32: The most common error. Multiplying by 9/5 without the final addition gives an incorrect result.
- Reversing the formula: Using °C to °F logic when going backward leads to large discrepancies.
- Ignoring negative values: When dealing with sub-zero temperatures, ensure proper handling of signs. For example, -10°C = 14°F, not -22°F.
- Over-relying on approximation: Rules like “double and add 30” give rough estimates (e.g., 20°C ≈ 70°F) but fail at extremes.
Mini Case Study: A Traveler’s Wake-Up Call
Sophie, a nurse from Boston, volunteered in Stockholm during winter. Accustomed to Fahrenheit, she initially dismissed a forecast of “-5°C” as mildly cold—equating it mentally to 23°F. Only after experiencing the actual conditions did she realize her mistake. Upon recalculating correctly: (-5 × 9/5) + 32 = 23°F—she realized her initial guess was right, but her perception of what that felt like was off due to lack of exposure. This experience prompted her to create a personal reference chart and practice conversions before future trips, improving both preparedness and communication with local colleagues.
Quick Reference Checklist
Use this checklist to reinforce learning and ensure accurate conversions:
- ☑ Know the basic formula: °F = (°C × 1.8) + 32
- ☑ Memorize three key points: freezing (0°C/32°F), body temp (37°C/98.6°F), boiling (100°C/212°F)
- ☑ Practice weekly with real-world examples: weather, cooking, travel plans
- ☑ Use rounding for estimation, but apply exact math when precision matters
- ☑ Verify high-stakes conversions with a calculator or app
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is the conversion formula structured with 9/5 and 32?
The 9/5 ratio accounts for the difference in scale increments—each degree Fahrenheit is smaller than a degree Celsius. The +32 adjusts for the offset in zero points: water freezes at 0°C but 32°F.
Is there a temperature where Celsius and Fahrenheit are the same?
Yes. At -40 degrees, both scales read the same value. This occurs because solving the equation °C = (°C × 9/5) + 32 yields -40.
Can I use mental math for quick estimates?
Yes. A fast approximation is to double the Celsius value and add 30. For example, 20°C ≈ (20×2)+30 = 70°F (actual: 68°F). It’s close enough for casual use but avoid it in technical settings.
Conclusion: Turn Knowledge Into Confidence
Mastering Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion empowers you to navigate a globalized world with greater ease and precision. Whether adjusting an oven for a new recipe, interpreting a weather report abroad, or ensuring accurate medical documentation, the ability to switch between scales fluently is a small skill with wide-reaching benefits. The formula is simple, the patterns memorable, and the practice rewarding. Start applying these techniques today—calculate one conversion manually each morning, test yourself with forecasts, or teach someone else. With consistent use, temperature conversion becomes second nature.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?