In today’s connected world, a strong and consistent Wi-Fi signal is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. From smart home devices to remote work, streaming, and online gaming, every activity depends on reliable internet coverage. Yet, many homes still suffer from frustrating dead zones—areas where the Wi-Fi signal is weak or nonexistent. Two popular solutions dominate the market: mesh router systems and traditional range extenders. While both aim to improve coverage, they differ significantly in performance, reliability, and user experience. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right system to eliminate dead zones once and for all.
How Wi-Fi Dead Zones Occur
Dead zones are areas in your home where the wireless signal from your router fails to reach or becomes too weak to support stable connections. These spots often occur due to physical obstructions such as thick walls, metal framing, mirrors, and large appliances like refrigerators. Distance also plays a role—especially in larger homes or multi-story buildings where the router may be located far from certain rooms.
Additionally, interference from neighboring Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth devices, and microwave ovens can degrade signal quality. Older routers using outdated standards (like 802.11n) struggle even more with coverage and speed. As households accumulate more connected devices—smart thermostats, security cameras, voice assistants—the demand on the network increases, making robust coverage essential.
Understanding Range Extenders: How They Work
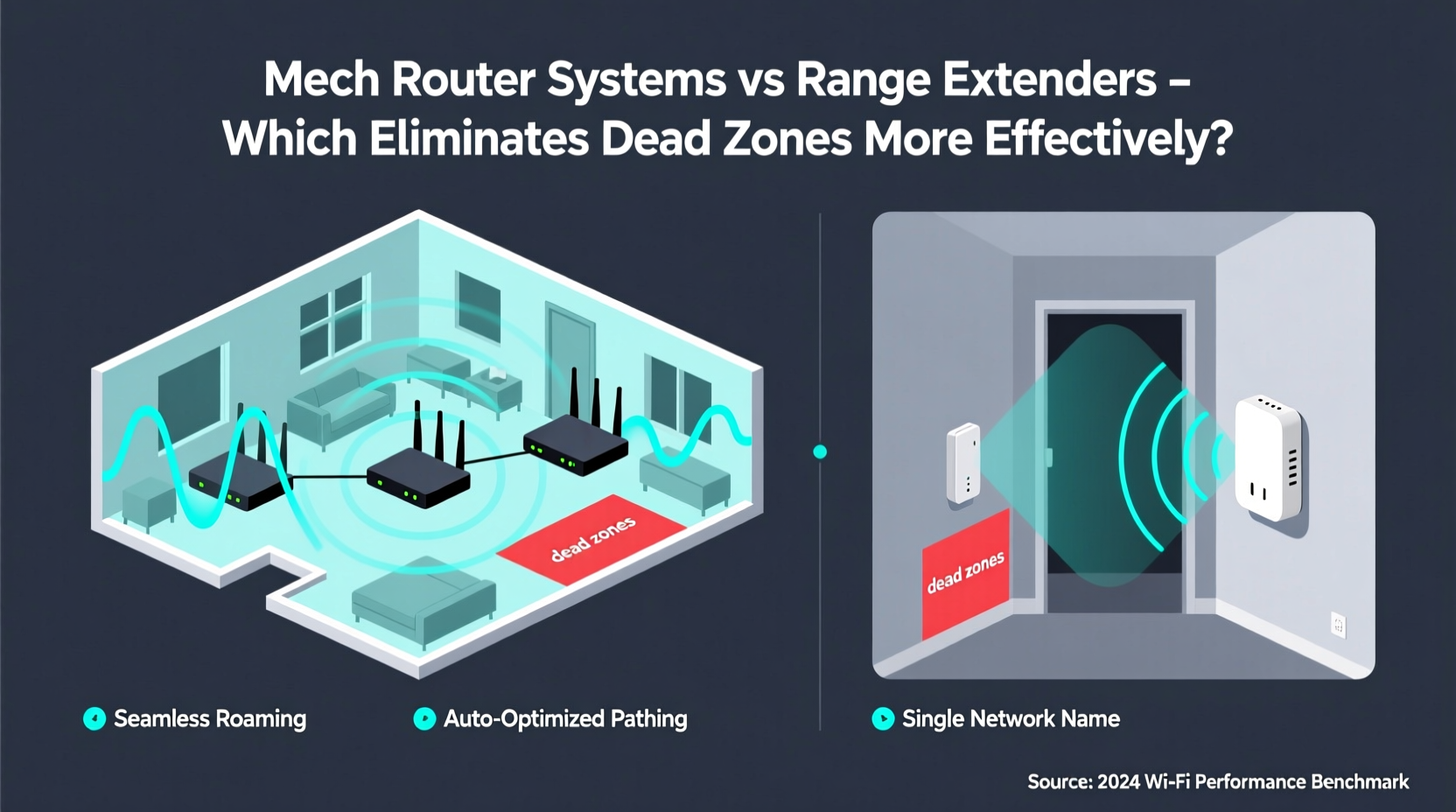
Range extenders, also known as Wi-Fi repeaters, are simple devices designed to boost an existing Wi-Fi signal. They are typically plugged into a wall outlet halfway between your router and the dead zone. The extender receives the signal from your main router, amplifies it, and rebroadcasts it to extend coverage.
While this sounds effective in theory, there are significant drawbacks. First, because most extenders operate on the same frequency band to receive and transmit data, they essentially cut available bandwidth in half—a process known as “half-duplex” operation. For example, if your original connection is 300 Mbps, the extended network might only deliver 150 Mbps or less.
Second, extenders create a separate network name (SSID), requiring users to manually switch between the main network and the extended one as they move through the house. This disrupts seamless roaming and can lead to dropped connections during video calls or streaming sessions.
Mesh Router Systems: A Modern Solution
Mesh Wi-Fi systems consist of multiple interconnected nodes that work together to create a single, unified network across your entire home. One node connects directly to your modem (the primary router), while additional satellite units are placed strategically throughout the space to fill coverage gaps.
Unlike range extenders, mesh systems use intelligent routing protocols to maintain a consistent network name and password across all nodes. Devices automatically connect to the strongest available signal without requiring manual switching. Many mesh systems also utilize tri-band technology, dedicating one entire band for communication between nodes (backhaul), preserving full bandwidth for end-user devices.
Advanced features like automatic firmware updates, built-in parental controls, and mobile app management make mesh systems not only more effective but also easier to manage than traditional setups. Brands like Google Nest Wifi, Eero, Netgear Orbi, and TP-Link Deco have made mesh technology accessible and user-friendly for non-technical homeowners.
“Mesh networks represent a fundamental shift in home networking—they’re designed for coverage, consistency, and scalability in ways that extenders simply can’t match.” — David Chen, Senior Network Engineer at Broadband Insights Group
Key Differences: Mesh vs Extenders
| Feature | Mesh Router System | Range Extender |
|---|---|---|
| Network Name (SSID) | Single, unified network | Duplicate SSID (separate network) |
| Bandwidth Efficiency | High (dedicated backhaul in tri-band models) | Low (shared band halves throughput) |
| Roaming Experience | Seamless handoff between nodes | Manual switching often required |
| Setup & Management | Mobile app guided setup, centralized control | Manual configuration, limited interface |
| Scalability | Easily add nodes for larger spaces | Limited expansion capability |
| Price Range | $150–$500+ depending on size | $30–$100 per unit |
| Interference Resistance | Dynamic channel selection, beamforming | Minimal optimization features |
Real-World Example: Eliminating Dead Zones in a Two-Story Home
Consider a typical two-story suburban home measuring 2,200 square feet. The internet service provider’s router is located in the basement near the utility room. Residents frequently experience poor connectivity in the upstairs bedrooms and backyard patio—classic dead zones.
The homeowner initially tries a $60 range extender in the hallway upstairs. It improves signal strength slightly, but streaming buffers constantly, and video calls drop when moving between rooms. The family grows frustrated with having to toggle between “Home” and “Home_Ext” networks.
After switching to a three-node mesh system (one main router in the living room, two satellites—one upstairs, one near the patio door)—coverage becomes uniform. All devices stay connected to the same network name. Streaming resumes without buffering, and smart devices respond instantly. The mobile app shows real-time device maps and allows scheduling of pauses for children’s devices. The investment pays off in both performance and peace of mind.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Right Solution
- Assess Your Home Layout: Measure square footage, note floor levels, and identify construction materials (e.g., brick, concrete, plaster). Larger or multi-level homes usually require mesh systems.
- Map Current Coverage: Walk through your home with a Wi-Fi analyzer app (like NetSpot or Wi-Fi Analyzer) to locate weak spots and signal drops.
- Evaluate Device Count: Homes with 15+ connected devices benefit more from mesh networks due to better traffic management.
- Check Internet Speed: If you have gigabit internet, a range extender will bottleneck your speed. Mesh systems preserve high-speed potential.
- Budget Consideration: While extenders are cheaper upfront, their limitations may lead to dissatisfaction. Mesh systems offer long-term value despite higher initial cost.
- Installation Plan: For mesh, place the first node near the modem, then position satellites within optimal range (not in dead zones). Avoid placing near microwaves or cordless phone bases.
- Test and Optimize: After setup, test speeds in previously problematic areas. Use the app to check node connections and adjust placement if needed.
When a Range Extender Might Still Be Useful
Despite their limitations, range extenders aren’t obsolete. They can serve as temporary or budget-conscious solutions in specific scenarios:
- Small apartments where only one extra room needs coverage.
- Secondary locations like garages or sheds used occasionally.
- Rental properties where installing permanent hardware isn’t allowed.
- Supplementing a mesh system in extremely distant areas beyond satellite reach.
However, even in these cases, newer access points that function as wired extenders (connected via Ethernet) outperform wireless-only models. When possible, powerline adapters with built-in Wi-Fi can also bridge gaps more reliably than standard repeaters.
Expert Checklist: Upgrade Your Wi-Fi Successfully
Use this checklist before investing in either solution:
- ✅ Confirm your current router supports modern standards (Wi-Fi 5/6/6E).
- ✅ Identify whether dead zones stem from distance, obstacles, or interference.
- ✅ Determine if wiring Ethernet cables is feasible for backhaul (ideal for mesh).
- ✅ Decide how many devices need simultaneous, high-bandwidth access.
- ✅ Choose a reputable brand with regular firmware updates and good customer support.
- ✅ Prioritize tri-band mesh systems if you have high-speed internet (300 Mbps or above).
- ✅ Test post-installation performance in actual usage conditions (streaming, gaming, etc.).
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a mesh system with my existing router?
Yes. Most mesh systems can operate in \"access point mode\" or replace your current router entirely. Connect the primary node to your modem via Ethernet and disable the modem’s built-in Wi-Fi to prevent conflicts.
Do mesh routers increase internet speed?
They don’t increase your base internet speed from the ISP, but they maximize its distribution by reducing latency, eliminating dropouts, and maintaining full bandwidth across the network—resulting in faster perceived performance.
Are Wi-Fi extenders completely obsolete?
Not entirely. For very small spaces or occasional use, they remain a low-cost option. However, for whole-home coverage, especially in modern, device-heavy environments, they fall short compared to mesh systems.
Conclusion: Building a Smarter, Seamless Network
Eliminating Wi-Fi dead zones isn’t just about adding another device—it’s about upgrading how your network functions. Range extenders offer a quick fix but come with trade-offs in speed, stability, and usability. Mesh router systems, though more expensive, provide a future-proof, intelligent solution that grows with your needs and delivers a truly seamless experience.
The choice ultimately depends on your home’s layout, internet usage, and long-term goals. But for most households seeking reliable, high-performance Wi-Fi everywhere, mesh technology is the clear winner. It transforms fragmented connectivity into a unified, responsive network that supports modern digital life without compromise.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?